- Contents
- Reference
이 글은 컴퓨터학부 확률과통계 수업에서 배운 자료들을 정리한 내용입니다.
Contents
-
4.1 The Uniform Distribution
-
4.2 The Exponential Distribution + ALOHA
-
4.3 The Gamma Distribution
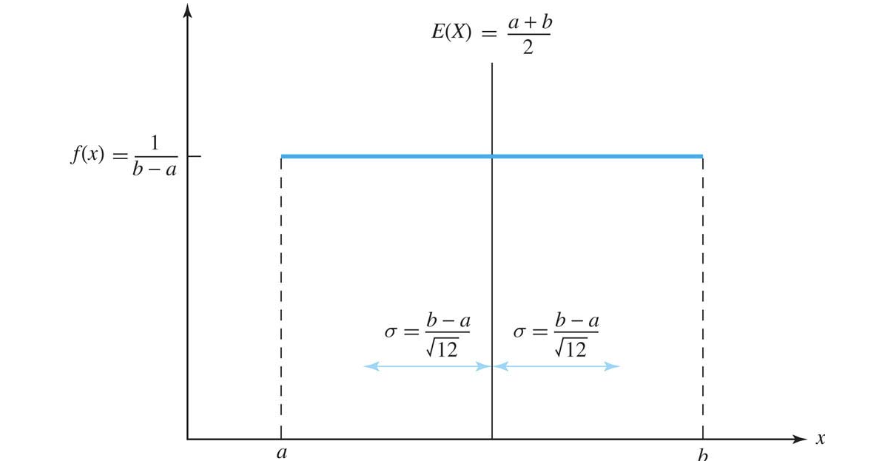
4.1.1 Definition of the Uniform Distribution
-
It has a flat pdf over a region
-
X~U(a, b)
-
Probability density function $f(x) = \frac{1}{b-a},$ a ≤ x ≤ b
-
Cumulative distribution function $F(x) = \int_{a}^{x} \frac{b-a}{1}\, dy = \frac{x-a}{b-a},$ for a ≤ x ≤ b
-
-
The Expectation and the variance
-
$E(X) = \frac{a+b}{2}$
-
$Var(X) = \frac{(b-a)^2}{12}$
-
-
$P^{th}$ quantile of the uniform distribution
-
p^{th} quantile: (1 - p)a + pb
-
Interquartile range: (1 - 0.75)a + 0.75b - (1 - 0.25)a - 0.25b = $\frac{b-a}{2}$
-
-
A standard uniform distribution, $Y \sim U(0,1)$
- $Y = \frac{X-a}{b-a}$
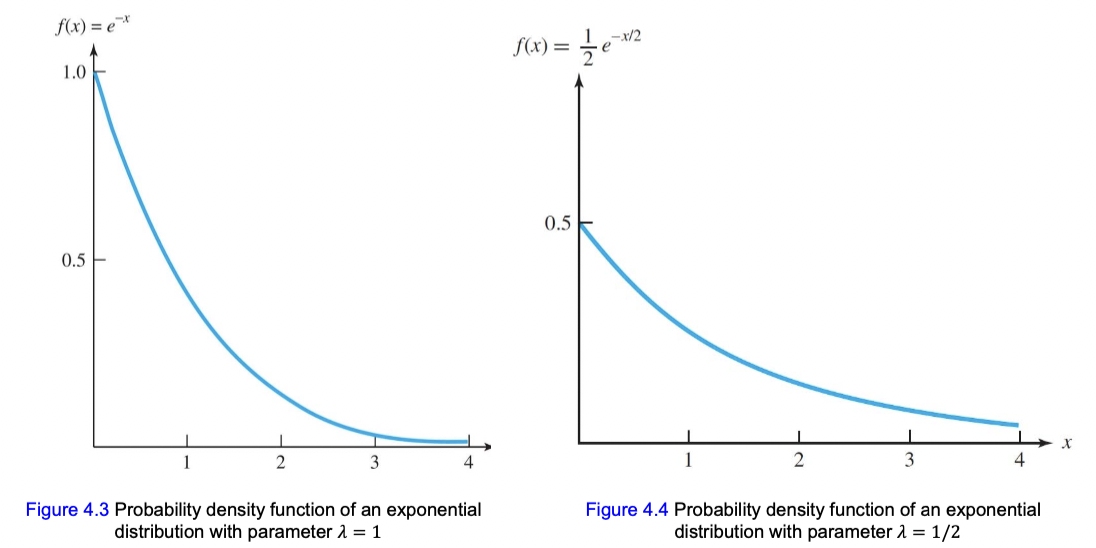
4.2.1 Definition of the Exponential Distribution
-
Probability distribution for failure or waiting times and inter-arrival times
-
Probability density function
-
$f(x) = \lambda e^{-\lambda x}$, for x ≥ 0
-
Depends upon a parameter $\lambda > 0$
-
-
Cumulative distribution function
- $F(x) = 1 - e^{-\lambda x}$, for x ≥ 0 ↔ otherwise → 0
-
Expectation and Variance
- E(x) = $\frac{1}{\lambda}$ and Var(x) = $\frac{1}{\lambda^{2}}$
-
$p^th$ quantile
-
$F(x) = 1-e^{\lambda x} = p$
-
$x = \frac{ln(1-p)}{\lambda} = E(X)\ln(1-p)$
-
The median of the distribution
- $x = -E(X)\ ln\ (1- \frac{1}{2}) = E(X)\ ln\ 2$
-
The lower quartile
- $x = -E(X)\ ln\ (1- \frac{1}{4}) = E(X)\ ln\ \frac{4}{3}$
-
The upper quartile
- $x = -E(X)\ ln\ (1- \frac{3}{4}) = E(X)\ ln\ 4$
-
The interval of interquartile (= upper - lower)
- $x = E(X)\ ln\ 4 - E(X)\ ln\ \frac{4}{3} = E(X)\ ln\ 3$
-
-
Examples of the exponential distribution
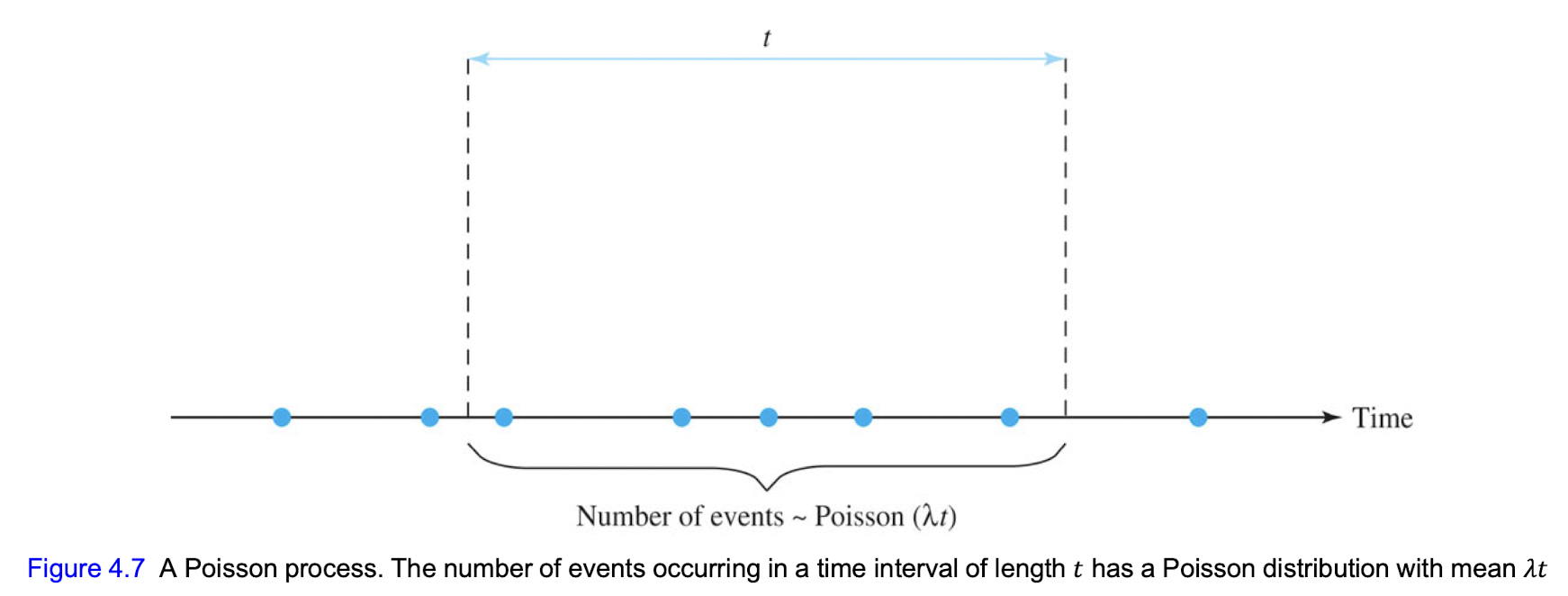
4.2.3 The Poisson Process
-
Expected waiting time and Expected number of events
-
Expected waiting time btw. two events in a Poisson process: $\frac{1}{\lambda}$
-
Expected number of events occurring within a fixed time interval $t: \lambda t$
-
Moreover, the number of events occurring within such a time interval has a Poisson distribution with mean $\lambda t$
-
Performance Analysis of ALOHA and Slotted-ALOHA
ALOHA Protocol
-
컴퓨터 네트워킹 시스템인 ALOHAnet 에서 사용한 프로토콜
-
하와이 여러 섬에 분산된 컴퓨터 간 무선통신으로 데이터 교환
-
위성 시스템, 5G 기지국에서도 사용 중
Performance of ALOHA
-
Vulnerable period $(V_p)$ (취약구간)
-
Time interval during which the packets are susceptible to collision
-
Vulnerable period 관련 예시
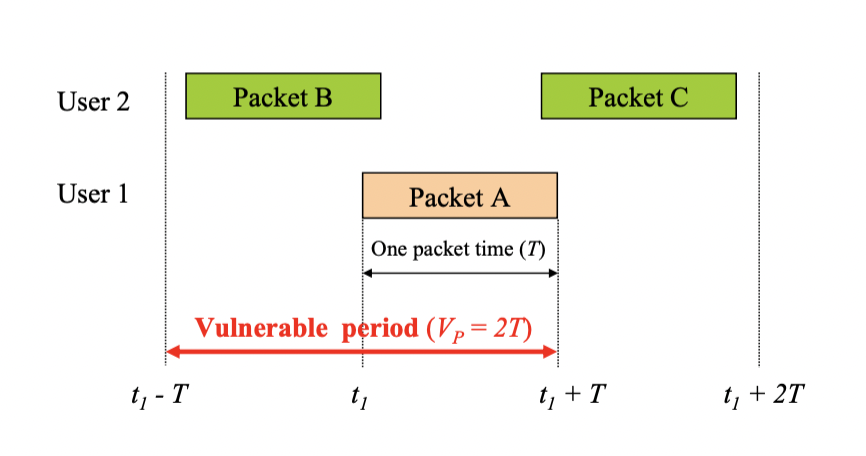
-
다음 그림을 통해 설명하면, Packet A를 기준으로 Packet A가 깨지지 않으려면, 충돌을 발생하는 Packet B구간 까지 포함해서 Vulnerable period(2T) 라고 한다.
2T라는 시간동안 다른 패킷이 끼어들면 안된다. -
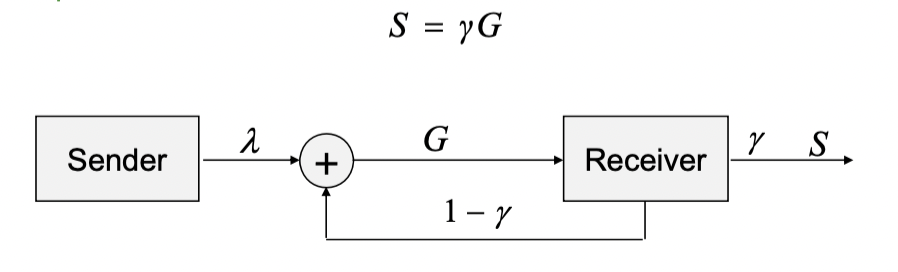
$S$ : average number of successful transmissions per transmission
-
$T$라는 시간동안 평균적으로 성공한 횟수
-
$S = \gamma G$
-
-
$G$ : average number of packet transmissions attempted per $T$ seconds
- $T$라는 시간동안 전송 시도했던 패킷의 평균 횟수
-
$\gamma$ : probability of successful transmission
- 성공한 전송의 확률
Throughput of ALOHA
-
Channel Throughput
- Average number of attempts per slot(G) x Probability of successful transmission($\gamma$)
$S = \gamma G = Ge^{-2G}$
-
Maximum throughput($S_{max}$)
$S_{max} = \frac{1}{2e} = 0.184$
Delay of ALOHA (1)
Average number of retransmissions
- Probability of success on the n-th attempt ($P_{s}$)
$(P_{s}){n} = (1 - \gamma)^{n-1} \gamma$ where $P{s} = \gamma = e^{-2G}$
- Average number of transmission($N$)
$E[N] = \sum_{n=1}^\infty n(1-\gamma)^{n-1} \gamma = \frac{1}{\gamma} = e^{2G}$
- Average number of retransmissions($N_{r}$)
$E[N_{r}] = E[N] - 1 = e^{2G} - 1$
-
$R$: Time between retransmission packets (재전송하는데 걸리는 시간)
- Normalized with respect to the packet transmission time T
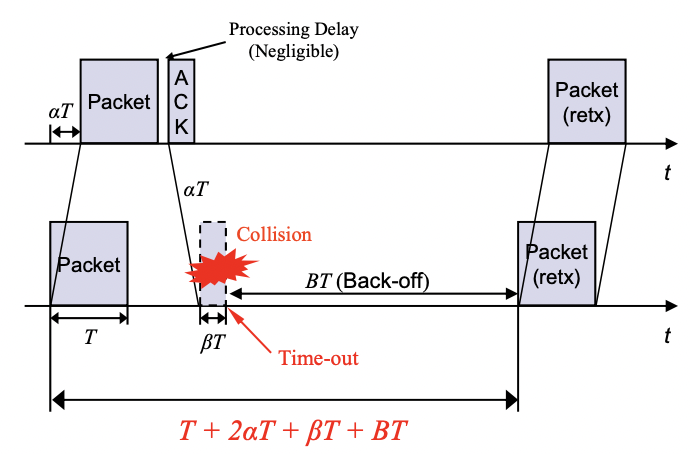
-
$RT = T + 2 \alpha T + \beta T + BT$
-
⇒ $R = 1 + 2 \alpha + \beta + B$
-
where
-
$\alpha T$: one -way propagation delay of the channel (오고 가고해서 총 2번)
-
$\beta T$: transmission delay of ACK packet
-
$BT$: random delay before retransmission (변수)
-
$E[R]$: Mean time between retransmission packets (재전송하는데 평균 시간)
- $E[R] = 1 + 2 \alpha + \beta + E[B]$ (times of T) ← B가 변수
Delay of ALOHA (2)
-
$E[B]$ : average back-off time after collision (충돌후 평균적으로 얼마만큼 delay가 생기는가)
- $E[B] = \frac{K-1}{2}$
-
$E[D]$ : average delay time consists of
-
The time to transmit one packet
-
The time between transmissions multiplied by the average number of retransmissions
-
The propagation delay
- $E[D] = (e^{2G} - 1)(2 \alpha + \beta + \frac{K + 1}{2}) + 1 + \alpha$
-
Slotted ALOHA
Slotted ALOHA
-
To improve the performance of ALOHA
-
System time is divided into slots fixed length
-
All transmitters and receivers are synchronized → ALOHA보다 단점
-
A packet is transmitted at the start of the upcoming slot
-
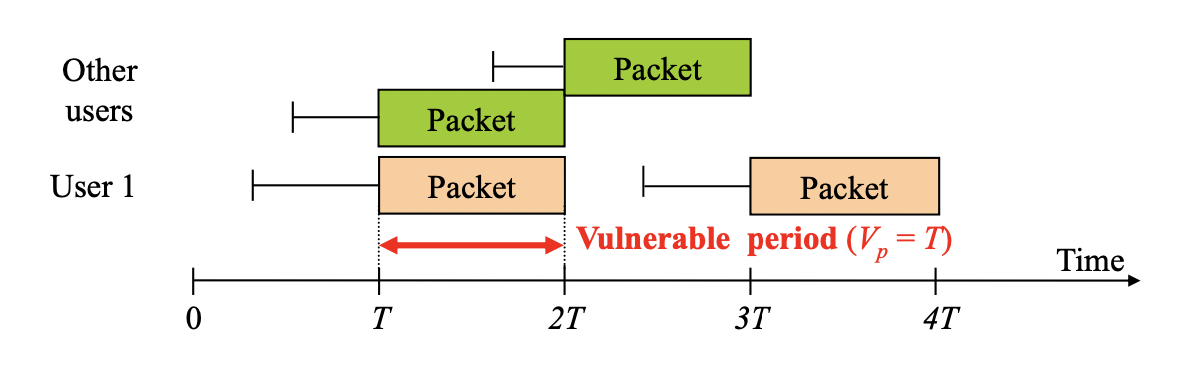
Vulnerable period 관련 예시
Throughput of S-ALOHA
-
Channel Throughput
- Throughput is defined as the expected number of successfully transmitted packet per slot
$S = p_{1} = \frac{G^{k}}{k!}e^{-G} _{k=1} = Ge^{-G}$ -
Maximum throughput($S_{max}$)
$S_{max} = \frac{1}{e} = 0.368$
Delay of S-ALOHA
-
$E[D]$ : average delay time consists of
-
The time to transmit one packet
-
The time between transmissions multiplied by the average number of retransmissions
-
The propagation delay
$E[D] = (e^{G} - 1)(2 \alpha + \beta + \frac{K + 1}{2}) + \frac{3}{2} + \alpha$
-
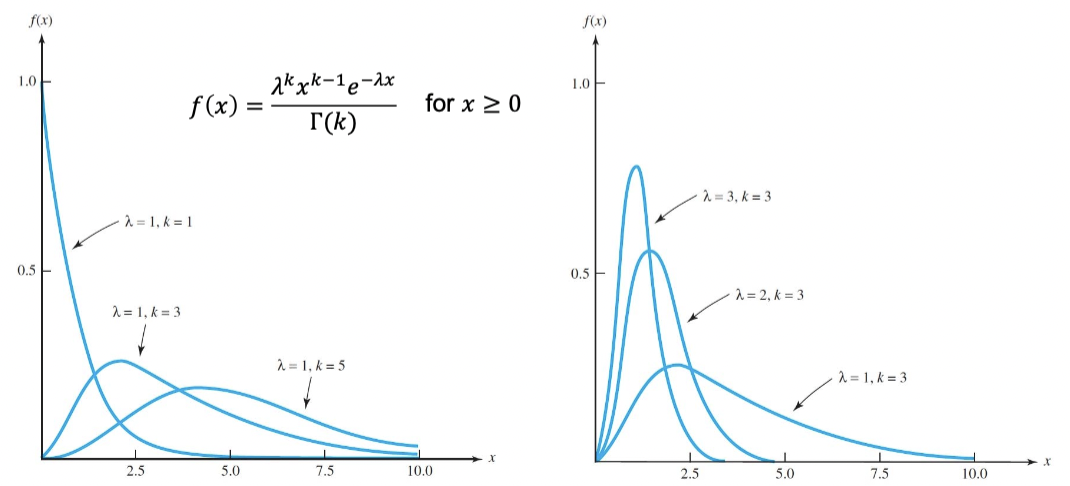
4.3.1 Definition of the Gamma Distribution
-
Gamma Distribution-
Used in the reliability theory and the analysis of a Poisson process
-
It has a state space x ≥ 0 and a pdf $f(x) = \frac{\lambda^{k}x^{k-1}e^{-\lambda x}}{\Gamma(k)}$ for x ≥ 0 and
-
f(x) = 0 for x < 0, which depends on two parameters $k > 0$ and $\lambda > 0$
-
the function $\Gamma(k)$ is known as the gamma function
-
If $k = 1$, the gamma distribution simplifies to the exponential distribution with parameter $\lambda$ ($f(x) = \lambda e^{-\lambda x}$ , for x ≥ 0)
-
-
The Gamma Function
-
$\Gamma(k) = \int_{0}^{\infty} x^{k-1}e^{-x} dx$
-
Some special cases are $\Gamma(1) = 1$ and $\Gamma(1/2) = \sqrt{\pi},$ and in general, $\Gamma(k) - (k-1)\Gamma(k-1)$
-
for k >1. If n is a positive integer, the
-
$\Gamma(n) = (n-1)!$
-
but except for these special cases there is in general no closed-form expression for the gamma function.
-
-
Curves of Gamma
- the parameter $k$ is often referred to as the shape parameter of the gamma distribution, and $\lambda$ is referred to as the scale parameter