- Cryptography
- Cryptography - 잘못된 예시
- Encryption and Decryption
- Symmetric Encryption
- Symmetric Encryption
- Asymmetric Encryption
- Asymmetric Encryption
- Hashes
- Cryptographic Hash Functions
- Digital Signatures
- Reference
이 카테고리는 경영학부 전자금융의 이해 수업을 듣고 정리한 내용을 바탕으로 글을 작성하였습니다.
Cryptography
-
Cryptography-
(eng) The practice and study of techniques for secure communication in the presence of adversarial behavior
-
(kor) 위험한 상황에서 메세지를 안전하게 보내기 위한 기술에 대한 연구
-
조건1) 엿들으면 안된다.
-
조건2) 메세지에 대한 조작이 있으면 안된다.
-
-
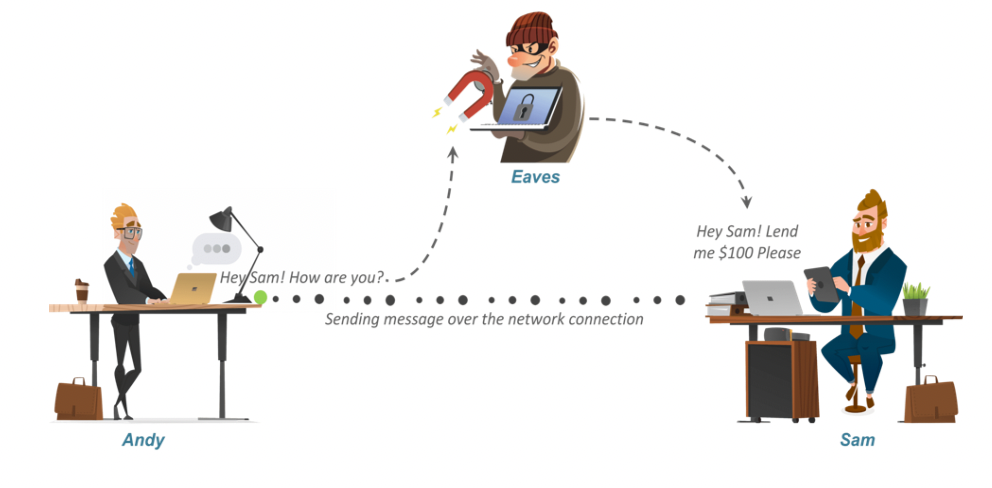
Cryptography - 잘못된 예시
Encryption and Decryption
-
Encryptionis the process of turning a plaintext human message intocyphertext.- 알아볼 수 있는 문장 → 알아볼 수 없는 문장
-
Decryptionis the process of turning thecyphertextback into readable plain text- 알아볼 수 없는 문장 → 알아볼 수 있는 문장
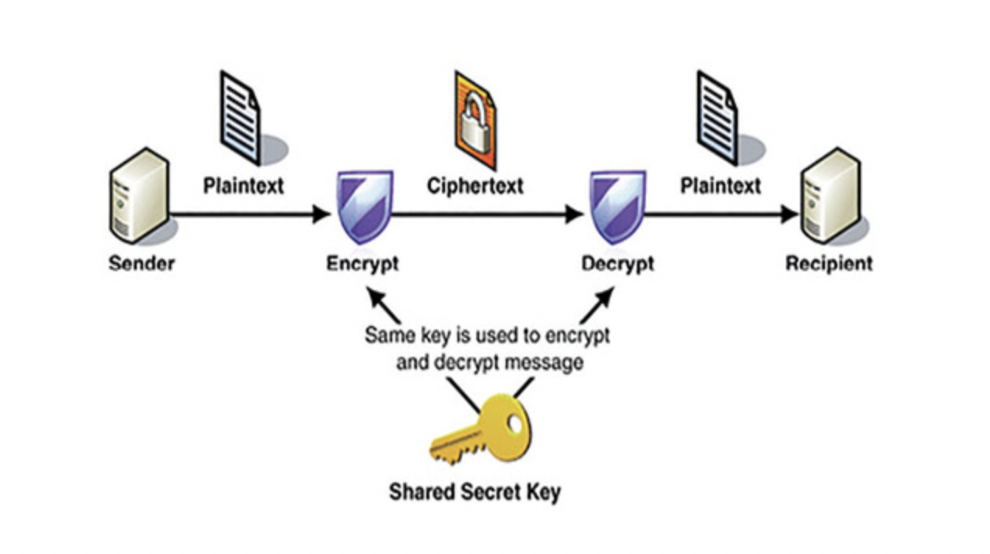
Symmetric Encryption
-
Suppose Alice → Bob (message)
Caesar cypher: They encrypt the text by shifting each letter a set number of places in the alphabet. (글자들을 정해진 칸 만큼 각각의 글자들을 옮기는 것)
- Symmetric encryption : a type of encryption where only one key (a secret key) is used to both encrypt and decrypt electronic information
- kor) 어떤 메세지를 encrypt 과 decrypt 하는 오로지 하나의 key가 같을 때 쓰는 encryption 유형
- 이런 유형은 실생활에서 사용하지 않는다.
- spot 하고 break 하기 너무 쉽다.
- 어떤 key를 사용해야할지 동의을 위한 의사소통이 필요하다. (They have to communicate to agree what key to use for scheme)
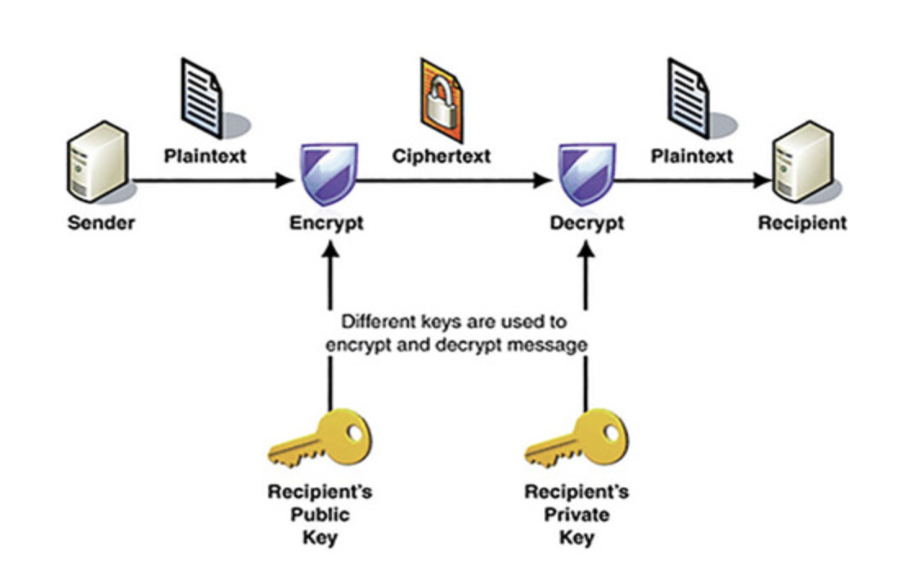
Symmetric Encryption
Asymmetric Encryption
-
ASymmetric Encryption(Public key Cryptography) : a cryptography system that uses pairs of keys. (서로 다른 키)-
The key used to decrypt a message is different to the key used to encrypt message.
-
You create two mathematically linked keys when you want to receive encrypted message.
-
Public key: You can share it with the world, and anyone can use it to encrypt message for you. (누구나 공유할 수 있는 키) -
Private key: It is know only to you. (오직 혼자만 아는 키)
-
-
Asymmetric Encryption
-
Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (
ESCADA)-
당신은 랜덤하게 발생되어 선택된 private key를 가지고 그것으로부터 mathematically 발생된 public key를 가집니다.
-
Private key: Pick a random number between 0 and $2^{256}$ - 1 (78 digits).
-
Public key: Do some ESCADA maths on the private key.
-
-
정리) 랜덤한 숫자를 추출해서 private key를 만든 후 수학적인 함수를 적용해서 public key를 만든다.
-
Hashes
-
Hash function: A mathematical function that converts an input value into another compressed(압축된) value-
The input to the function is called preimage or message.
-
The output of the function is called fingerprint, digest, or hash
-
Hash functions are deterministic because the output is determined by the input.
-
Basic hash function (not used in blockchain)
-
input를 받으면 첫글자를 출력하는 것
-
예) Hash(‘What time is it?’) ⇒ ‘W’
-
-
Cryptographic hash function (used in blockchains)
- 예) MD5, SHA-256
-
Cryptographic Hash Functions
-
Cryptographic hash Functions는 특별하고 유용하게 만드는 몇가지 특징들이 있습니다.
-
이상적인 Cryptographic Hash Functions 위한 5가지 특징들
-
[1] It is deterministic so the same message always results in the same hash.
-
[2] It is quick to compute the hash value for any given message (you can easily go ‘forwards’). ⇒ 계산이 빨라야한다 = 답을 간단하게 출력해야 한다.
-
[3] It is not feasible to generate a message from its hash value except by trying all possible messages (you can’t go ‘backwards’).
- 가능한 메세지를 시도하는 것을 제외한다면, 주어진 hash value로부터 원래의 메세지를 찾는 것이 불가능하다. ex) ‘W’ (hash value) → ‘What time is it?’(Digital message)
-
[4] A small change to a message should change the hash value so extensively that the new hash value appears uncorrelated with the old hash value (a small change makes a big difference). ⇒ 조금의 변화라도 해쉬 값에 큰 차이를 가진다.
-
[5] It is not feasible to find two different messages with the same hash value (it is hard to create a hash clash). ⇒ 같은 해쉬값을 가진 두가지 다른 메세지를 찾는것이 불가능하다.
-
Cryptographic Hash Functions - Properties
-
Cryptographic functions are sometimes called trapdoor function (Properties 2 and 3).
- message → hash (O) But, hash → message(X)
-
Message 가 조금만 달라도 전혀다른 hash 값이 나온다. 즉, 유추가 불가능하다.
What is Good Cryptographic Hash Functions ?
-
Is the hash function ‘Use the first character’ be good cryptographic hash functions ?
-
[1] Yes, it is deterministic
-
[2] Yes, it is quick to compute the output.
-
[3] Yes, by knowing only ‘W’ it is not feasible to guess the original sentence.
- ex) ‘W’ → ‘What time is it?’ (X)
-
[4] No, a small change in the message doesn’t necessarily change the output. ‘What time is at¿ also hashes down to ‘W’.’
-
[5] No, we can easily create loads of inputs that will all hash down to the same output. Anything starting with ‘W’ will work.
-
=> 4,5 번에 의해 좋은 cryptographic hash function 될 수 없다.
-
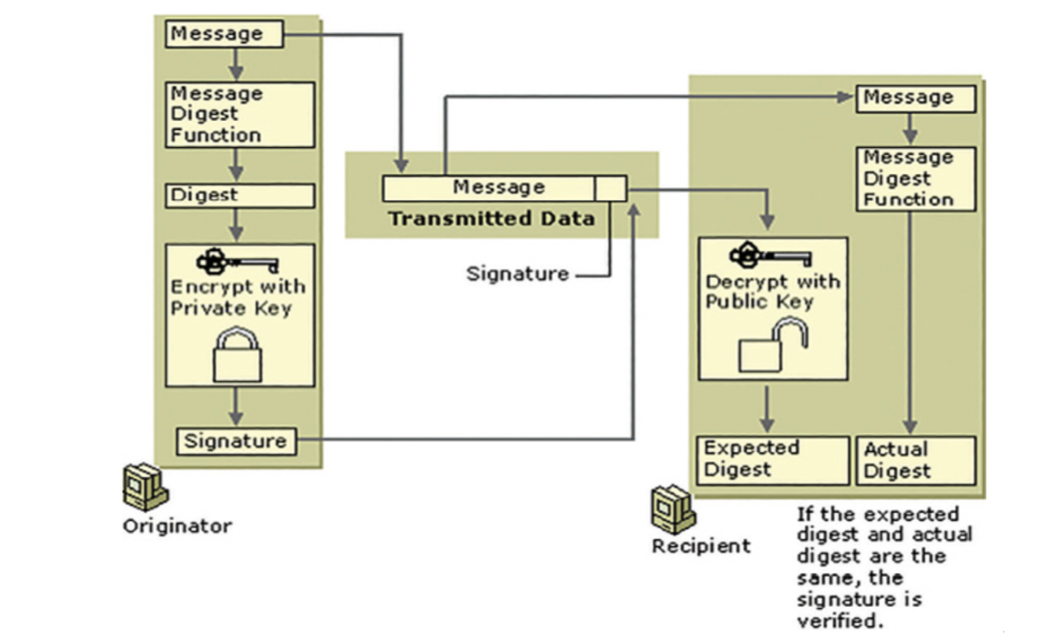
Digital Signatures
-
Digital signature: a specific type of electronic signature that requires the signer to authenticate their identity using a certified digital ID-
It is created by taking the message you want to sign and applying a mathematical formula with your private key.
- Message + Private key → Digital signature
-
Anyone who knows your public key can mathematically verify that this signature was indeed created by the holder of the private key.
- Message + Digital signature + Public key → Valid / Invaild
-
Digital Signatures - 그림
- Here, you encrypt data with private key and decrypt it with a public key.
Wet-ink-on-paper signature
-
There is no way of knowing if a document has been tampered after your signature is made. ⇒ 서명한 이후 조작되더라도 알 방법이 없다.
-
Your signature can easily be copied and re-used with other documents without your knowledge. ⇒ 서명이 쉽게 copy 되고, 다른 문서와 함께 재사용할 수 있다.
Digital Signatures
-
Any tampering with the message will result in the signature being invalidated. ⇒ 문서(메세지) 조작이 불가능하다
-
It is only valid for that exact piece of data, and so it cannot be copied and pasted underneath another piece of data. ⇒ 한번 사용하는 것으로 복사/붙여넣기 할 수 없다.
-
Digital signatures are used in blockchain transactions.
-
They prove account ownership.
-
No central organization (제 3자 개입 X)
-
Reference
-
- The Impact of Fintech, AI, and Crypto on Financial Services, Henry Arslanian and Fabrice Fischer, 2019, Springer
-
Bitcoin, Blockchain, and Cryptoassets
- A Comprehensive Introduction, Fabian Schär and Aleksander Berentsen, 2020, MIT Press