이 글은 컴퓨터학부 확률과통계 수업에서 배운 자료들을 정리한 내용입니다.
Contents
-
3.1 The Binomial Distribution
-
3.2 The Geometric and Negative Binomial Distributions
-
3.3 The Hypergeometric Distribution
-
3.4 The Poisson Distribution
-
3.5 The Multinomial Distribution
3.1.2 Definition of the Binomial Distribution
-
A binomial distribution(이항 분포) with parameter $n$ and $p$
-
The random variable is defined by the parameter $p$, 0 ≤ p ≤ 1 , which is the probability that the outcome is 1
-
The number of successes within a fixed number of trials $n$
-
n independent Bernoulli trials $X_{1}, … , X_{n}$
- $X = X_{1} + . . . + X_{n}$
-
$X \sim B(n, p)$
-
$P( X = x) = {n \choose x} p^{x} (1 - p)^{n-x}$
-
${n \choose x} == \frac{n!}{x!(n - x)!}$
-
-
-
Consider an experiment consisting of $n$ Bernoulli trials with a constant probability $p$ of success
-
A random variable $X$: the total number of successes
-
A binomial distribution with parameter $n$ and $p$
-
$X \sim B(n, p)$ → 성공 확률이 p인 실험을 n번 실행하였을 때, 성공 횟수의 분포 ⇒ 이항 분포
-
-
The probability mass function of a $B( n, p )$
-
$P( X = x) = {n \choose x} p^{x} (1 - p)^{n-x}$, for $x = 0, 1, 2, …, n$
-
the expectation and the variance
- $E(X) = np$ and $Var(X) = np(1-p)$
-
-
The cumulative distribution function of a $B(n, p)$
- $P( X ≤ x ) = \sum_{j = 0}^{i} P( X ≤ x_{j} )$
3.2.1 Definition of the Geometric Distribution → 첫 성공
-
The Geometric Distribution(기하 분포) with Parameter p
-
A probability mass function
-
$P( X = x) = (1 - p)^{x-1}p$, for $x = 1, 2, 3, 4, …$
-
$(1 - p)^{x-1}$ → The probability value of x - 1 failures
-
$p$ → The probability value of $x{th}$ success
-
베르누이 시행이 처음 성공할 때까지의 시행횟수를 확률변수 X라고 했을 때, 이 확률변수 X의 분포를 말한다.
-
최초로 발생한 것 (처음 성공할 확률)
-
-
The cumulative distribution function
-
$P( X ≤ x) = \sum_{i = 1}^{x} P( X = i ) = 1 - ( 1 - p)^{x}$
-
의미: $x$ 번을 시도했을 때 다 실패하지 않은 값 ( ⇒ $x$번째까지 성공한 것을 다 더한 값)
-
-
3.2.2 Definition of the negative binomial distribution
-
Definition of the negative binomial distribution → x번 시도해서 r번 성공할 확률
-
The number of trials up to and including the $r^{th}$ success
$P( X = x) = {x - 1 \choose r - 1} p^{r-1} (1 - p)^{(x-1)-(r-1) } \times p = {x - 1 \choose r - 1} (1 - p)^{x-r} p^{r}$, for $x = r, r + 1, r + 2, r + 3, …$
-
x - 1 번 시도해서 r - 1번 성공할 확률 X(곱하기) r번째 성공할 확률
-
The expectation of $X$ and the variance
$E(X) = \frac{r}{p}$
$Var(X) = \frac{r(1-p)}{p^{2}}$
-
-
3.4.1 Definition of the Poisson Distribution <중요>
-
A random variable that counts the number of “events” that occur within certain specified boundaries
-
A probability mass function for a random variable Poisson distribution
-
$X \sim P(\lambda)$
-
$P( X = x ) = \frac{e^{-\lambda}\lambda^{x}}{x!}$ , for $x = 0, 1, 2, 3, …$ 해석) $x$ 개 이벤트가 발생할 확률
-
-
The Poisson distribution can be used to approximate the $B(n, p)$ distribution
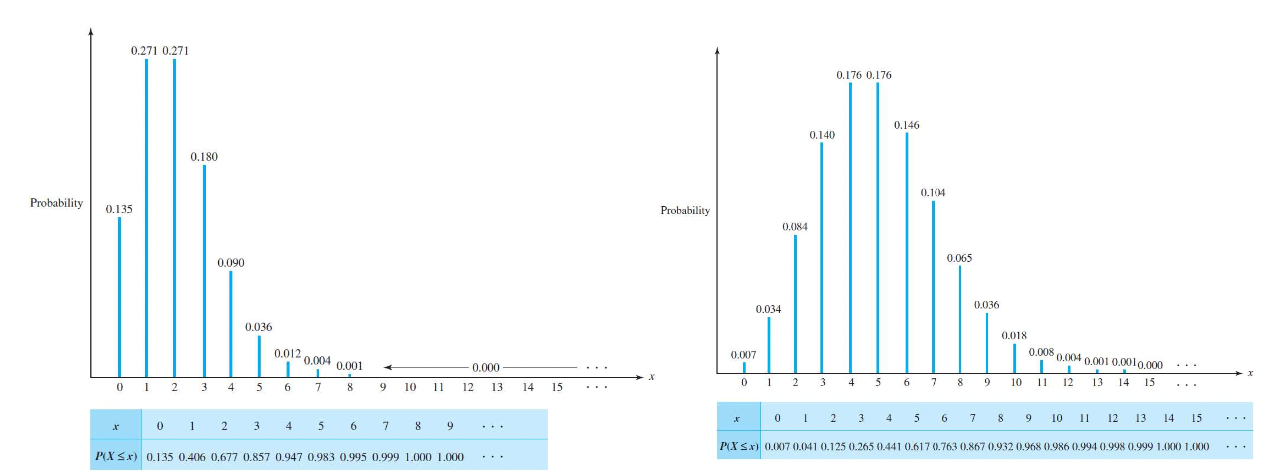
-
when 1) $n$ is very large (larger than 150, say) and 2) the success probability $p$ is very small (smaller than 0.01, say).
-
A parameter value of $\lambda = np$ should be used for the Poisson distribution, so that it has the same expected value as the binomial distribution.
3.5.1 Definition of the Multinomial Distribution <중요>
The Multinomial Distribution
-
Consider a sequence of $n$ independent trials where each individual trial can have $k$ outcomes that occur with constant probability values $p_{1}, …, p_{k}$ with $\sum_{i = 1}^{k} p_{i} = 1$
-
The random variables $X_{1}, …, X_{k}$ that count the number of occurrences of each outcome are said to have a multinomial distribution, and their joint pmf, $P( X_{1} = x_{1}, …, X_{k} = x_{k} ) = \frac{n!}{x_{1}! … x_{k}!} \times p_{1}^{x_{1}} \times … \times p_{k}^{x_{k}}$, for non-negative integer values of the $x_{i}$ satisfying $x_{1} + … + x_{k} = n$
-
The expectation of the variance of each random variable $X_{i}$
-
$E(X_{i}) = np_{i} , Var(X_{i}) = np_{i}(1 - p_{i})$
-
The random variables $X_{1}, …, X_{k}$ are not independent
-