성능 요약
- 메모리: 92592 KB, 시간: 1076 ms
구분
- 그래프 이론, 그래프 탐색, 너비 우선 탐색, 깊이 우선 탐색
Answer Code(2023.11.29)
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
static final int MAX = 100000 + 10;
static ArrayList<Integer>[] graph;
static boolean[] visited;
static int N, M, R; // 정점(N)과 간선(M)
static int[] answer;
static int order;
public static void dfs(int idx) {
visited[idx] = true;
answer[idx] = order;
order++;
for(int i = 0; i < graph[idx].size(); i++) {
int next = graph[idx].get(i);
if(visited[next] == false) {
dfs(graph[idx].get(i));
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
// 0. 입력 및 초기화
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
R = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
// 1. graph에 연결 정보 채우기
graph = new ArrayList[MAX];
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
graph[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
visited = new boolean[MAX];
answer = new int [MAX];
order = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int x = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int y = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
graph[x].add(y);
graph[y].add(x);
}
// 2. 오름차순 정렬
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
Collections.sort(graph[i]);
}
// 3. dfs(재귀함수 호출)
dfs(R);
// 4. 출력
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
bw.write(String.valueOf(answer[i]));
bw.newLine();
}
bw.close();
br.close();
}
}
문제풀이
Step0. 입력 및 초기화
public class Main {
static final int MAX = 100000 + 10;
static ArrayList<Integer>[] graph;
static boolean[] visited;
static int N, M, R; // 정점(N)과 간선(M)
static int[] answer;
static int order;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 0. 입력 및 초기화
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
R = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
}
-
N의 최대값이 10만이므로, 2차원 배열로 쓰기에는 저장하기에 크기가 너무 커진다.
-
그래서 필요할 때마다 쓰는, 동적 할당을 가능하게 해주는
ArrayList을 사용한다.-
어떤
특정 노드를 기준으로 봤을 때, 나랑 연결되어 있는 노드가 누가 있는지 는 이전에 배열로 썼던 것과 동일하다. -
다만,
ArrayList로 만들었기 때문에 M개의 간선 정보에 맞춰서 그때그때마다 하나씩 노드를 추가해가는 구조이다.
-
-
answer를 하나의 배열 형태로 만들어준 이유는 각각의 노드가 몇번째로 방문했는지 기록하고, 그것을 오름차순으로 출력하기 위해서이다. -
visited는 이전 바이러스, 연결 요소의 개수 문제와 동일하게, 특정 노드를 방문했는지를 기록하기 위해 boolean 타입의 배열인 자료구조를 사용했다.
Step1. graph에 연결 정보 채우기
public class Main {
static final int MAX = 100000 + 10;
static ArrayList<Integer>[] graph;
static boolean[] visited;
static int N, M, R; // 정점(N)과 간선(M)
static int[] answer;
static int order;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1. graph에 연결 정보 채우기
graph = new ArrayList[MAX];
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
graph[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
visited = new boolean[MAX];
answer = new int[MAX];
order = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int x = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int y = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
graph[x].add(y);
graph[y].add(x);
}
}
}
-
graph[x].add(y)는 x번째 ArrayList 에서 y라는 값을 추가하겠다는 의미이다.반대 역시 마찬가지로,
graph[y].add(x)은 y번째 ArrayList 에서 x라는 값을 추가하겠다는 의미이다.
Step2. dfs(재귀함수 호출)
public class Main {
static final int MAX = 100000 + 10;
static ArrayList<Integer>[] graph;
static boolean[] visited;
static int N, M, R; // 정점(N)과 간선(M)
static int[] answer;
static int order;
public static void dfs(int idx) {
visited[idx] = true;
answer[idx] = order;
order++;
for (int i = 0; i < graph[idx].size(); i++) {
int next = graph[idx].get(i);
if (visited[next] == false) {
dfs(graph[idx].get(i));
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 2. 오름차순 정렬
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
Collections.sort(graph[i]);
}
// 3. dfs(재귀함수 호출)
dfs(R);
}
}
-
여기서
order라는 변수는 내가 지금 몇번째인지 순서를 담고 있는 변수이고, 순서를answer라는 배열에 해당하는 인덱스 번째에 담는 것이다.그런 다음에, 1등, 2등, 3등 처럼 순서대로 담길 수 있도록
order에 +1을 증가시켜준다. -
for(int i = 0; i < graph[idx].size(); i++)은 인덱스번째의 노드랑 연결되어 있는 애들이 이 그래프의 인덱스번째의 ArrayList에 담겨져 있으므로 이 ArrayList를 하나씩 뒤져보겠다는 의미이다.예를 들어, 1번째 노드와 연결되어 있는 게 2,4라면 -> 2번 만큼 반복문을 돌리는 것이다.
그리고
dfs(graph[idx].get(i))은 인덱스와 연결되어 있는 i번째 노드를 가져와서, i를 기준으로 DFS를 태우겠다는 의미이다.그런데 조건 없이 불러오면, 무한 루프에 빠질 수 있기 때문에 위에 조건문
if(visited[next] == false)추가해준다.해당 조건문의 의미는 인덱스를 기준으로 i번째 연결되어 있는 요소를
next라는 int형 변수에 담고, 다음 방문하려는 하는 곳이 방문할 기록이 없다면 DFS를 태우겠다는 것이다.
정리
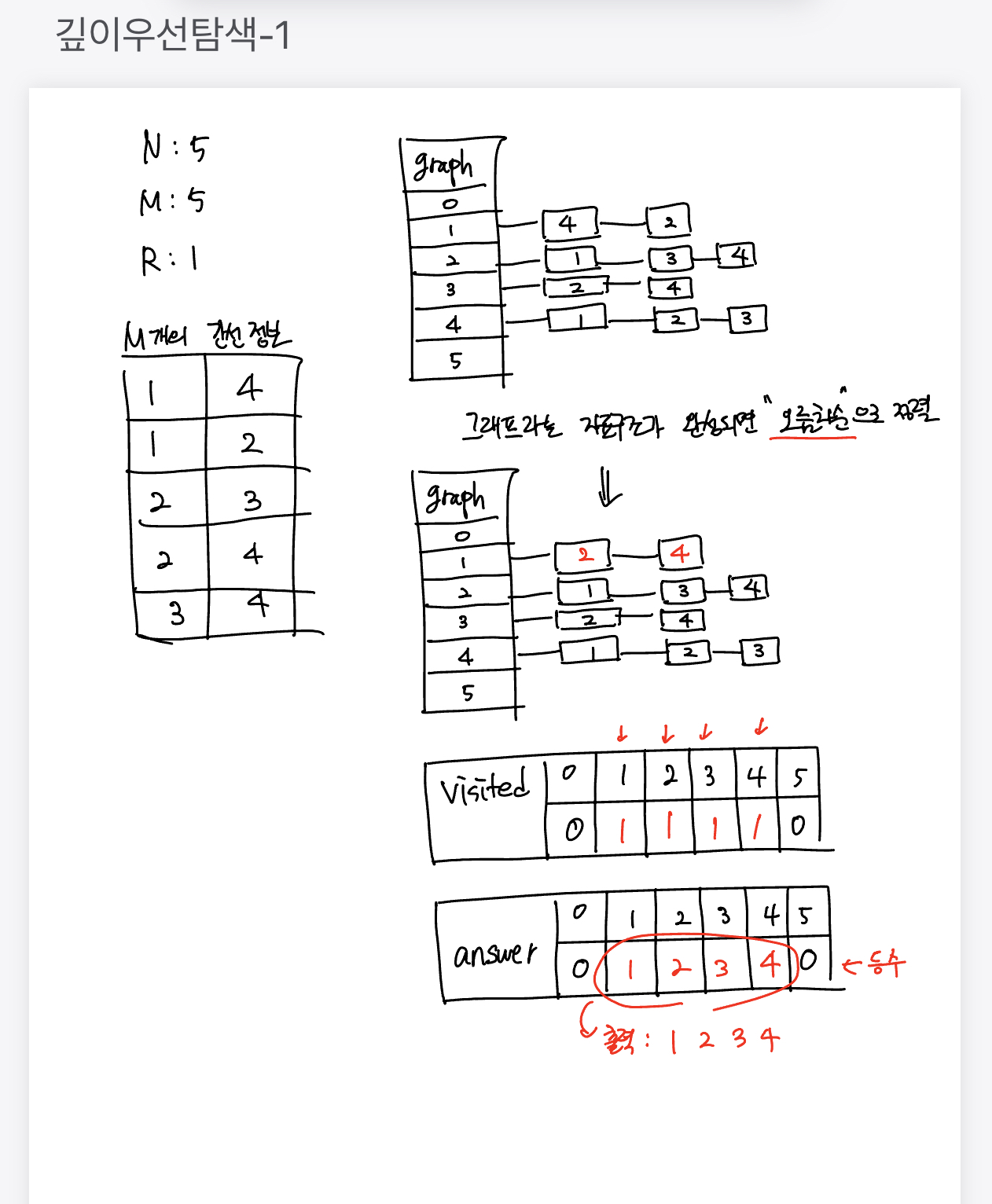
해당 문제를 풀면서, 아래의 순서에 맞게 생각하고 구현하면 풀 수 있는 문제였다.
-
DFS, 정점, 간선, 무방향 그래프 -> DFS/BFS
-
서로 연결되었다는 정보를 어떻게 하나의 자료구조로 통합할까? -> 2차원 배열 vs ArrayList -> 범위가 크기 때문에
ArrayList를 사용했다. -
이미 방문한 지점을 다시 방문하지 않으려면 어떤 자료구조를 사용해야 될까?
-
어떻게 오름차순으로 방문할 수 있을까?
-
방문 순서를 담기 위해서는 어떤 자료구조를 사용해야 될까?
Review
-
이전 DFS 유형인
연결 요소의 개수문제와 다른 점은 크게 2가지 였다.-
시작점이 주어진 것(R)이고,
-
N이라는 값이 10만개까지 들어오기 때문에 단순히 2차원 배열로 쓸 수 없어서, 동적 할당을 가능하게 해주는
ArryList를 사용했다.
-
-
해당 문제에서 요구했던 건 몇 개를 방문했냐라는 하나의 정수값이 아니라 각각의 노드를 몇 번째로 방문했는지 그걸 알고 싶었기 때문에 이번에는 배열이라는 자료구조를 써야 됐다.