- Bitcoin
- Problems
- Which Coins?
- Ethereum
- Reference
이 카테고리는 경영학부 전자금융의 이해 수업을 듣고 정리한 내용을 바탕으로 글을 작성하였습니다.
Bitcoin
Bitcoin: a decentralized digital currency that can be sent from user to user on the peer-to-peer bitcoin network without intermediaries (만들어내고 유통화하고 관리하는 것이 중앙화 되지 않고 모든 사람이 참여가능한 decentralized digital currency 입니다)

-
Node: machines running the appsMiner: a specialist node which bundles together valid transactions into blocks and distribute those blocks to nodes across the network (block을 만드는 역할의 노드들)
Problems
[1] Accounts Need Permission
-
[1] Problem : Accounts Need Permission → 기관 승인 없이 계좌 생성 블가능하다.
-
[1] Solution : Use Public Keys as Account Numbers
-
Public key를 이용해서 address를 만든다.
-
Private key + Disital signature를 통해 Public key를 생성하고, 그것을 가공해서 address를 만든다.
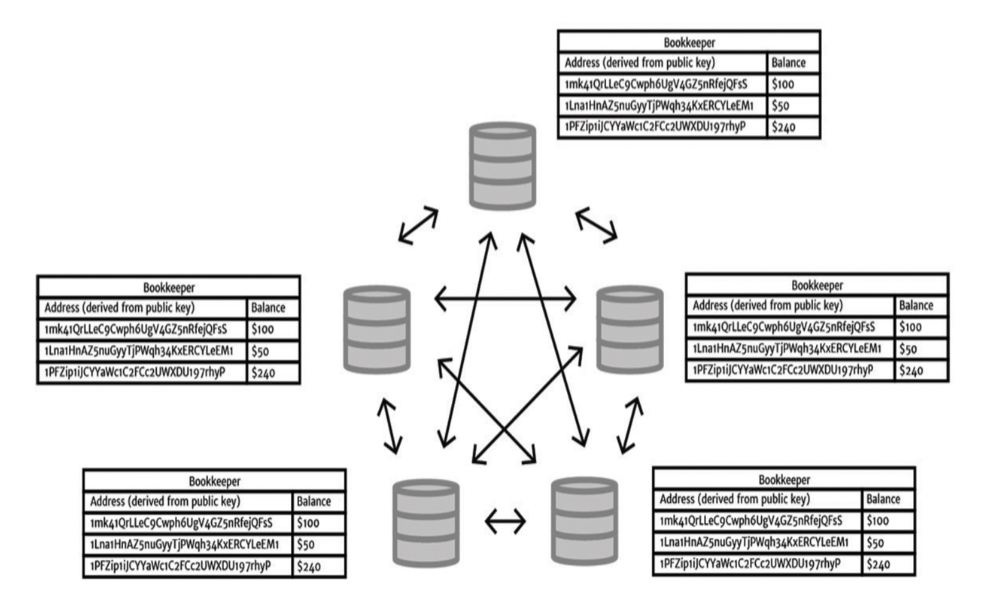
[2] Single Central Bookkeeper
-
[2] Problem : Single Central Bookkeeper → 장부들이 어떻게 안전하게 관리될까 ?
-
Central bookkeeper: the coordinator(은행 역할) who maintains the list of transactions and balances, and validates and orders the transactions -
[2] Solution : Replicate the Books (장부를 복제해서 배포하기)
-
누구든지 허가없이, 위계질서 없이 bookkeeper가 될 수 있고, 모든 bookkeeper들은 모든 정보가 있는 장부를 확보한다. 그리고 만약 조직을 강요받는다면, 그런 bookkeeper가 보유하고 있는 장부를 무시하거나 제외하면 된다.
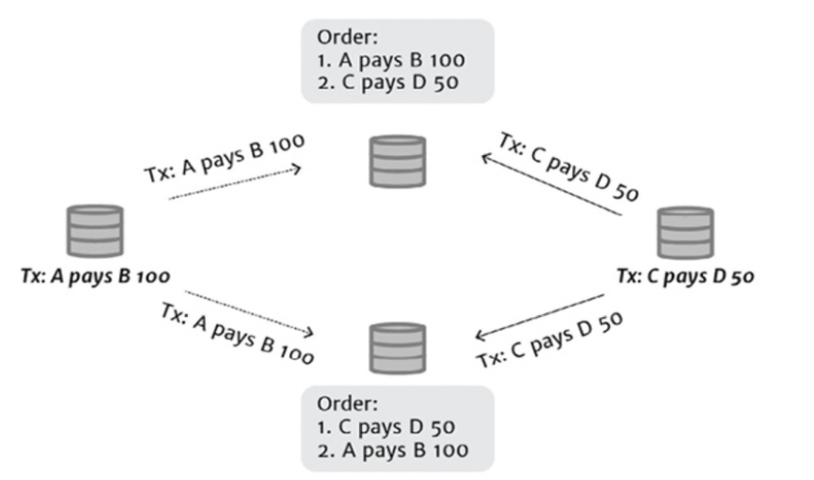
[3] Transaction Ordering
-
[3] Problem : Transaction Ordering → 거래주문이 많아 통일이 어려움
- transaction이 너무 많아서 node들이 실시간으로 그 transaction들을 ordering 하는 것이 불가능하기 때문에 통일된 형태의 block을 가질 시간이 없다.
-
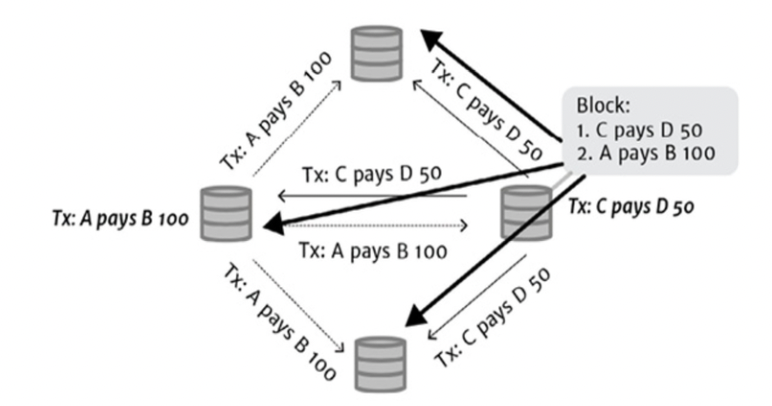
[3] Solution : Blocks
-
장부에 들어가는 속도는 컨트롤이 가능하다.
-
따라서 많은 transaction 들을 block으로 묶어서 장부에 넣는다.
-
Block이 transaction 보다 훨씬 덜 자주 만들어진다.
-
Bookkeeper들이 여유있게 검증할 수 있다. (the ordering of blocks of transactions)
-
Blocks의 숫자가 훨씬 더 적고, 하나의 transaction보다 네트워크에 있는 노드들이 block에 대해서 합의에 이를 가능성이 훨씬 더 높다.
-
Bookkeeper의 수행기능 2가지
-
보류중인 transaction 승인 및 알림(전파)
-
blocks of transactions 검증, 저장 및 알림(전파)
-
[4] Who Can Create Blocks, and How Often?
-
[4] Problem : Who Can Create Blocks, and How Often? → 누가 얼마나 자주 blocks 만드는가 ?
-
[4] Solution : Proof-of-Work (작업 증명) → ‘나 고생했어요’ 라고 증명하는 것
-
Proof-of-Work: 한 노드가 다른 노드들한테 ‘내가 특정한 형태의 computational effort를 굉장히 많이 했다’ 라는 것을 보여주는 형태
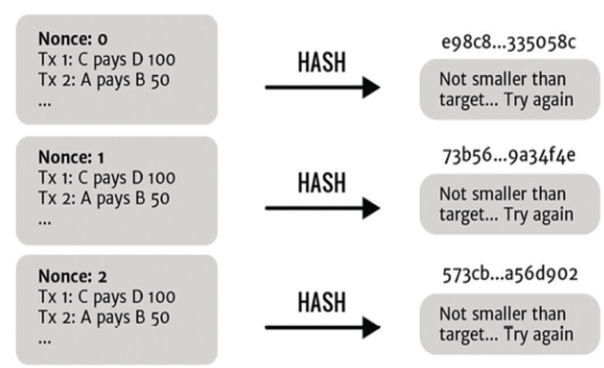
The rule of Bitcoin’s proof-of-work game
-
nonce 값을 바꾸면서 Tx(transaction)를 긁어모은다. → hash function에 돌린다.
-
만약 hash 값이 target number 보다 작으면 Tx 긁어모은 block이 정식 block으로 인정받게 된다.
-
한마디로 표현하면,
노가다혹은삽질이다. -
이러한 과정들을
Mining이라고 한다. -
Mining: hash 값 < target number ⇒ 진짜 Bitcoin block 으로 넣는 과정이다. (Bitcoin’s public ledger)
!
-
One-CPU-One-Vote-
Your chance of winning a block is proportional to how much hashing power you control.
-
(해석) target number 보다 작은 hash 값을 찾기 위해 누가 더 많이 CPU 를 쓰는가에 달려있다.
-
[5] Incentivising Block-Creators
-
[5] Problem : Incentivising Block-Creators → Hashing 하는것도 많은 돈이 필요함
-
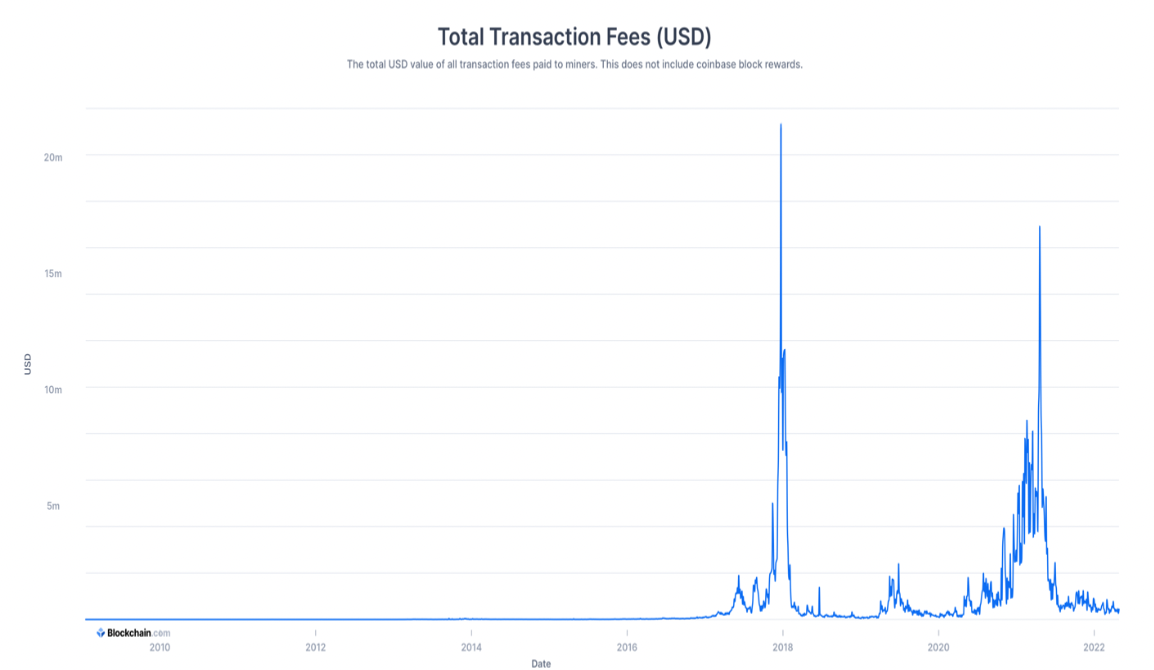
[5] Solution : Transaction Fees (송금 수수료 - block을 만든 사람에게 주는 인센티브)
-
거래가 되는 금액의 일부로 block 을 만든 사람에게 보상해준다.
-
보상금액은 “시장 원리”에 의해 결정된다.
-
Fees → 예시)
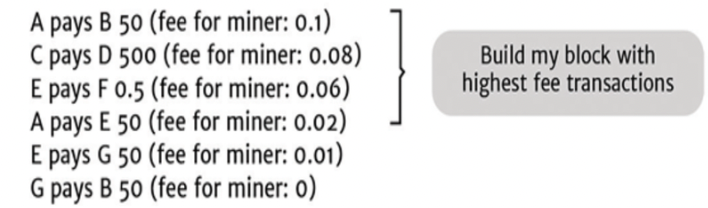
- Total Transaction Fees(USD) 관련 그림
[6] How to Bootstrap?
-
[6] Problem : How to Bootstrap? → 거래가 없을 때 시스템을 어떻게 유지해야할까 ? (거래량이 적어질때 시스템을 유지하는 방법)
-
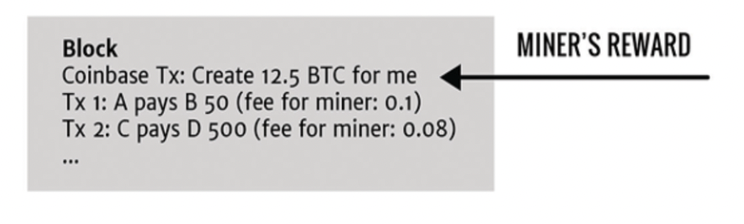
[6] Solution : Block Rewards -> Transaction fee 외에 추가적인 보상시스템
-
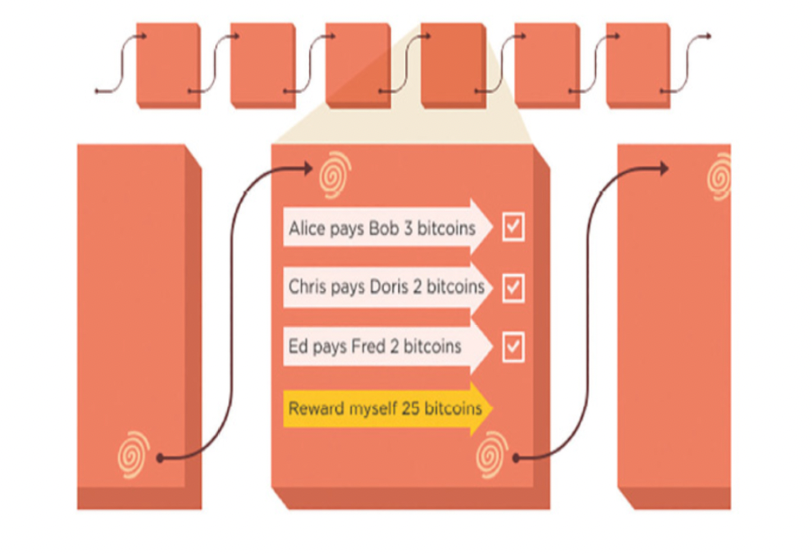
Block-creator는 정해진 한도내에서 최대한 bitcoin을 원하는 address로 나 또는 타인에게 보낼 수 있는 transaction을 생성할 수 있다.
-
Coinbase transaction 개념
-
block을 만든 사람에게 추가적으로 본인 스스로 transaction을 만들 수 있다.
-
블록체인에서 가장 먼저 발생한 transaction
-
기존에 없는 bitcoin을 새롭게 만들어내는 transaction
-
[7] More Hashing, Faster Blocks, More Monetary Supply
-
[7] Problem : More Hashing, Faster Blocks, More Monetary Supply → 적당한 속도로 block이 만들어질 수 있도록 조건이 필요함
-
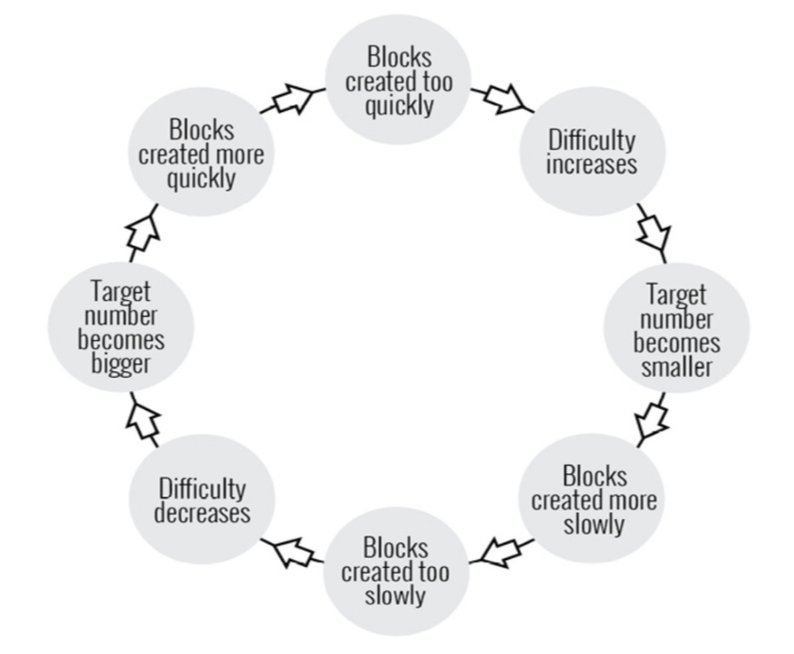
[7] Solution : Difficulty -> “게임의 난이도 조절”
-
block이 예상 목표보다 빠르게 생성한다면 네트워크 속도를 느리게 한다.
-
또한, 난이도 수준을 어렵게 하기 위해서 target number를 더 낮게 설정한다.
[8] Block Ordering
-
[8] Problem : Block Ordering → 정렬을 어떻게 하는가?
-
[8] Solution : Block Chain
-
각각의 block은 성공적으로 인정받는 이전 block의 hash 값을 넣게(포함시키게)만든다.
- Block Chain 조작이 어려운 이유: 각각의 block이 이전 block의 hash값을 참조하고 있고, 그 block의 hash값을 거래정보가 바뀌면 완전히 바뀌기 때문에, 하나만 건드려도 전체가 영향을 받고 있기 때문에 Block Chain은 조작이 어렵습니다.
[9] Block Clashes/Consensus
-
[9] Problem : Block Clashes/Consensus → 비슷한 타이밍의 서로다른 miner(=block-creator)들이 나타난 경우
-
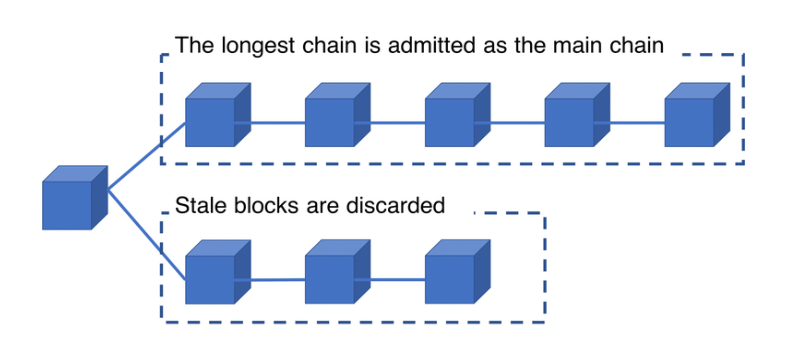
[9] Solution : Longest Chain Rule - block간의 충돌이 발생했을 때의 해결 방안
-
다수의 체인이 존재할 때, 가장 긴 체인의 blocks을 만들어서 “true version”으로 (인정받는)선택받는다.
-
버려지는 block은
orphan이라 부른다.
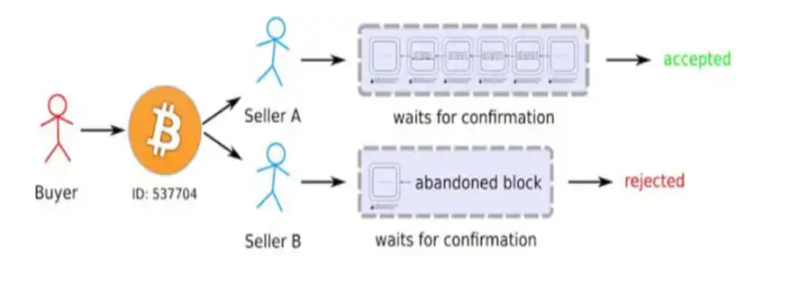
[10] Double Spend
-
[10] Problem: Double Spend
-
Double Spend → 실물 화폐에서는 불가능하지만, 디지털 화폐에서는 가능할 수 있다.
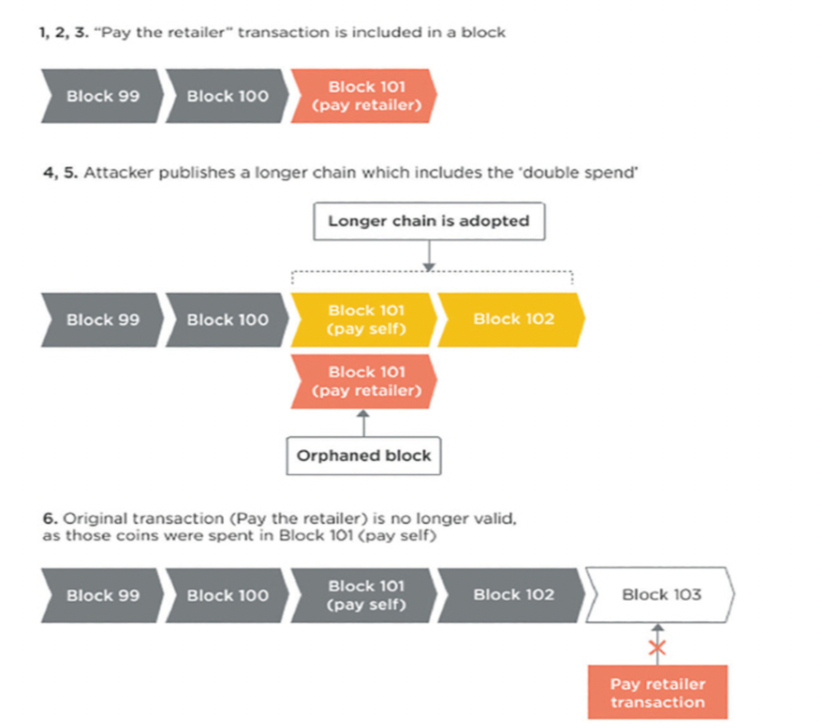
Double Spend 과정
-
(1) 같은 비트코인에 두개의 transaction를 생성시킨다. (하나는 online retailer, 다른 하나는 당신계좌)
-
(2) retailer에게 지불한다는 거래만 알린다.
-
(3) 지불한다는 거래가 포함된 block이 만들어지면, retailer는 block을 확인하고 물건을 보내준다.
-
(4) 당신이 물건이 받고서, 추가적으로 retailer에게 지불한다는 것을 제외하는 더 긴 체인의 block을 만든다. 그리고 당신에게 지불하는 것으로 대체한다.
-
(5) 가장 긴 체인이 공식 블록으로 인정받게 된다.
-
(6) 기존에 retailer에게 지불한다는 block은 인정받지 않게 되고, 가장 긴 체인만 인정받게 되는 결과를 낳는다.
-
Double Spend 과정 -> 그림
-
[10] Solution: Wait about Six Blocks → 1시간 기다리고 물건을 보내라
-
최소 6개 block을 만들때까지 1시간정도 기다린 후에 물건을 보낸다.
-
51% Attack개념, 현실적으로 불가능한 이유-
If someone wants to replace blocks, they have to create blocks quickly and overtake the rest of the (presumably honest) network.
-
If more than 50% of the total hash power of the network is used to re-write blocks, then it will be able to do so.
-
이것이 현실적으로 불가능한 이유: 돈이 많이 들고, 조작적으로 해서 비트코인을 많이 갖고싶어서일텐데, 비트코인 가치가 떨어지게 바라진 않는다. 51% Attack이 가능하게 되면, 비트코인 가치가 아무 쓸모가 없게 되기 때문
-
Which Coins?
-
비트코인 특징: Bitcoin is digial + physical cash + 과거기록이 추적가능하다.
-
Bitcoin transaction
- Mining fee: Miner에게 지불하는 비용. miner가 당신의 거래를 block에 등록해주는 대가로 지불하는 값
-
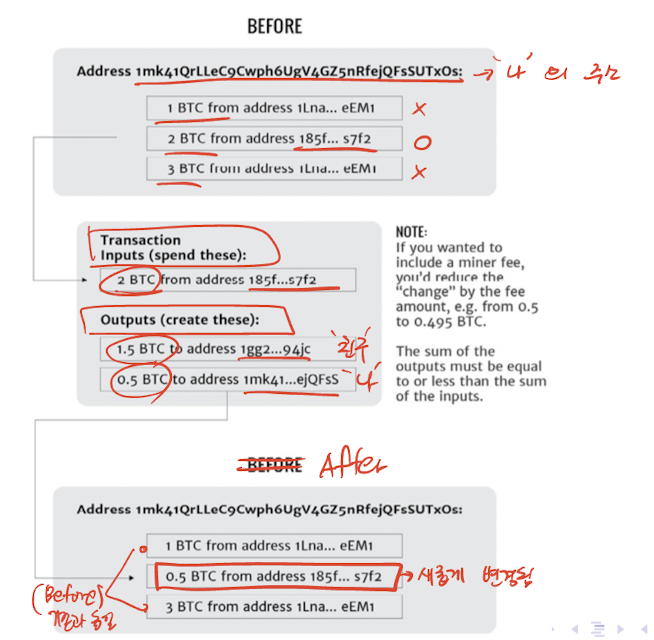
Lump of money → 거래가 이루어지는 방식(input, output)
-
The lumps of money in your account are called
UTXOs(쌓여있는 돈) -
상황 - (1.5 BTC를 친구에게 보내는 경우)
-
2 BTC를 보낸다면 0.5 BTC를 되돌려받는다.
-
Input : 2BTC
-
Output: 1.5BTC(친구) , 0.5BTC(나)
-
-
Peer-to-Peer 방식
-
중앙서버 없이 요청하고, 중개없자가 있지만 불특정 다수이다.
-
Peer-to-peer 모델은 각각의 peer가 서로 업데이트를 공유하는 gassip network(주변 네트워크)와 같다.
-
노드들이 새로운 정보가 발생할 때마다 업데이트를 해야해서 덜 효율적임
-
만약 몇몇의 노드가 일시적으로 연결성을 잃어도, 개개인이 스스로 검증하기 때문에, 각각의 peer는 독립적이고, 위계없이 계속적으로 운영할 수 있음
-
Miscreants
-
개인의 사익을 갖고있는(악의를 갖고있는) bookkeeper의 영향이 매우 제한되어 있음 → 다수의 노드들이 스스로 검증하기 때문에 나쁜 짓을 할 확률이 적다.
-
Malicious miners can:
-
block을 포함하고 제외하는 것이 가능하다.
-
긴 체인(’longer chain’)을 만들어서 Double Spend를 만들 수 있다.
-
-
Malicious miners can’t:
-
Bitcoin을 훔칠 수 없다. Private key를 알고 있지 않은 한 조작이 불가능하다.
-
Bitcoin을 마음대로 만들 수 없다.
-
Bitcoin in Practice
-
비트코인이 탈 중앙화가 되기 힘든 이유
-
Bookkeeping nodes are mostly running the same software, and thus controlled by a very small number of people.
-
(중요) Only a few entities can mine profitably(수익창출), usually using special purpose mining farms clustered in the area of cheap electricity.
-
The ownership of BTC shows a concentration in a small number of hands.
-
Upgrades to the Bitcoin network and protocols are centralised.
-
Account Balance
-
Full node wallet-
전체 비트코인 블록체인 정보를 저장 및 업데이트를 한다.
-
특히 모바일 폰에서 현실적으로 쓰기 어렵다.
-
-
Lightweight wallet-
전체 블록체인에 접속하여 가장 최신버전만 획득, 다운받을 수 있다. (필요한 정보만 다운받을 수 있음)
-
핸드폰으로도 계좌잔고를 볼 수 있다.
-
-
Hardware wallets: private keys are stored in chips on small handheld devices.-
Purpose : 오직 제한된 방식의 요구에 반응하여 Private key를 안전하게 보관할 수 있게 설계되어 있다.
-
The user interface software is run on an online machine.
- Private key를 내부(안)에서 처리한다. (노출시키지 않는다)
-
Since the private key is stored on hardware not connected to the internet, it is harder for a hacker to gain access to the private keys.
-
Hardware wallets - 그림
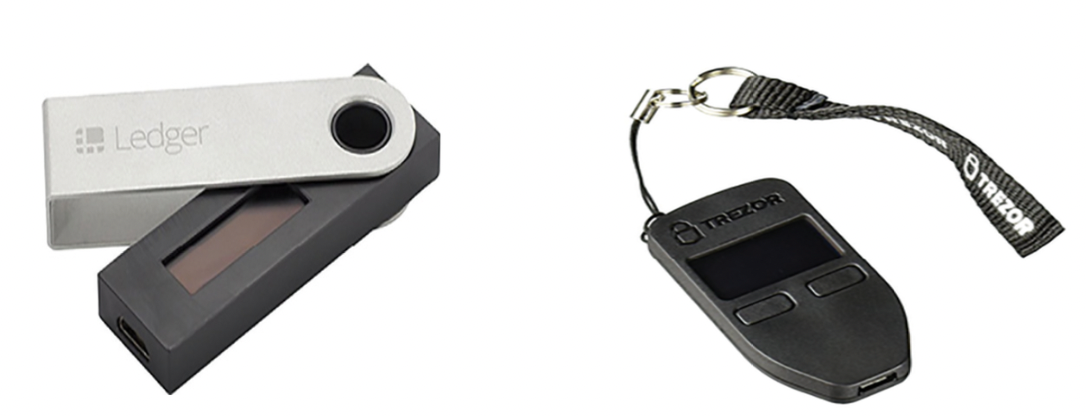

-
-
Cold Storage and Hot Wallets
-
Cold Storage: 인터넷에 연결하지 않는 컴퓨터나 종이와 같은 오프라인 미디어에 Private key를 보관한다.
-
Hot wallet: 중간의 간섭없이 거래에 서명하고 알릴 수 있는 지갑이다.
-
Ethereum
-
Ethereum: a decentralized, open-source blockchain with smart contract functionality (기능적으로 smart contract가 있는 탈중앙화된 오픈소스 블록체인입니다)- Ethereum: trustless validation, distributed storage and processing of data and logic

-
Smart Contract: a self-executing contract with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller being directly written into lines of code- 코드를 통해서 자동으로 실행되는 contract
How Is Ethereum Similar to Bitcoin ?
-
Public and permissionless → 누구나 접근가능하고, 허가가 필요없는 네트워크
-
Proof-of-work (PoW) mining
-
공통점 : Mining participants create valid blocks by spending electricity to find solutions to a mathematical challenge (Ethash).
-
차이점 : Ethash allows more common hardware to be used.
-
비트코인은 컴퓨터 성능이 좋아야 빠르게 계산하여 hash값을 찾을 수 있다.
-
이더리움은 일반적인 모습을 갖춘 하드웨어도 mining을 효율적으로 작업할 수 있게 알고리즘을 만들었다.
-
-
What is the features Ethash algorithm ?
-
Ethash algorithm features
-
[1] It is highly dependent on operations in RAM memory, consuming large amounts of bandwidth. (RAM에 크게 의존한다)
-
[2] The algorithm is GPU friendly. (GPU를 많이 활용한다)
- 그래픽 카드를 많이 활용하는 것은 이더리움에 있는 채굴 알고리즘 때문이고, GPU에 RAM 메모리가 붙어있기 때문이다.
-
[3] Offers excellent verification capabilities for thin clients.
Ethereum 2.0 (Serenity)
Ethereum 2.0(Serenity)
-
In Serenity, there is a plan to move from proof-of-work mining to a proof-of-stake mining protocol (Casper).
-
Proof-of-stake “지분 증명” (중요)
- 이더리움이 많을 수록 다음 block을 채굴 할 수 있게끔 알고리즘을 짜는 것임 (채굴할 수 있는 가능성이 높아진다)
-
Ethereum 2.0(Serenity) 을 정착시키기 위해 해야될 일
- Difficulty bomb(난이도 폭탄): the increasing difficulty level of puzzles in the mining algorithm used to reward miners with Ether on its blockchain
Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)
-
Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM): the part of Ethereum that handles smart contract deployment and execution -
EVM 특징
-
이더리움 소프트웨어를 다운로드하여 실행하면, 컴퓨터에 분리된 가상의 컴퓨터가 생성되고 시작된다.
-
EVM은 모든 이더리움 거래와 블록을 처리하고 모든 계정 잔액과 smart contracts를 추적한다.
-
이더리움 네트워크의 각 노드들은 동일한 EVM을 실행하고 동일한 데이터를 처리한다.
-
Replicated state machine : All the nodes running Ethereum are coming to consensus about the state of the Ethereum Virtual Machine
-
Gas
-
Gas: “가격 리스트”-
Different transaction types have different computational complexities.
-
Ethereum has a concept of gas a sort of price list, based on the computational complexity of the different types of operation.
-
-
Gas Limit
-
The gas limit you set provides a ceiling for how much gas you are prepared for a transaction to consume.
- maximum mining fee = gas limit(양) x gas price(가격)
-
Gas Limit → 거래 예시) Consider a basic transaction of a transfer of ETH from one account to another uses 21,000 gas.
-
21,000이상 입력하게 되면 → 21,000만 사용하게 됨
-
21,000보다 낮게 입력하게 되면 → 거래 인정이 안되고 mining fee 환불이 안된다.
-
-
Uncles
-
Uncle: a block which does not form a part of main chain -
특징
-
In Bitcoin, they are called
orphan -
In Ethereum,
uncles→ 전체 시스템에 chain의 security를 향상시키는데 공헌한다.
-
GHOST Protocol
-
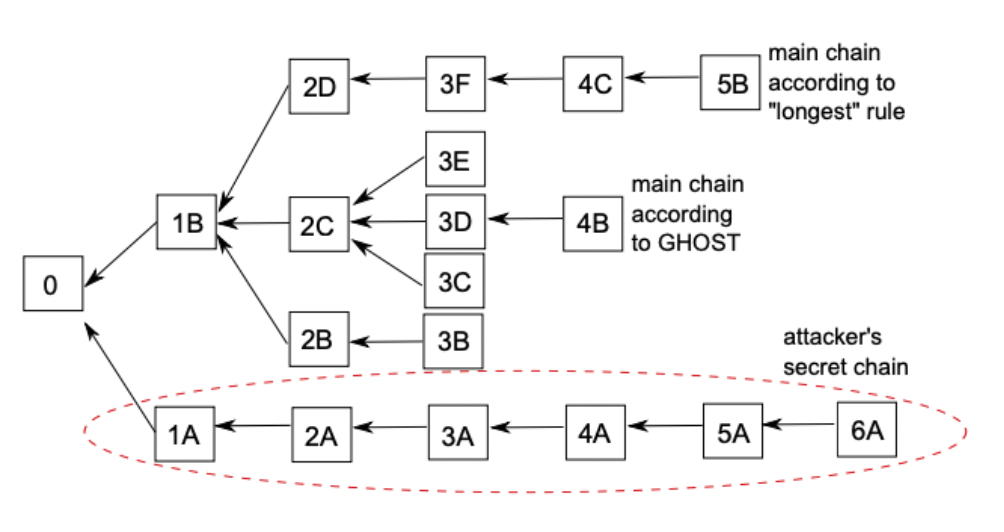
GHOST(Greedy Heaviest Observed Subtree) Protocol: An algorithm for dealing with stale blocks. -
문제점
-
[1] Security issue - A먼저 생성후 B 생성하게 되면, B는 main chain에 인정받지 않게 되고 네트워크 보안에 기여하지 않게 됨
-
[2] Centralization issue - 더 빨리 만드는 miner가 독점할 수 있음
-
-
해결 방안
-
[1] Security issue - Stale blocks are added to the calculation of which is the main chain of the blockchain.
-
[2] Centralization issue: There are block rewards to stales.
-
Modified GHOST Implementation
-
Modified GHOST Implementation- GHOST protocol에 개선된 것-
A block must specify a parent, and it must specify 0 or more uncles.
-
uncle : 자신의 직계조상의 다른 child를 의미함
-
An uncle included in block B must have the following properties:
-
It must be a direct child of the kth generation ancestor of B, where 2 ≤ k ≤ 7.
-
직계 조상이 될 수 없다.
-
만약 이전 block이 uncle인 B_1을 쓴다면, 다른 block이 B_1을 uncle에서 제외시켜야 한다.
-
-
-
Modified GHOST Implementation
-
조상의 직계자식들만 uncle이 된다.
-
가장 무거운 Subtree을 선택한다(가장 많은 block을 가진 것)
-
4B의 uncle: 3E, 3C, 2D, 2B
Reference
-
- The Impact of Fintech, AI, and Crypto on Financial Services, Henry Arslanian and Fabrice Fischer, 2019, Springer
-
Bitcoin, Blockchain, and Cryptoassets
- A Comprehensive Introduction, Fabian Schär and Aleksander Berentsen, 2020, MIT Press
-
The Basics of Bitcoins and Blockchains
- An Introduction to Cryptocurrencies and the Technology that Powers Them , Antony Lewis, 2018, Mango