이 글은 실제 히빗 프로젝트(ver.2)를 혼자서 개발하면서 경험한 내용을 정리한 글입니다.
- 예상 독자:
@EntityGraph가 무엇이고 어떻게 적용해야할지 궁금한 개발자
문제 상황
현재, 특정 게시글 조회를 위한 API에 대한 성능 테스트를 진행하면서 다음 가정을 설정했다.
- 1초 동안 서로 다른 100명의 사용자가 동시에 특정 게시글을 10번 반복해서 조회했을 때 (총 1000번), TPS(Traffic Per Second)가 얼마나 나오는지 확인했다.
아래와 같이 조회수는 정상적으로 1000이 나오는 걸 볼 수 있다.
{
"id": 1,
"writerId": 1,
"writerName": "mjy",
"title": "디뮤지엄 전시 보러가요",
"content": "오스린티 전시회 보러가실 분 있나요?",
"exhibition": "오스틴리 전시",
"exhibitionAttendanceAndTogetherActivity": [
"4인 관람",
"맛집 가기"
],
"possibleTime": "2024-01-05 12:00",
"openChatUrl": "https://kakao",
"postStatus": "HOLDING",
"imageName": "exhibition.png",
"viewCount": 1000
}
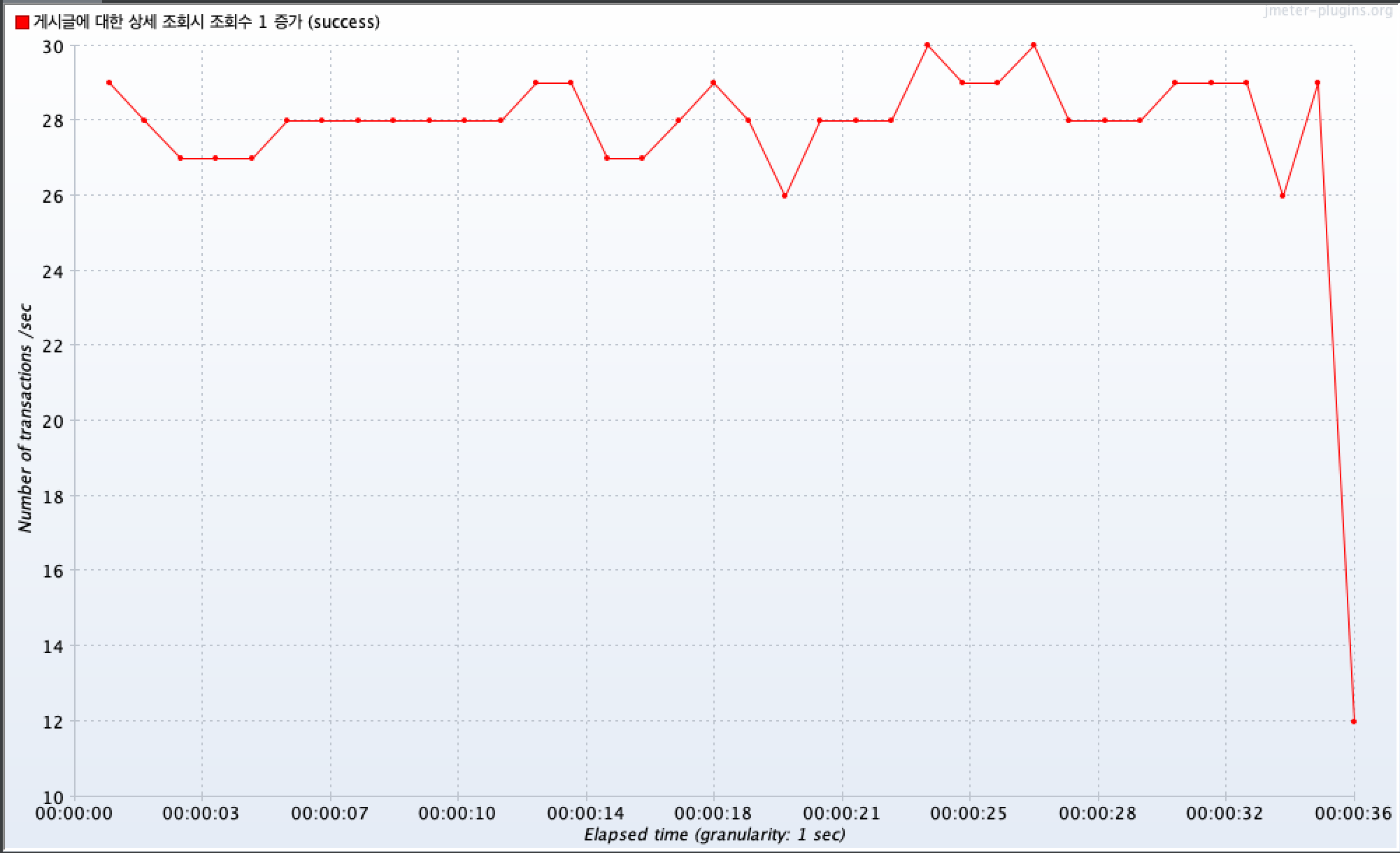
JMeter를 통한 성능 테스트에서 요약 보고서를 확인했을 때, 아래와 같이 평균 처리량(TPS)이 27.9/sec 나오는 걸 확인할 수 있다.

TPS가 27.9라는 것은 Traffic Per Second(초당 처리 건수)가 27.9건이라는 의미이다.
이는 1초 동안 시스템이 27.9번의 요청을 처리할 수 있다는 것을 나타낸다.
TPS에 대한 그래프를 확인했을 때, 최대 30 이 나왔다.
현재 게시글(Post)와 게시글을 작성한 회원(Member)의 관계는 다대일 단방향 매핑 으로 이루어져 있고, 지연 로딩을 사용했다.
여기서 지연 로딩을 사용한 이유는 Post 엔티티와 연관된 엔티티(Member)를 실제로 사용할 때 엔티티를 조회할 때 프록시를 통해 가져오기 때문이다.
즉, Post 엔티티를 로드할 때 Member 엔티티의 정보는 필요한 시점에만 로드되고, 이때 프록시(Proxy)를 통해 지연 로딩이 이루어진다.
그 후 해당 프록시 객체를 호출할 때마다 그때그때 select 쿼리가 실행된다. (자세한 내용은 이전에 작성한 [JPA] 프록시와 연관관계 관리 글을 참고하자)
Post(게시글) 엔티티
@Table(name = "posts")
@Entity
public class Post extends BaseEntity {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "id")
private Long id;
@ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.LAZY)
@JoinColumn(name = "members_id")
private Member member;
// ...
}
Member(회원) 엔티티
@Table(name = "members")
@Entity
public class Member extends BaseEntity {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "id")
private Long id;
// ...
}
그리고 하나의 게시글을 조회할 때 JPA에서 제공해주는 findById()를 사용했다.
그래서 PostRepository 인터페이스에는 아무런 코드를 입력하지 않았다.
PostService 클래스
@Service
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public class PostService {
// ...
@Transactional
public PostDetailResponse findPost(final Long postId, final LoginMember loginMember, final String cookieValue) {
if (viewCountManager.isFirstAccess(cookieValue, postId)) {
postRepository.updateViewCount(postId);
}
Post foundPost = findPostObject(postId);
return PostDetailResponse.of(foundPost, loginMember);
}
// ...
private Post findPostObject(final Long postId) {
return postRepository.findById(postId)
.orElseThrow(NotFoundPostException::new);
}
}
그 결과, 특정 게시글에 대한 조회 api에 대한 쿼리를 확인했을 때 아래와 같이 나왔다.
Hibernate:
select
post0_.id as id1_2_0_,
post0_.created_date_time as created_2_2_0_,
post0_.updated_date_time as updated_3_2_0_,
post0_.content as content4_2_0_,
post0_.exhibition as exhibiti5_2_0_,
post0_.exhibition_attendance as exhibiti6_2_0_,
post0_.image_name as image_na7_2_0_,
post0_.members_id as members14_2_0_,
post0_.open_chat_url as open_cha8_2_0_,
post0_.possible_time as possible9_2_0_,
post0_.post_status as post_st10_2_0_,
post0_.title as title11_2_0_,
post0_.together_activity as togethe12_2_0_,
post0_.view_count as view_co13_2_0_
from
posts post0_
where
post0_.id=?
// ...
Hibernate:
select
member0_.id as id1_0_0_,
member0_.created_date_time as created_2_0_0_,
member0_.updated_date_time as updated_3_0_0_,
member0_.display_name as display_4_0_0_,
member0_.email as email5_0_0_,
member0_.is_profile as is_profi6_0_0_,
member0_.main_image as main_ima7_0_0_,
member0_.social_type as social_t8_0_0_
from
members member0_
where
member0_.id=?
게시글을 조회할 때, 연관된 회원도 같이 조회가 된다. 근데, 여기서 select 절이 2번 조회되는 걸 볼 수 있다.
매번 특정 게시글을 조회할 때마다 게시글안에 회원 정보도 필요하기 때문에, 한 번에 select 하는게 더 낫지 안을까? 라는 생각이 들었다.
기본적으로 Post 엔티티는 Member 엔티티를 로딩할 때 지연 로딩으로 사용되는데, 위와 같이 특정 상황에서는 즉시 로딩 전략이 필요 할 수 있다.
이때 사용하는 방법이 바로 @EntityGraph 어노테이션이다.
해결 방안: @EntityGraph 적용
@EntityGraph 는 Data JPA에서 fect 조인을 어노테이션으로 사용할 수 있도록 만들어 준 기능이다.
@EntityGraph를 사용하면 특정 엔티티나 연관된 엔티티들을 로딩할 때 그래프를 명시적으로 정의할 수 있다.
PostService 클래스, PostRepository 인터페이스
// PostService
@Service
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public class PostService {
// ...
@Transactional
public PostDetailResponse findPost(final Long postId, final LoginMember loginMember, final String cookieValue) {
if (viewCountManager.isFirstAccess(cookieValue, postId)) {
postRepository.updateViewCount(postId);
}
Post foundPost = findPostObject(postId);
return PostDetailResponse.of(foundPost, loginMember);
}
// ...
private Post findPostObject(final Long postId) {
return postRepository.findPostById(postId)
.orElseThrow(NotFoundPostException::new);
}
}
// PostRepository
public interface PostRepository extends JpaRepository<Post, Long> {
// ...
@EntityGraph(attributePaths = "member")
@Query("SELECT p FROM Post p")
Optional<Post> findPostById(Long id);
}
위와 같이 특정 게시글(Post)을 조회할 때 해당 게시물에 대한 회원(Member) 정보를 함께 조회하게 된다.
이렇게 함으로써 지연 로딩을 사용하더라도 특정 게시글을 가져올 때마다 작성자 정보를 필요한 경우에만 가져오게 되어 효율적인 쿼리를 수행할 수 있다.
그 결과 쿼리는 아래와 같이 나오게 된다.
Hibernate:
select
post0_.id as id1_2_0_,
member1_.id as id1_0_1_,
post0_.created_date_time as created_2_2_0_,
post0_.updated_date_time as updated_3_2_0_,
post0_.content as content4_2_0_,
post0_.exhibition as exhibiti5_2_0_,
post0_.exhibition_attendance as exhibiti6_2_0_,
post0_.image_name as image_na7_2_0_,
post0_.members_id as members14_2_0_,
post0_.open_chat_url as open_cha8_2_0_,
post0_.possible_time as possible9_2_0_,
post0_.post_status as post_st10_2_0_,
post0_.title as title11_2_0_,
post0_.together_activity as togethe12_2_0_,
post0_.view_count as view_co13_2_0_,
member1_.created_date_time as created_2_0_1_,
member1_.updated_date_time as updated_3_0_1_,
member1_.display_name as display_4_0_1_,
member1_.email as email5_0_1_,
member1_.is_profile as is_profi6_0_1_,
member1_.main_image as main_ima7_0_1_,
member1_.social_type as social_t8_0_1_
from
posts post0_
left outer join
members member1_
on post0_.members_id=member1_.id
where
post0_.id=?
위의 쿼리를 통해 알 수 있듯이, @EntityGraph 어노테이션을 적용하면 left outer join을 사용하는 걸 확인할 수 있다.
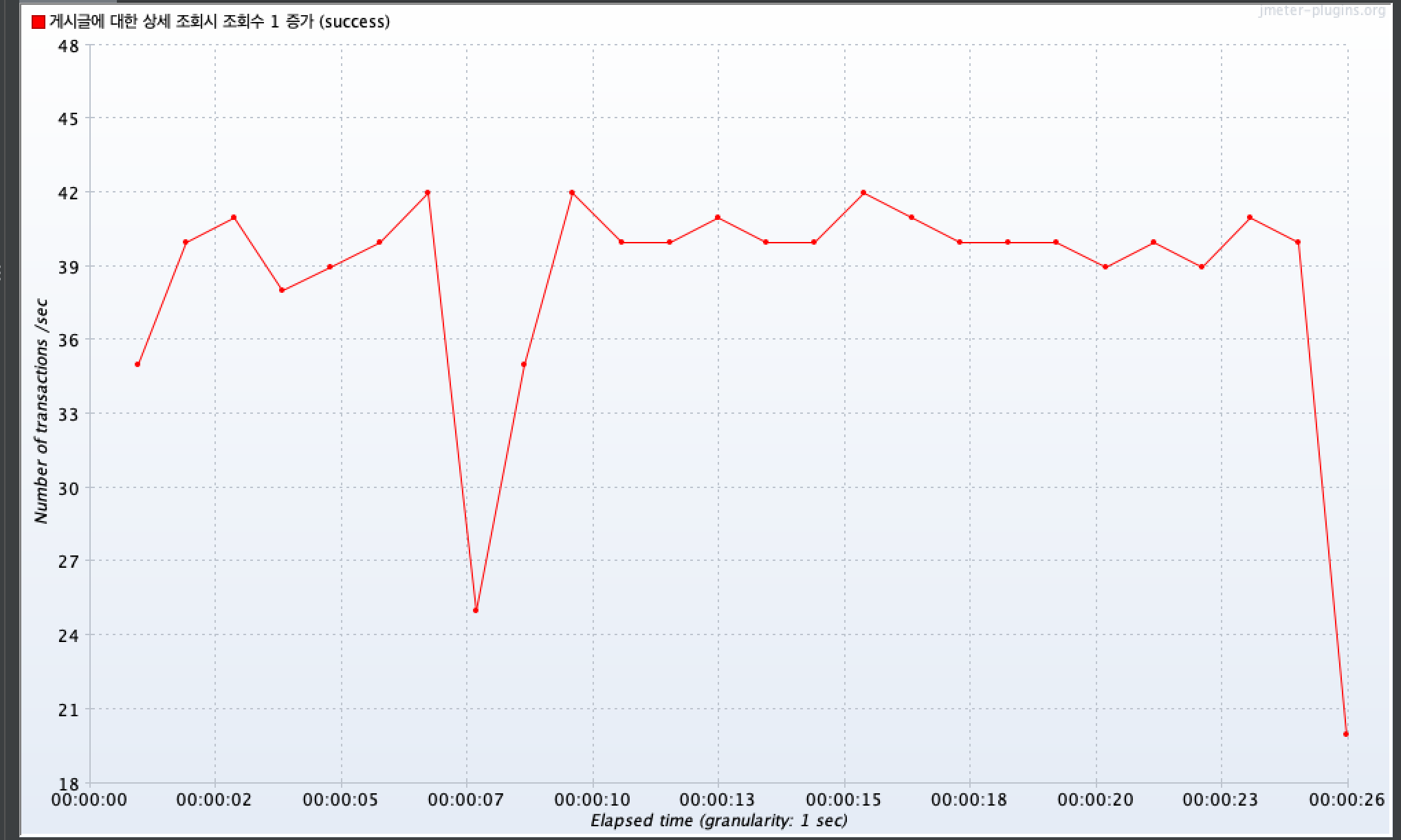
그리고 처음과 같이, 1초 동안 서로 다른 100명의 사용자가 동시에 특정 게시글을 10번 반복해서 조회하는 성능 테스트를 실행했다.
결과를 확인해보니, 평균 TPS 값이 39.1로 이전 평균 TPS(27.9) 보다 40.14% 개선된 것을 확인할 수 있다.

TPS에 대한 그래프에서는 최대 TPS 값이 42로 이전 최대 TPS(30)보다 40% 개선된 것을 확인할 수 있다.
이처럼 쿼리를 명시적으로 작성하지 않아도 fetch join 과 같은 효과를 나타낼 수 있으나, 약간의 차이점이 있다.
@EntityGraph의 경우 fetchType을 eager로 변환하는 방식으로 outer left join을 수행하여 데이터를 가져오지만,
fetch join의 경우 따로 outer join으로 명시하지 않는 경우 inner join을 수행한다는 점이다.
이 때문에 1:N(일대다) 연관 관계에서 fetch join을 사용할 때, 일반적으로 1개의 컬렉션만 함께 조회할 수 있다.
그러나 이로 인해 distinct가 필요한 상황에서도 @EntityGraph를 사용하면 이러한 단점을 극복할 수 있다.
@EntityGraph type
@EntityGraph은 다음과 같이 2가지 유형이 있다. 기본 값은 FETCH이다.
-
FETCH: entity graph에 명시한 attribute는EAGER로 패치하고, 나머지 attribute는LAZY로 패치 -
LOAD: entity graph에 명시한 attribute는EAGER로 패치하고, 나머지 attribute는 entity에 명시한fetch type이나 디폴트 FetchType으로 패치 (@OneToMany는LAZY, @ManyToOne은EAGER등이 기본 값이다)
마무리
위에서 소개한 @EntityGraph를 이용한 성능 개선은 현재 프로젝트에 적용하기에는 아직 간단한 수준이다.
현재 개발 중인 히빗 프로젝트(ver.2)는 EC2 인스턴스 서버 2개를 활용하고 있다. (NGINX 서버 - 백엔드 서버 인스턴스 유형: t2.micro)
데이터베이스 레플리케이션을 활용한 쿼리 성능 개선은 고려사항 중 하나이지만, 혼자 개발 중인 프로젝트의 비용 부담도 고려해야 한다.
따라서 추가로 비용을 발생시키지 않는 방법을 고민하며 성능을 향상시킬 수 있는 다양한 접근 방법을 모색해보자.
Reference
- https://docs.spring.io/spring-data/jpa/docs/current/api/org/springframework/data/jpa/repository/EntityGraph.html