지금의 기록이 미래의 자산이 된다.
Today's records become tomorrow's assets.-
[Programmers] 150370. 개인정보 수집 유효기간
성능 요약
- 메모리: 78.4 MB, 시간: 0.68 ms
구분
- 코딩테스트 연습 > 스택/큐
Answer Code1(23.10.05)
/** * 개인정보 수집 유효기간 * @param today 오늘 날짜 YYYY.MM.DD * @param terms 약관의 유효기간 (약관종류 유효기간) : 공백으로 구분, 유효기간은 개월수 * @param privacies 수집된 개인정보 (날짜 약관종류) : 공백으로 구분 * @return 파기해야할 개인정보의 번호 오름차순 */ import java.util.*; class Solution { public int[] solution(String today, String[] terms, String[] privacies) { int[] answer = {}; Map<String, String> termsMap = new HashMap<>(); // key: 약관 종류, value: 유효 기간 for(String term: terms) { String[] termSplit = term.split(" "); termsMap.put(termSplit[0], termSplit[1]); } Integer number = 1; // privacies의 번호 List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>(); // 현재 총 날짜 수 Integer todayTotalDate = getTotalDate(today, 0); for(String p : privacies) { String[] privateSplit = p.split(" "); // 개인별 날짜 String privateDate = privateSplit[0]; // 개인별 약관 종류 String privateTerm = privateSplit[1]; // 약관 개월수 Integer termsMonth = Integer.valueOf(termsMap.get(privateTerm)); // 기간 경과후 총 날짜 수 Integer privateTotalDate = getTotalDate(privateDate, termsMonth) - 1; // 기간 경과후 날짜가 현재날짜보다 미만이면 폐기 대상 if(privateTotalDate < todayTotalDate) { // 현재 당일은 아직 폐기 대상 아님 // 유효기간 경과하여 폐기대상인 번호를 추가 result.add(number); } // privacies의 번호 + 1 number++; } answer = result.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray(); return answer; } /** * (YYYY.MM.DD)을 총 날짜 수로 환산 * @param strDate YYYY.MM.DD * @param termsMonth 약관 개월 수 * @return 날짜로 환산한 총 날짜 수 */ private Integer getTotalDate(String strDate, Integer termsMonth) { String [] dateSplit = strDate.split("\\."); Integer year = Integer.valueOf(dateSplit[0]); Integer month = Integer.valueOf(dateSplit[1]) + termsMonth; Integer day = Integer.valueOf(dateSplit[2]); // 모두 일 수로 환산, 한 달은 28일 return (year * 12 * 28) + (month * 28) + day; } }문제 풀이
조건) 모든 달은 28일 까지 있다고 가정
today: 오늘 날짜를 의미하는 문자열 → “YYYY.MM.DD”terms: 약관의 유효 기간을 담은 1차원 문자열 배열 → “약관 종류,유효 기간”privacies: 수집된 개인정보의 정보를 담은 1차원 문자열 배열 → “날짜,약관 종류”출력) 파기해야할 개인정보의 번호를 오름차순으로 1차원 정수 배열에 담아 return
-
약관의 종류별로 유효 기간을 취득하기 위해 약관의 유효 기간을 담는
terms를 Map으로 변환해준다.(key: 약관 종류, value: 유효 기간)
Map<String, String> termsMap = new HashMap<>();
-
오늘 날짜를 총 날짜 수로 변환해준다.
참고) 연월일을 총 날짜수로 변환하는 식: (연도 * 12개월 * 28일) + (월 * 28일) + 일
Integer todayTotalDate = (
today의 YYYY * 12 * 28) + (today의 MM * 28일) + (today의 DD) -
개인정보
privacies배열을 하나씩 확인해가며 약관이 유효한지 만료되었는지 확인한다.- 배열 privacies에서
날짜와약관종류를 분리하여 취득한다.- 공백으로 분리되어 있으므로 공백으로 자르면 인덱스
0은 날짜이며, 인덱스1은 약관 종류가 된다. - String privateDate = privacies원소.split(” “)[0] // 날짜
- String privateTerm = privacies원소.split(” “)[1] // 약관 종류
- 공백으로 분리되어 있으므로 공백으로 자르면 인덱스
- 약관 종류로 Map에서 유효 기간을 취득한다.
- Integer termsMonth = Integer.valueOf(termsMap.get(privateTerm)); A에 해당하는 유효 기간(달)을 갖는다.
- 날짜의 달에 유효기간 달 수를 더해준다.
- Integer privateMonth = Integer.valueOf(privateDate.split(”\.”)[1]) + termsMonth
- 유효 기간 경과후 총 날짜 수를 구한다.
- Integer privateTotalDate = (privateDate의 YYYY * 12 * 28) + (privateMonth * 28) + (privateDate의 DD)
-
계산된 전체 날짜 수를 비교하여 폐기 대상인지 확인한다.
(유효 기간을 고려한 약관 날짜 수 < today의 총 날짜수) 이면, 폐기 대상이다.
if( privateTotalDate < todayTotalDate) 폐기대상
today 당일의 경우에도 아직 유효 기간이 지나지 않아 폐기 대상이 아니므로 today 미만으로 계산한다.
- 배열 privacies에서
-
[Goodfriends] 우리팀의 기능별 패키지 구조 적용기
이 글은 우리FISA 1기 굿프렌즈팀의 기술 블로그에 게시된 글 입니다.
굿프렌즈팀은 프로젝트를 진행하면서 어떠한 패키지를 구성하면 좋을지 고민했습니다. 보통 패키지를 구조를 나누는 방법으로 대표적인 패키지 구조인
계층별,기능별이 있습니다.
-
[Goodfriends] PR 라벨로 Jenkins Build 유발 구분하기 🏷
- Repository 구성
- Github 이슈 라벨로 구분하기
- Generic Webhook Trigger 설치
- Github WebHook 설정
- Generic Webhook Trigger 설정
- Post content parameters 설정
- Optional filter 설정
- Token 설정
- 응답 확인하기
- 트러블 슈팅
- 마치며
- Reference
이 글은 우리FISA 1기 굿프렌즈팀의 기술 블로그에 게시된 글 입니다.
저번에 포스팅 했던 젠킨스를 사용하여 CI/CD Pipeline 구축기(프론트엔드편) 에 이어서 이번 글은 프론트엔드/백엔드의 코드가 PR시 병합되었을 때 라벨로 구분하여 젠킨스를 빌드하는 과정을 소개하고자 합니다.
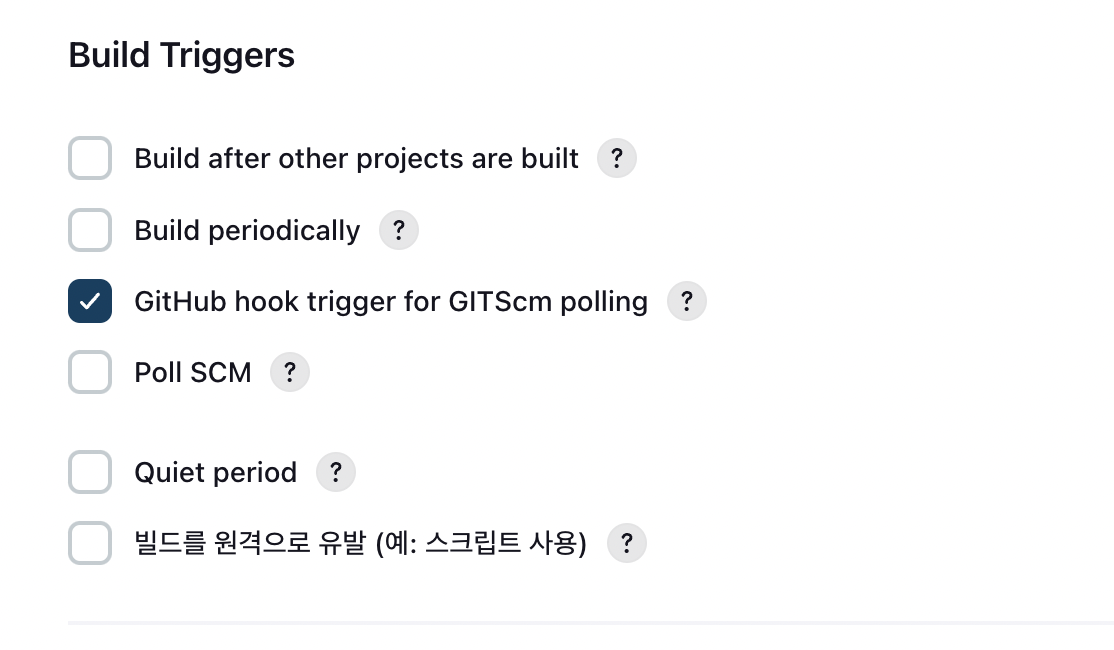
현재 굿프렌즈팀의 젠킨에서 빌드 트리거로
Github hook trigger for GITScm polling을 사용하고 있습니다.파이프라인 스크립트 부분에서 아래와 같이 빌드 트리거가 동작하기 위한 스크립트 작성 부분입니다.

Repository 구성
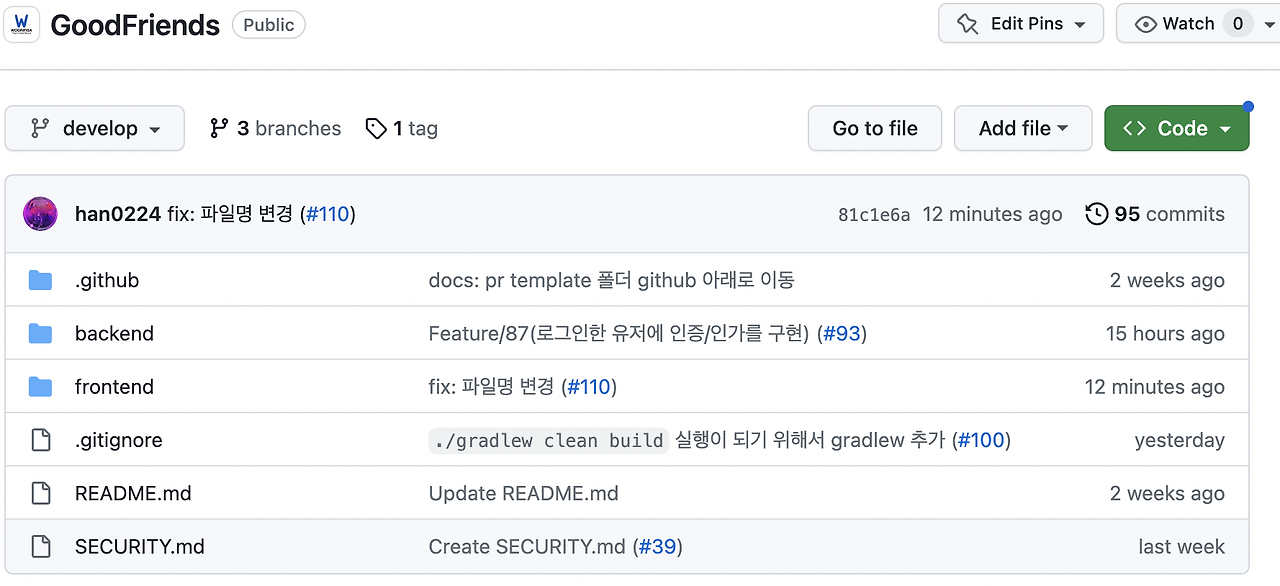
현재 굿프렌즈팀의 레포지토리를 보시면, 프론트엔드와 백엔드 코드가 같이 관리되고 있습니다. 두 개의 코드 중 하나라도 병합(Merge)되었을 때 프론트엔드, 백엔드 같이 빌드 및 배포되고 있습니다.
PR시 Merge되었을 때 각 트랙별로 코드가 빌드 및 배포될 수 있도록 빌드 트리거를 조금 더 세분화하여 Github의 라벨을 기반으로 트리거를 개선하려고 합니다.
Github 이슈 라벨로 구분하기
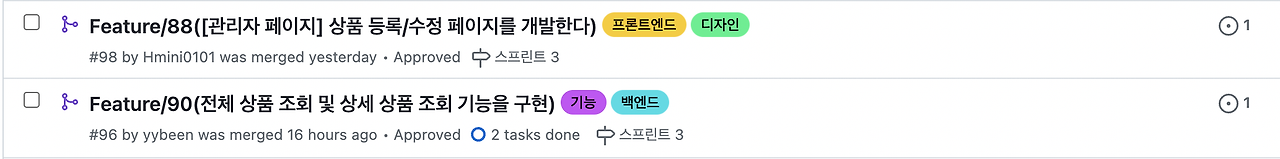
현재 굿프렌즈팀은 라벨을 이용하여 트랙별 작업 구분을 하고 있습니다.
따라서 이를 이용하여 라벨별로 빌드 및 배포를 진행할 수 있도록 구성하였습니다.
Generic Webhook Trigger 설치
Plugins - Available plugins에서
Generic Webhook Trigger설치후 재시작합니다.그런 다음 Plugins - Installed plugins - 설치된
Generic Webhook Trigger가 있는지 확인합니다.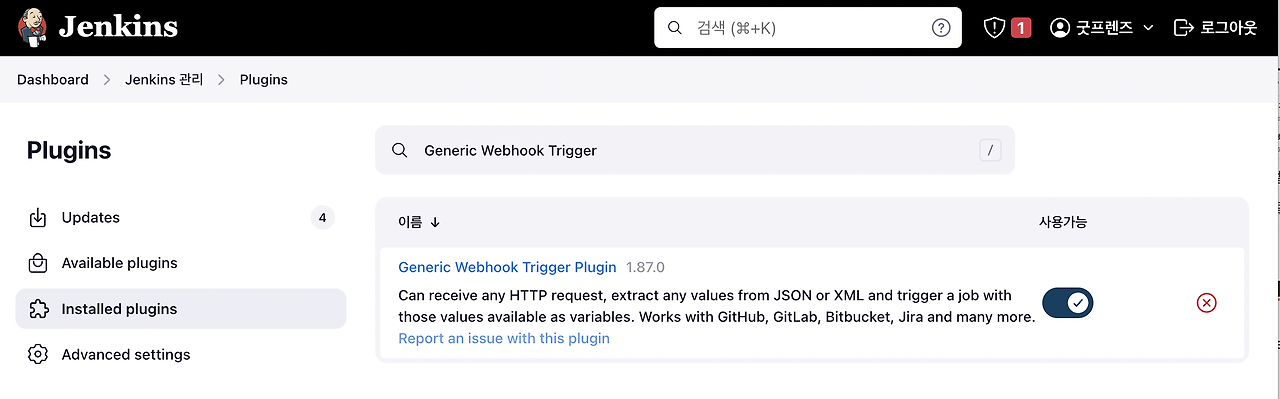
Generic Webhook Trigger는 젠킨스에서 제공하는 플러그인으로 HTTP 요청을 수신하여 JSON, XML 형태의 데이터를 추출하여 트리거를 지정할 수 있는 플러그인입니다. Generic Webhook Trigger를 사용하여 빌드 유발 상황을 구분하려고 합니다.
플러그인을 설치했다면 젠킨스 파이프라인의 Build Triggers 설정에서 아래와 같이 Generic Webhook Trigger를 확인할 수 있습니다.
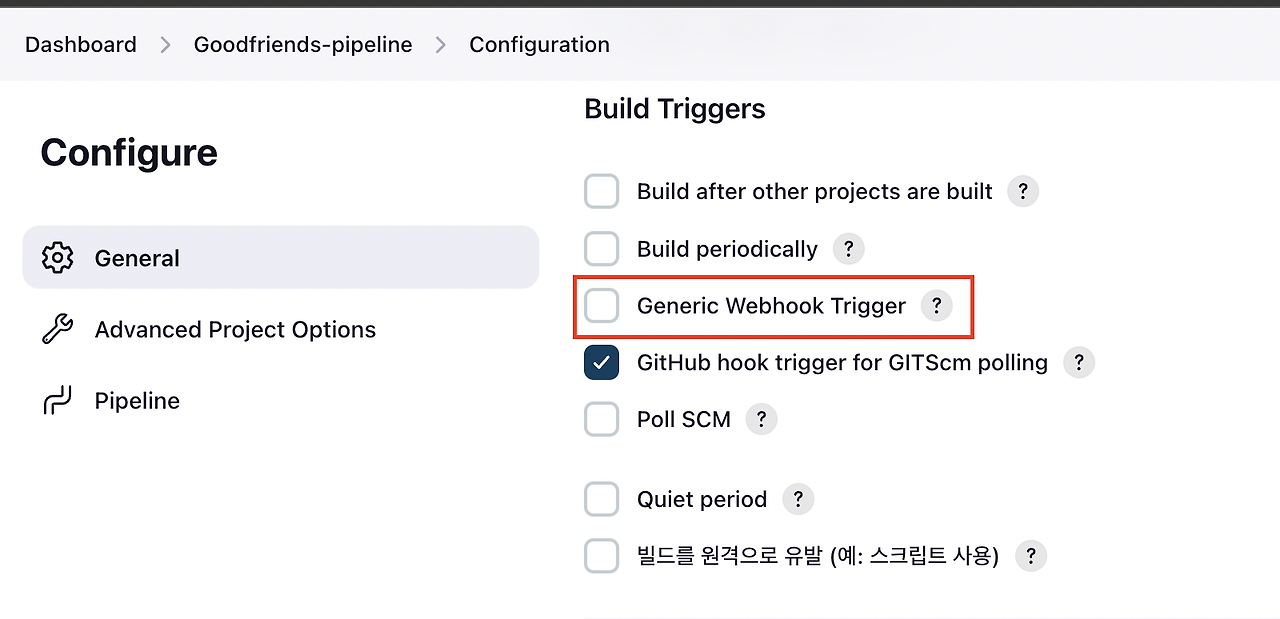
해당 부분을 클릭하면 아래와 같은 설명을 확인하실 수 있습니다.
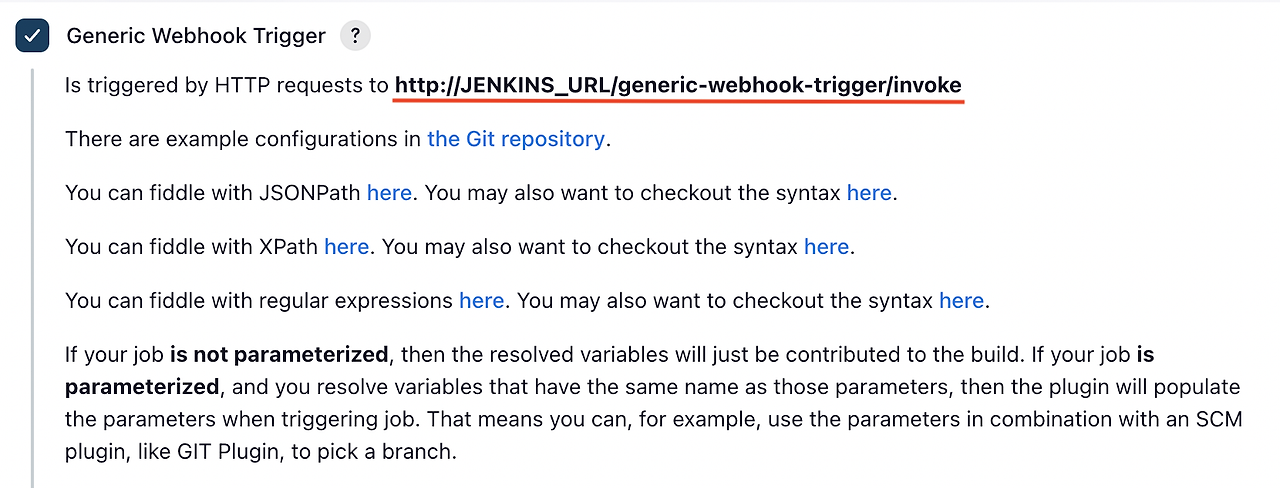
http://JENKINS_URL/generic-webhook-trigger/invoke로 오는 요청에 대해 트리거가 수행된다는 말이 적혀 있습니다.위 설명에 맞춰 GitHub에서 WebHook 설정을 변경해주어야 합니다.
위에서 설명한 탭에 대해서는 아직 저장하지 않고 깃허브로 넘어와서 진행합니다.
젠킨스 설정은 아래에서 설명하는 Github WebHook 설정 이후에 이어서 진행합니다.
Github WebHook 설정
기존에 설정된 한개의 Webhook을 확인하실 수 있습니다.
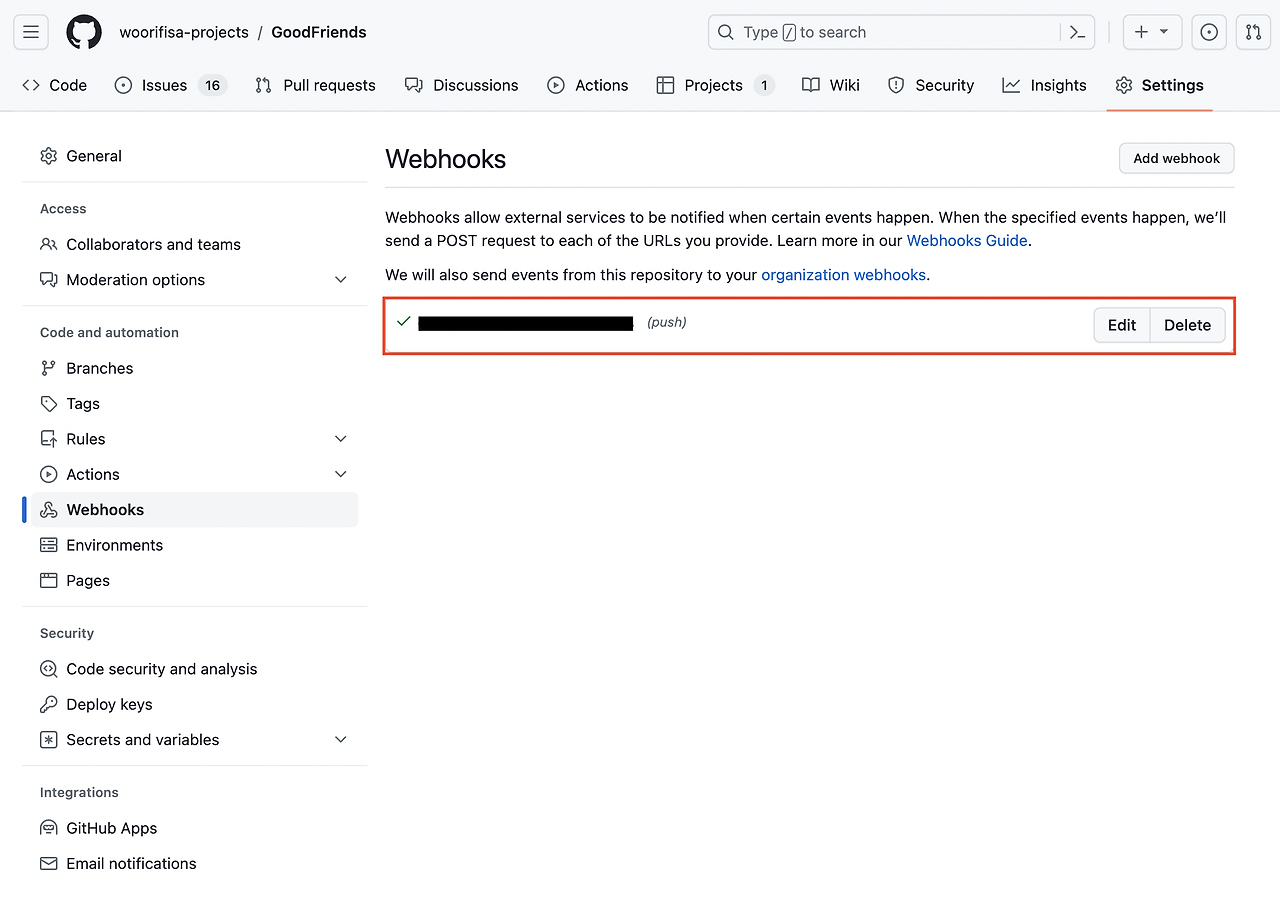
프로젝트 레포지토리 -> Setting -> Webhook 탭에 들어와서 웹훅을 새로 만듭니다. (Add Webhook 버튼 클릭)
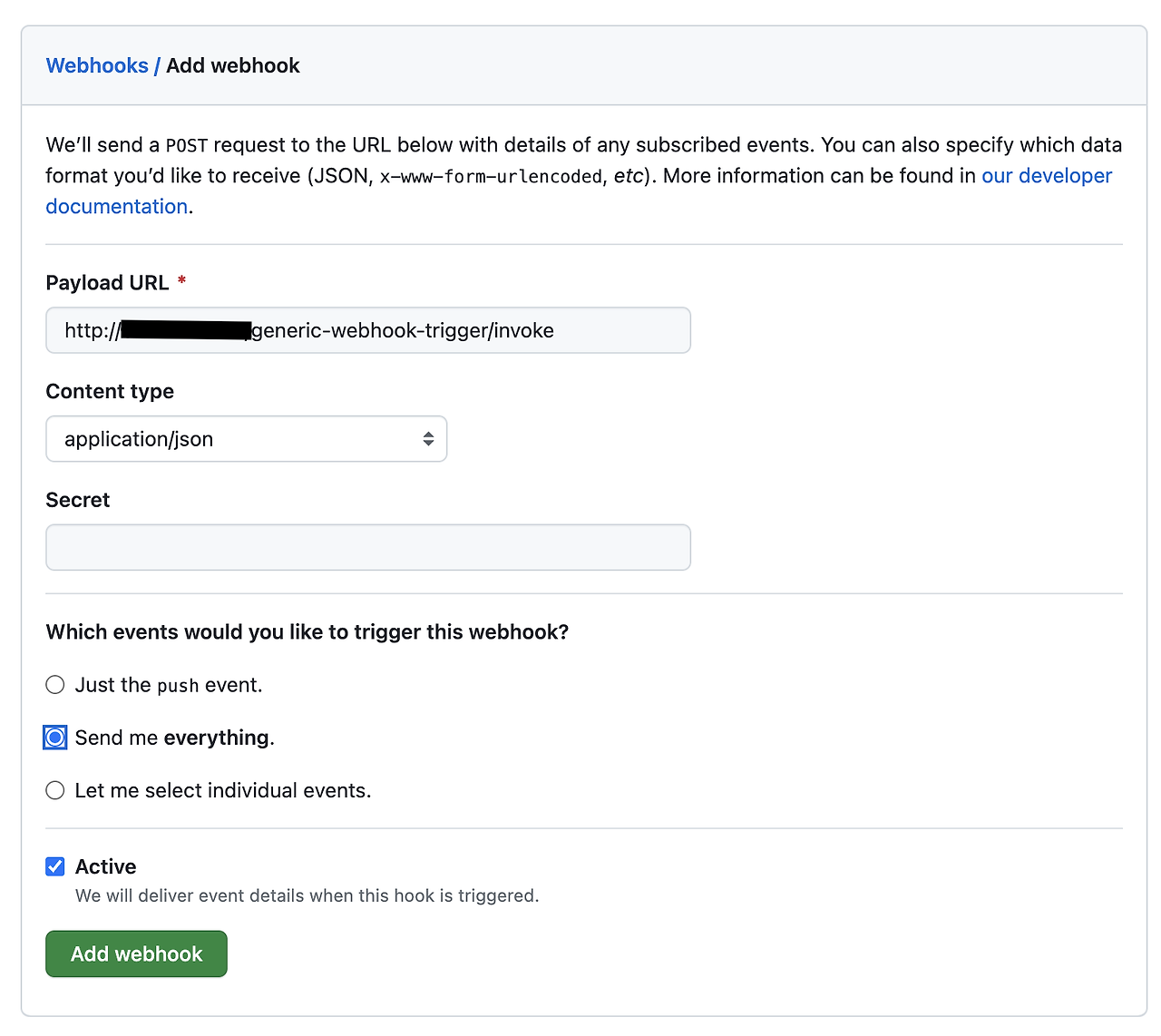
payload URL:
http://{jenkins 퍼블릭 ip 주소}:80/generic-webhook-trigger/invokePayload URL을 위에서 확인한 Generic Webhook Trigger의 설정에 맞게 작성합니다.
그리고 트리거가 동작하는 이벤트에 대해서 Send me everything 옵션을 체크합니다.
Webhooks / Manage webhook
Add webhook을 한 뒤 다시 등록한 웹 훅을 클릭하여 Recent Deliveries 탭을 확인하면,
Webhooks / Manage webhook (detail)
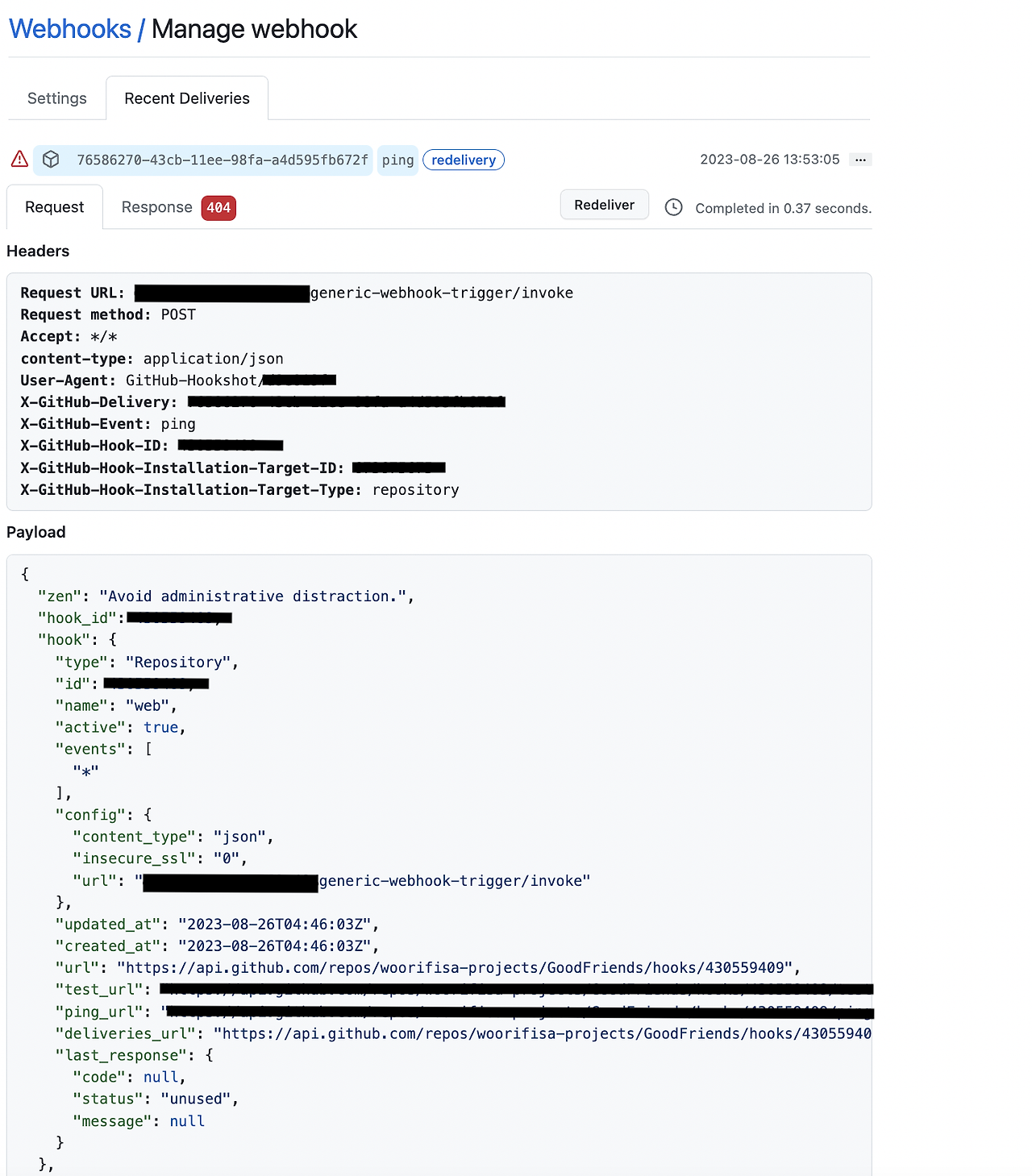
내용을 보면 요청을 보낼 때 Payload에 다양한 정보들이 담겨있는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
Generic Webhook Trigger 설정
젠킨스 파이프라인 설정 구성에 들어와서 작업을 이어나갑니다.
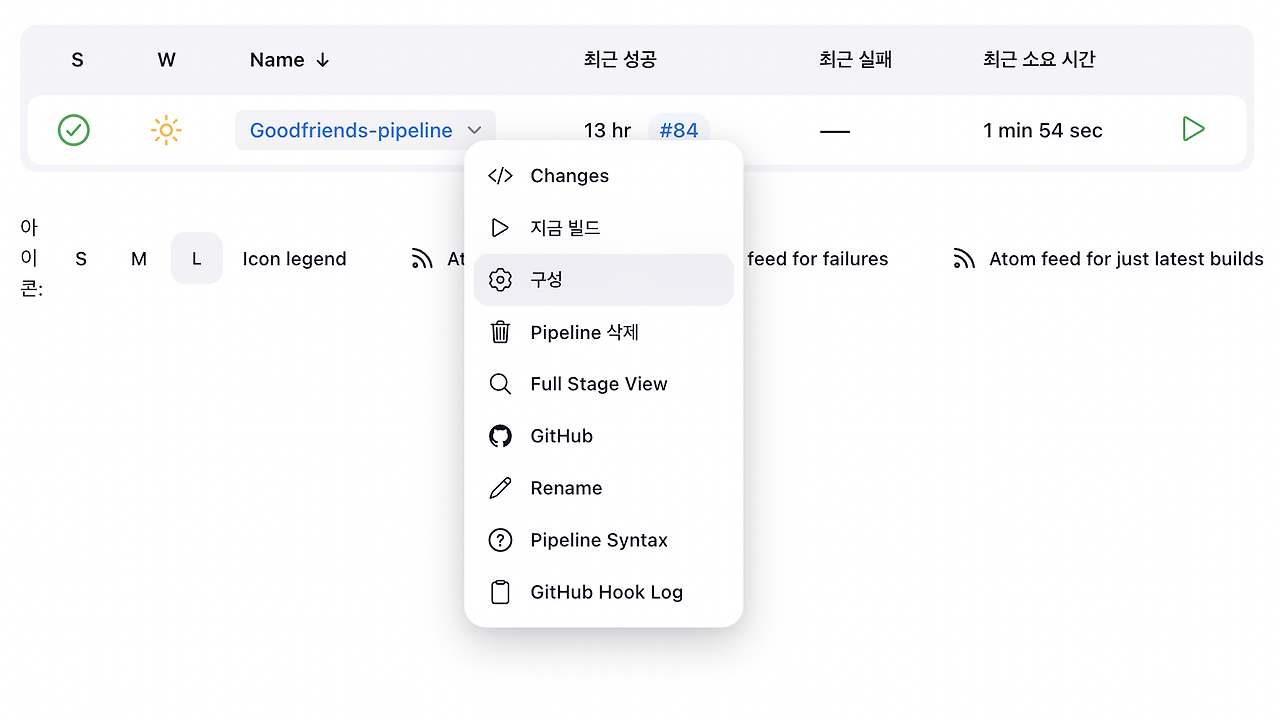
기존에 설정해둔 GitHub hook trigger for GITScm polling 설정을 해제한 다음, Generic WebHook Trigger 를 활성화합니다.
Post content parameters 설정
Post content parameters의 추가 버튼을 눌러 파라미터를 추가합니다.
MERGED
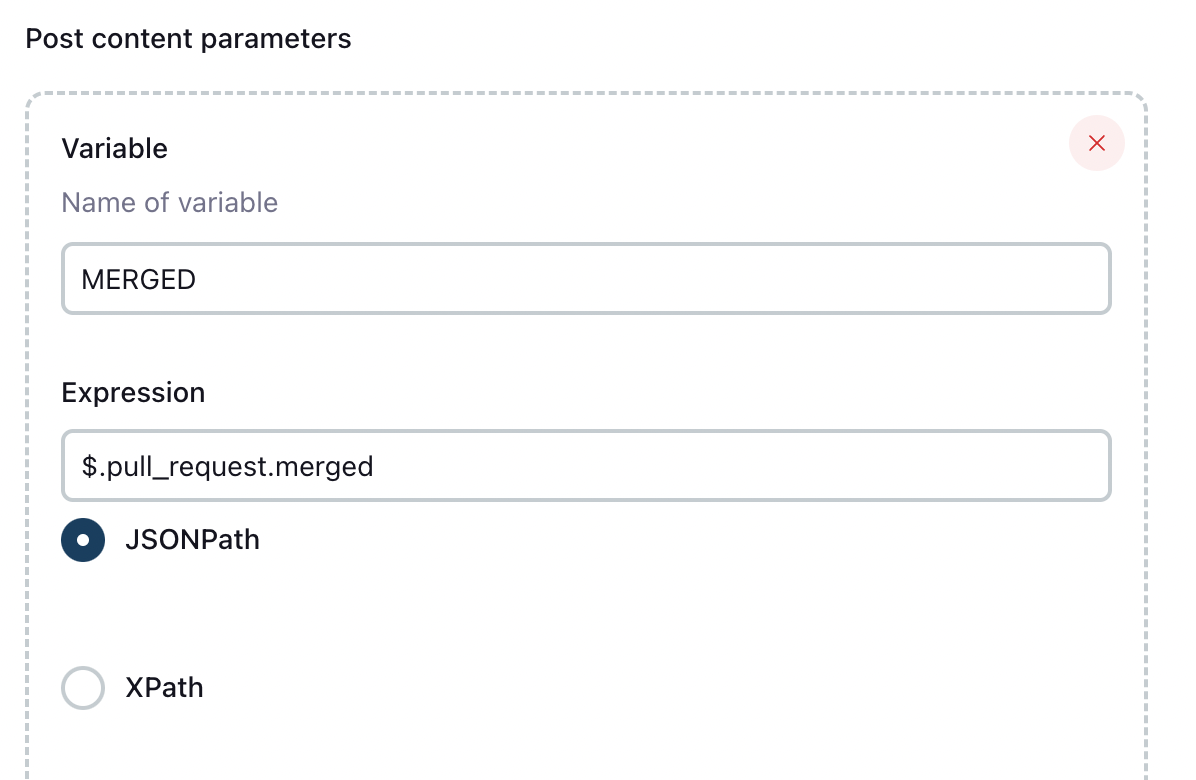
$.pull_request.merged를 등록하여 Merge 되었는지 여부를 가져옵니다.BRANCH
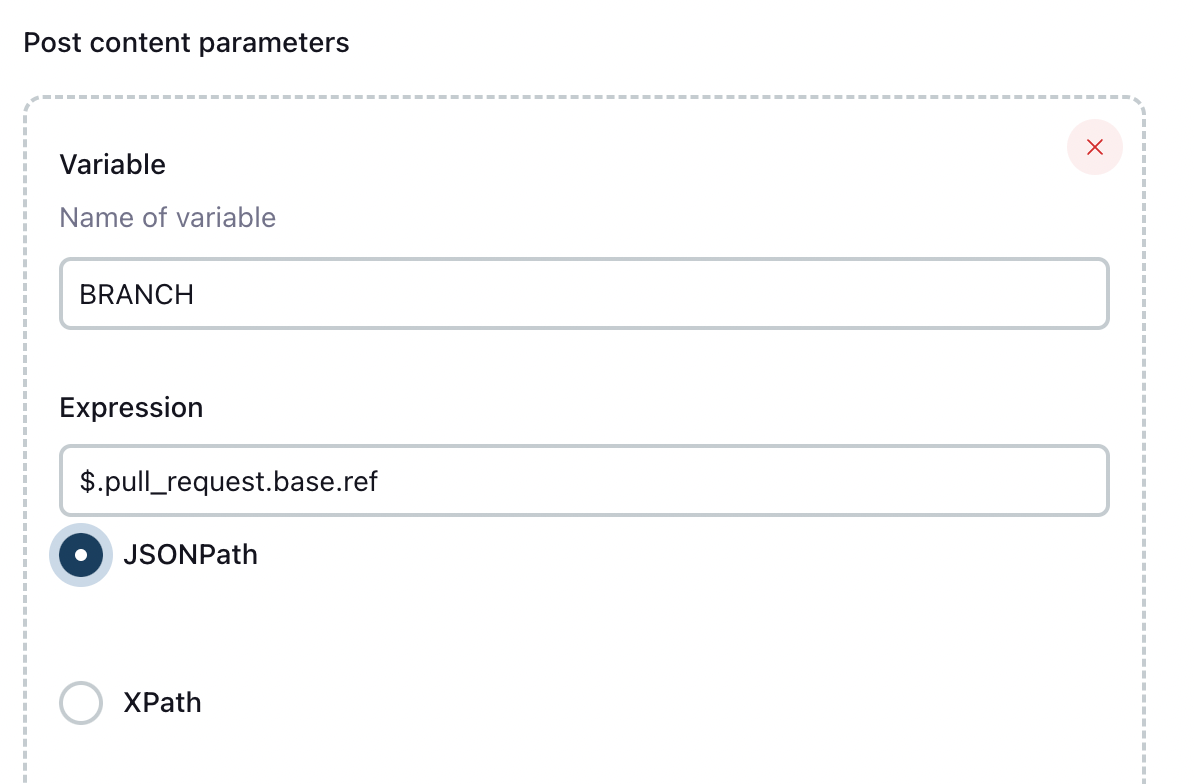
$.pull_request.base.ref를 등록하여 base 브랜치를 가져옵니다.원하는 값은 develop 브랜치가 될 것입니다.
LABELS
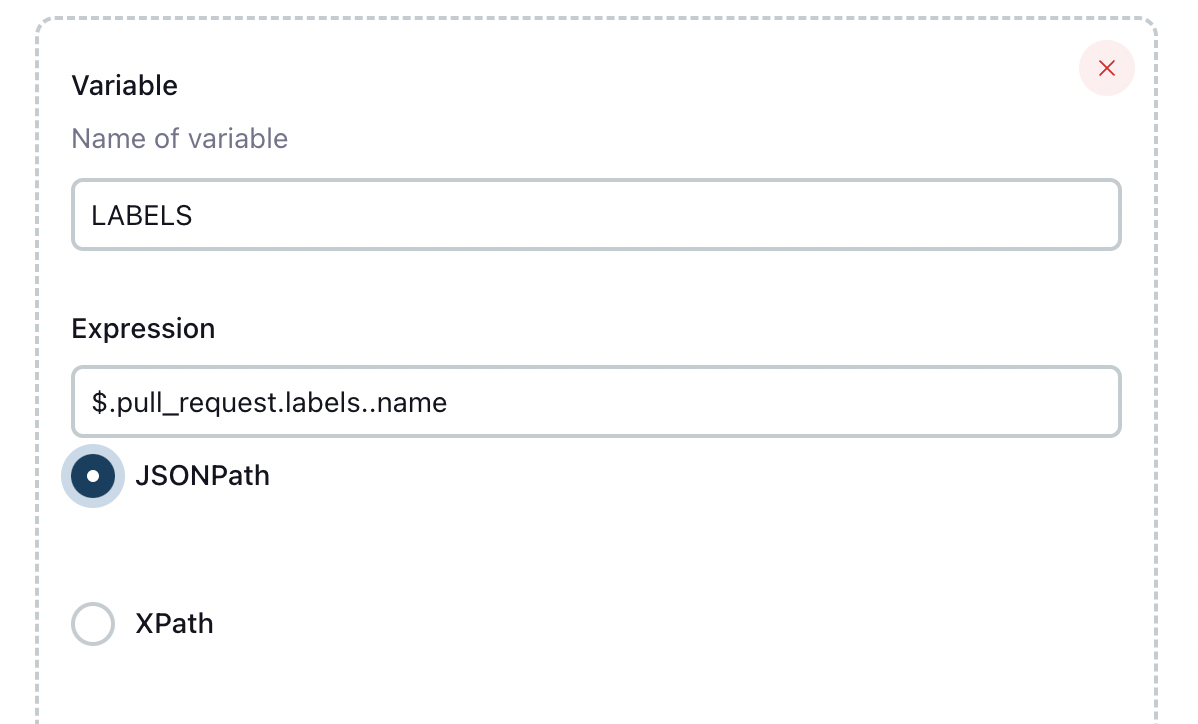
$.pull_request.labels..name를 등록하여 라벨들의 이름을 가져옵니다.원하는 값은 등록된 라벨들 중에 백엔드를 포함하는 값이 존재하는 상황이 될 것입니다.
Optional filter 설정
아래로 내리다 보면
Optional filter탭을 볼 수 있습니다.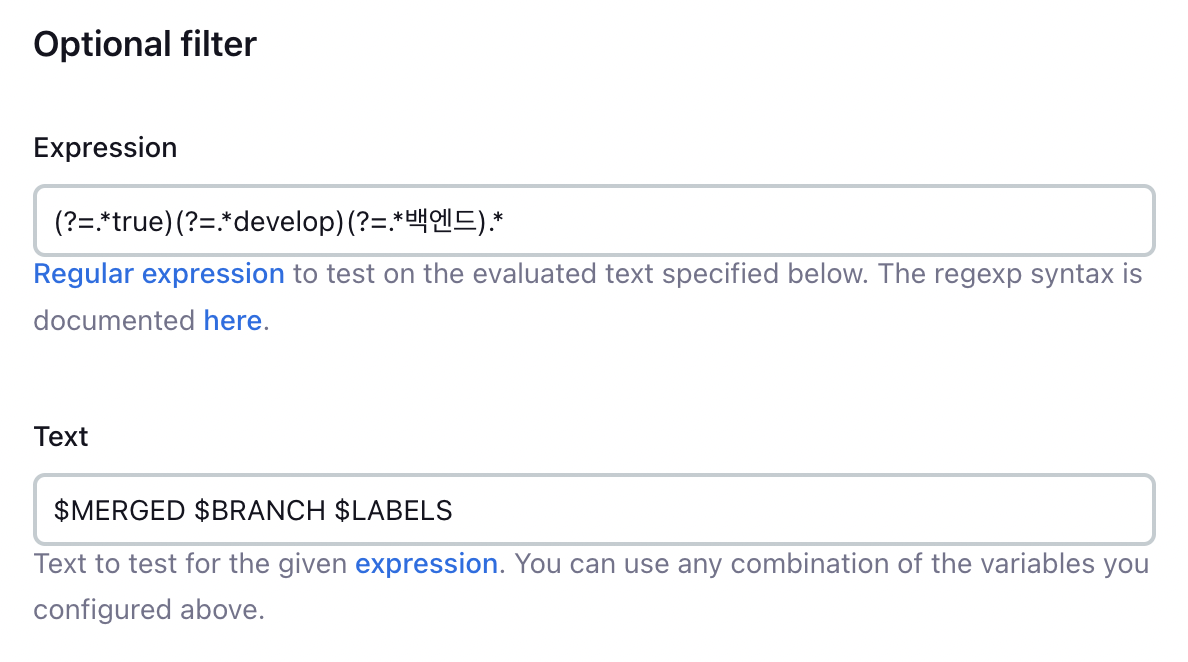
- Expression: (?=.true)(?=.develop)(?=.백엔드).*
- Text: $MERGED $BRANCH $LABELS
Expression에 다음과 같은 정규표현식을 작성했습니다.
(?=.*true)(?=.*develop)(?=.*백엔드).*또한 Text 부분에는 위에서 파라미터로 선언한 값들을 사용했습니다.
위 표현식으로 다음과 같은 효과를 기대할 수 있다.
merge가 true이고, 브랜치가 develop이고, 라벨에 백엔드가 존재하는 작업에 대해 트리거를 수행하는 것을 기대할 수 있습니다.
Token 설정

Token: goodfriends_build_webhook_tokenToken 탭에 토큰 이름을 작성합니다.
그리고 다시 Github - Webhooks로 이동합니다.
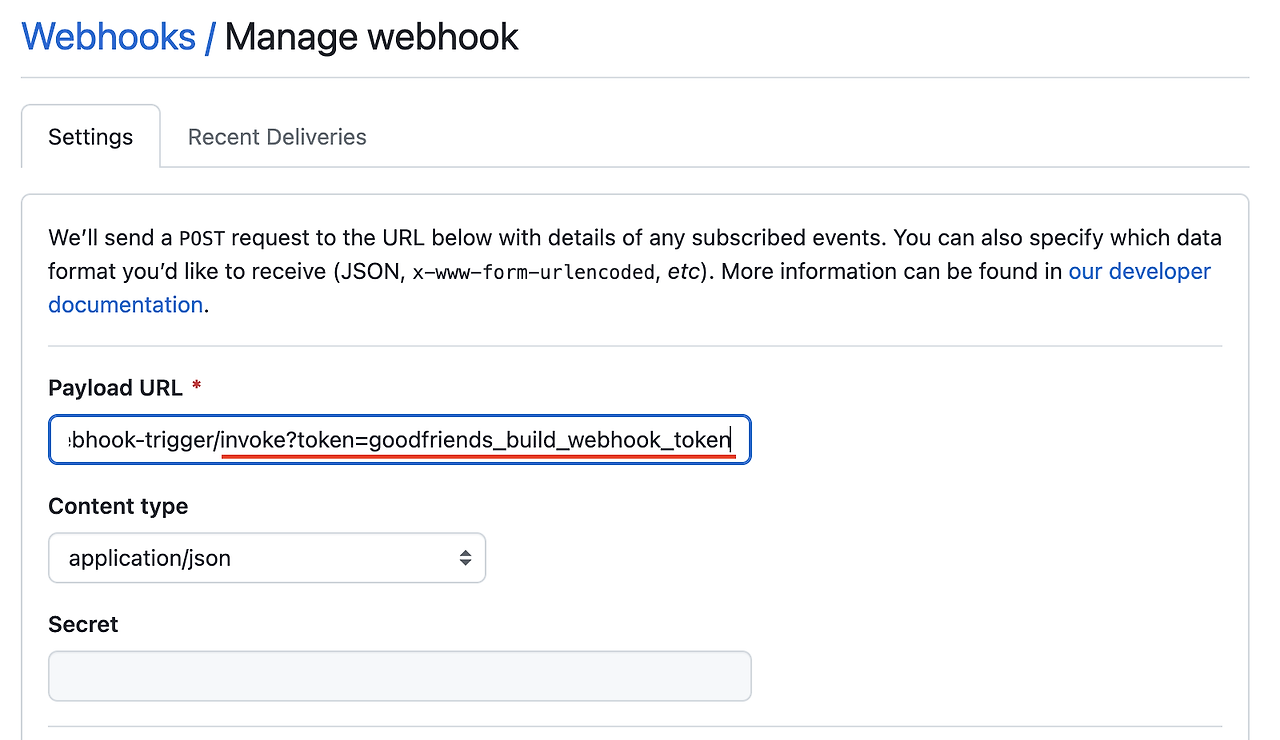
이때 GitHub WebHook 설정에 들어가서
Payload URL에 token 파라미터를 포함하도록 수정합니다.Payload URL: http://{jenkins 퍼블릭 ip 주소}:80/generic-webhook-trigger/invoke?token=goodfriends_build_webhook_token
바로 아래 탭에서 TokenCredential에 토큰에 대한 Secret Key를 추가해주어야 합니다.
외부에서 빌드를 유발하기 위해서는 token을 확인하는 방식이 존재하는데 이때 Jenkins의 Credential에 있는 정보를 기반으로 수행합니다.
token을 사용하지 않는 경우 계정정보를 입력할 수도 있지만 해당 과정에서는 token을 등록하는 방식을 사용합니다.
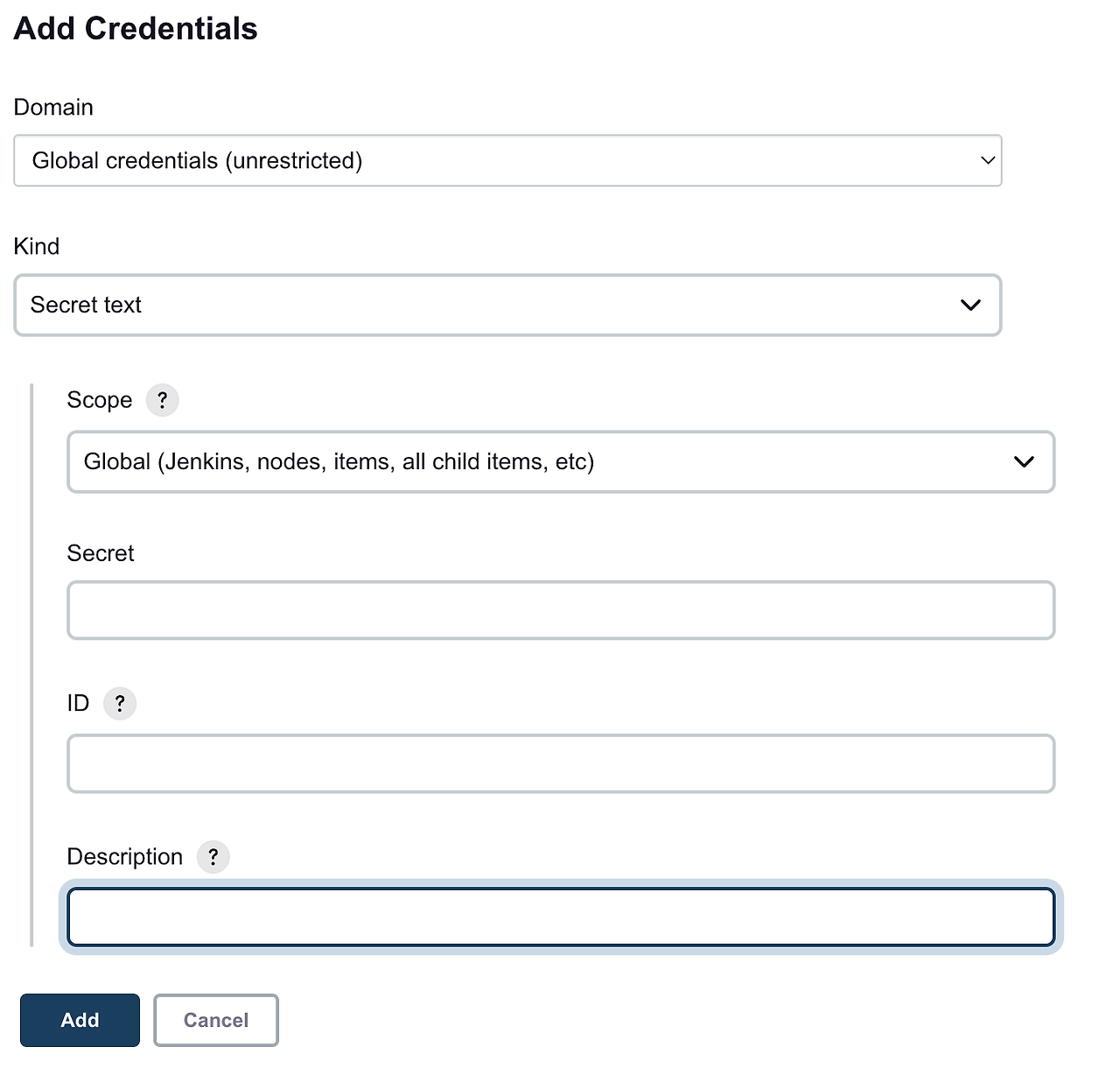
Domain: Global credentialsKind: Secret textSecret: goodfriends_build_webhook_tokenID: GoodFriends_Web_Hook_TokenDescription: GoodFriends Web Hook Token입니다.
위와 같은 정보로 Secret text를 작성하고 등록하고 적용합니다
응답 확인하기
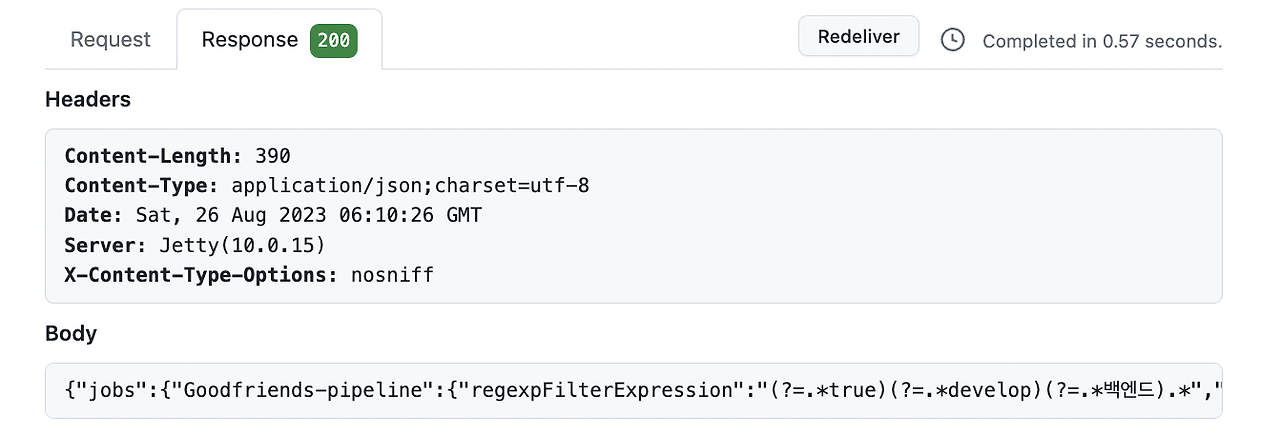
GitHub의 WebHook 탭의 Recent Deliveries 탭으로 가서 확인해 보면 Response Body 값에 응답이 담겨있는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
트러블 슈팅
젠킨스 - General 부분의 Generic Webhook Trigger 설정 - Token 설정하는 부분에서 많은 시간을 할당했습니다.
{ "jobs":null,"message":"Did not find any jobs with GenericTrigger configured! If you are using a token, you need to pass it like ...trigger/invoke?token=TOKENHERE. If you are not using a token, you need to authenticate like http://user:passsword@example.org/generic-webhook... " }404 에러와 함께 위 메시지가 반환되었는데, 젠킨스에서 Token에 대해 이해를 하지 못해서 생긴 문제였습니다.
“외부에서 빌드를 유발하기 위해서는 token을 확인하는데 이때, 젠킨스의 Credential에 있는 정보를 기반으로 수행한다”
즉, Jenkins의 Credential에서 token에 대한 Credential를 추가해 주고, 이를 적용해야 한다는 의미였습니다.
마치며
젠킨스의 Generic Webhook Trigger 플러그인을 이용하여 Merge 여부, target branch, label 값을 비교하고 빌드를 유발하는 설정을 했습니다. 이후에는 백엔드를 기준으로 했기 때문에, 백엔드의 코드가 병합했을 경우에만 젠킨스에서 빌드 및 배포 처리가 됩니다.
경우에 따라 세부적인 검증을 추가할 수 있습니다.
Reference
-
[Goodfriends] 젠킨스를 사용하여 CI/CD Pipeline 구축기(프론트엔드편)
이 글은 우리FISA 1기 굿프렌즈팀의 기술 블로그에 게시된 글 입니다.
직전 포스팅에서 굿프렌즈팀 백엔드의 CI/CD를 구축한 방법을 소개해드렸습니다. 이번 포스팅에서는 프론트엔드의 CI/CD를 구축하는 방법을 소개하고자 합니다.
프론트엔드 CD 다이어그램
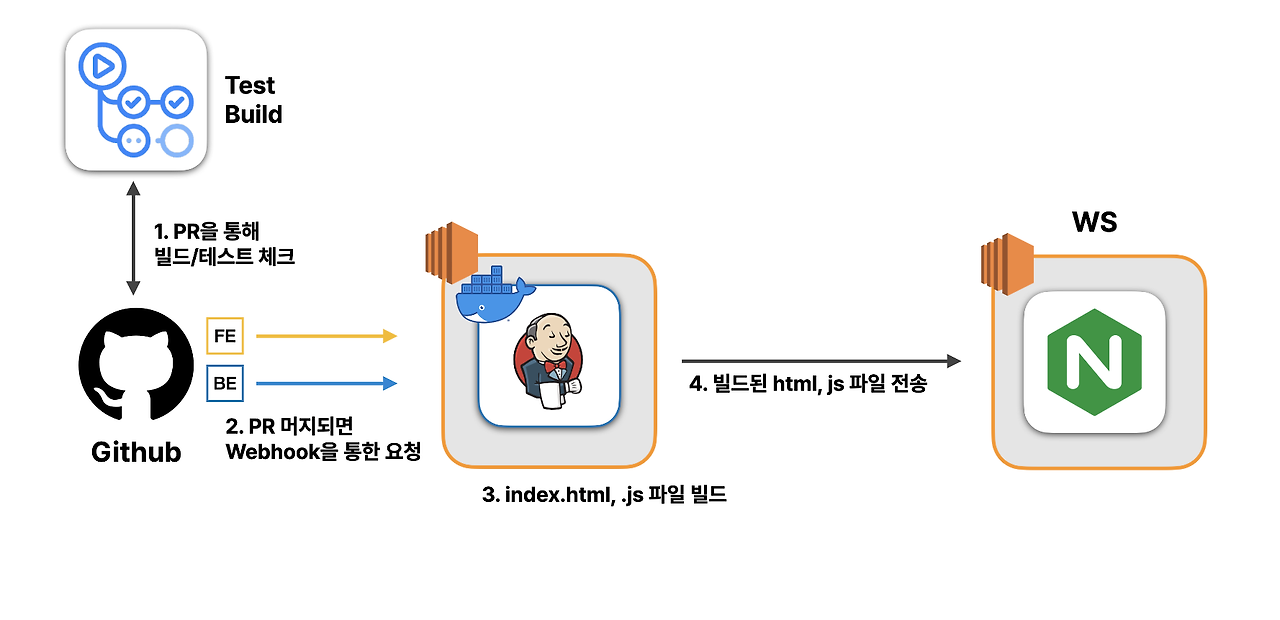
프론트엔드의 지속적 배포 환경은 백엔드와 크게 다른점은 없습니다. PR이 생성되고, 병합되어 Webhook을 통해 젠킨스 서버에 전달됩니다. 젠킨스 서버는 Webhook을 이용하여 뷰(Vue) 프로젝트를 빌드하고, index.html과 관련 js 파일을 생성합니다. 그리고 생성된 정적 파일들을 프론트엔드 EC2 인스턴스에 있는 NGINX 디렉토리를 통해 전송됩니다.
파이프라인 작성
1) 사전작업
굿프렌즈팀 프론트엔드 팀은 뷰(Vue)를 사용합니다.
젠킨스에는 백엔드 언어인 Java와 다르게 NodeJs의 빌드를 기본적으로 제공하고 있지 않습니다. 하지만 이를 지원하는 NodeJs 플러그인이 존재하여 사용자는 해당 플러그인을 설치하는 과정만으로 NodeJs 프로젝트를 빌드할 수 있는 환경을 구축할 수 있습니다.
이를 위해 굿프레즈팀은 젠킨스에 NodeJs 플러그인을 설치했습니다.
설치하는 과정은 젠킨스 홈페이지에서 Dashboard - Jenkins 관리 - Plugins - Available plugins → NodeJs 선택 후 설치해주면 됩니다. 그런 다음 젠킨스를 재시작해줍니다.
다시 Dashboard - Jenkins 관리 - Tools 에서 아래 그림과 같이 설정한 뒤 저장합니다.
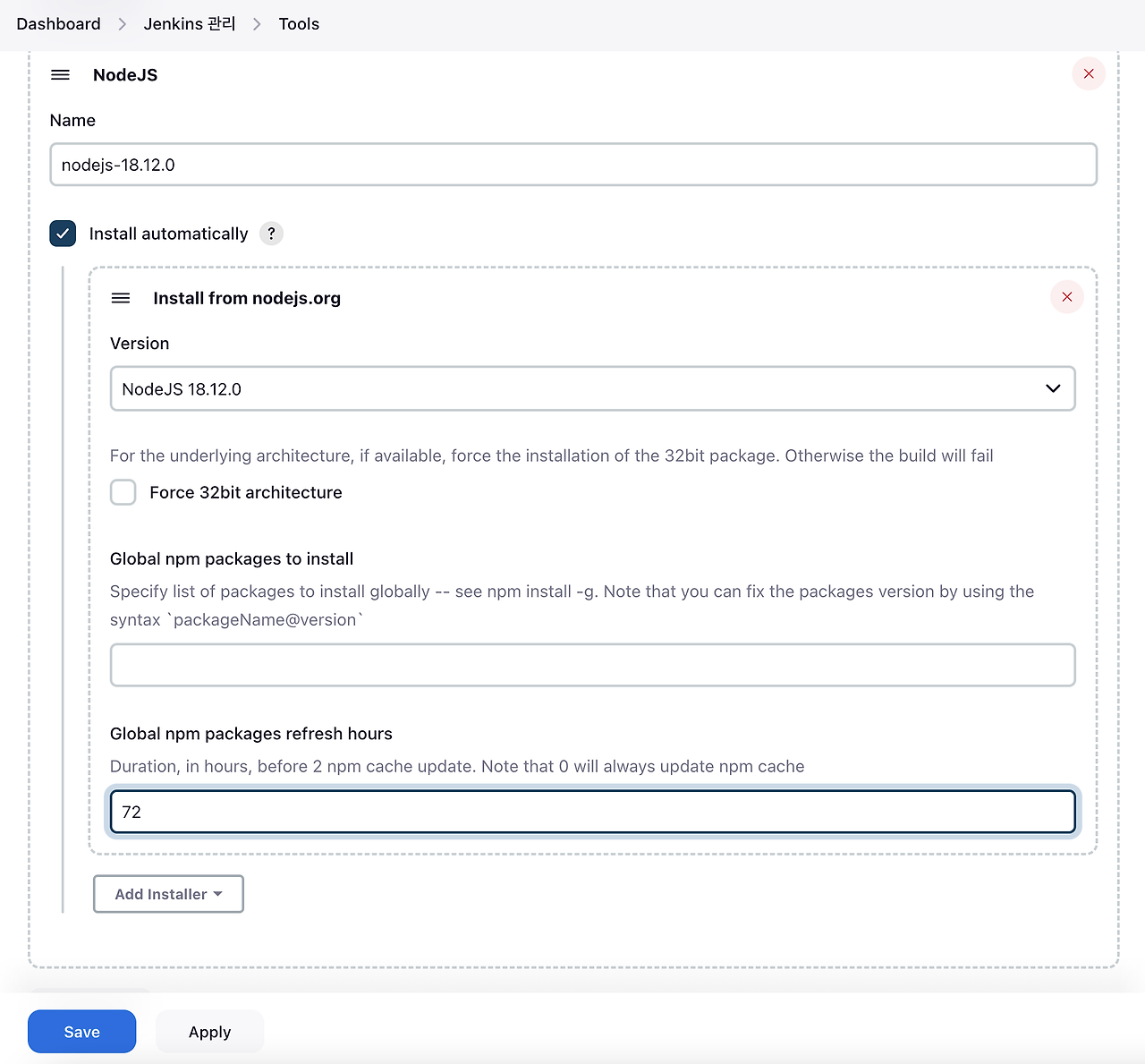
굿프렌즈팀은 개발 환경에서 node.js 18.12.0 버전을 사용하므로 18.12.0 버전을 선택하고 이름을
NodeJS 18.12.0으로 지정했습니다.2) Jenkins 서버에서 Nginx 서버에 접속하기 위한 EC2 SSH 키 추가
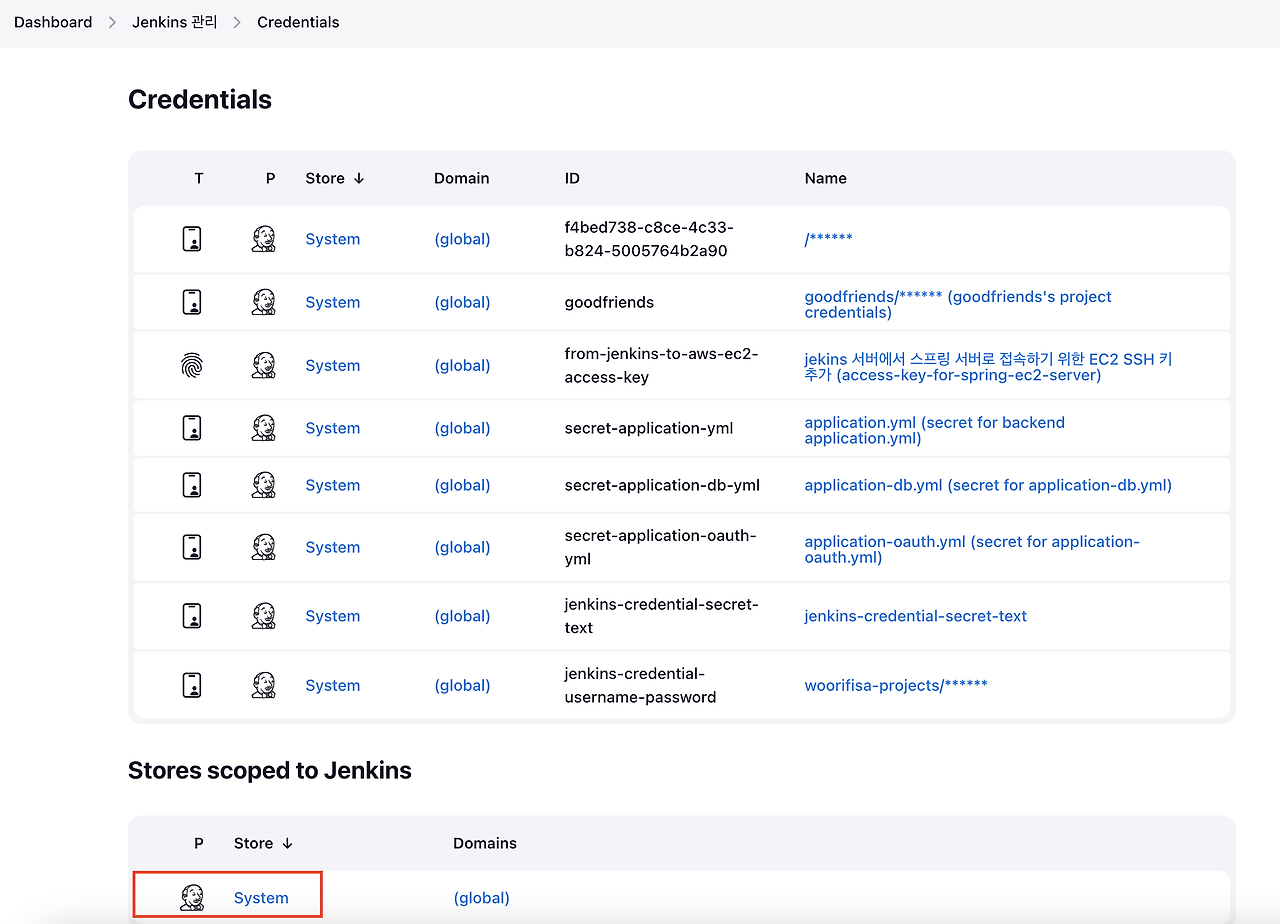
Jenkins 관리 → Credentials → Stores scoped to Jenkins 탭에서 System 하이퍼링크 클릭
Global credentials 클릭 → 우측 상단 Add Credentials 선택(Add domain 아님)
Credentials
Systyem
Global credentials
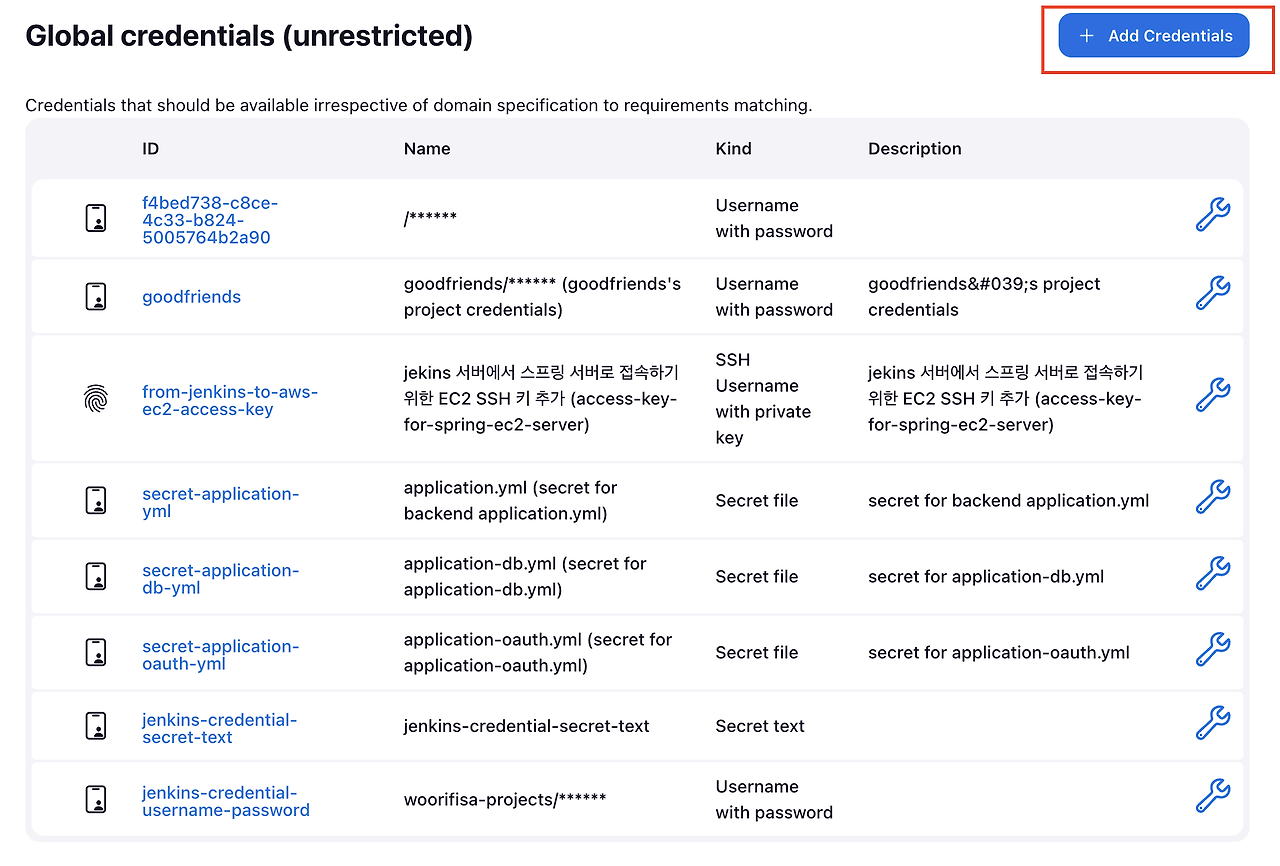
Kind: SSH Username with private keyScope: GlobalUsername: ubuntu (linux 계정이름)Password: 프론트엔드 EC2 서버에 접속할 때 사용하던 pem 키의 값(하단 pem 키 조회참조)ID: from-jenkins-to-aws-nginx-ec2-access-keyDescription: access-key-for-nginx-ec2-serverTreat username as secret: 체크Private Key 탭 하단-> Enter directly 선택 -> Key 부분 하단 Add 버튼 누른 후 프론트엔드 EC2 서버에 연결할 때 사용되는 pem 키의 내용 입력 후 저장
3) 프론트엔드(NGINX) 서버 설정
프론트엔드 운영 서버에서 실행시킬 deploy.sh를 작성해줘야 합니다.
프론트엔드 서버에 ssh 연결한 뒤 deploy.sh를 아래와 같이 작성합니다.
#!/bin/bash tar -xvf dist.tar rm -rf dist.tar sudo rm -rf /var/www/html/dist # remove origin's dist file sudo mv dist /var/www/html # move new dist file to /var/www/html sudo service nginx restart4) 프론트엔드 인바운드 규칙 편집
젠킨스 서버에서 프론트엔드 운영 서버로 접속하기 위해 프론트엔드 보안 그룹내에 있는 인바운드 규칙을 설정해줘야 합니다.
유형: SSH, 소스에는 젠킨스 Private IP 주소를 넣어서 프론트엔드 서버 접속을 가능하게 합니다.5) 5) 운영 서버로의 배포를 위한 파이프라인 스크립트 작성
pipeline { agent any tools { gradle 'gradle' } triggers { githubPush() } stages { stage('Copy Repository') { steps { git branch: 'develop', credentialsId: 'jenkins-credential-username-password', url: 'https://github.com/woorifisa-projects/GoodFriends' } } stage('Frontend secret file download') { steps { dir("./frontend") { sh 'rm -rf .env' } script { withCredentials([ file(credentialsId: 'secret-env', variable: 'ENV') ]) { sh 'cp $ENV frontend/.env' } } } } stage('Frontend Build'){ steps{ sh "echo '########### FE MODULE INSTALL AND BUILD START ###########'" dir("./frontend"){ nodejs(nodeJSInstallationName: 'nodejs-18.12.0') { sh 'npm install && npm run build' } } sh "echo '########### FE MODULE INSTALL AND BUILD SUCCESS ###########'" } } stage('Frontend Compression') { steps { dir("./frontend") { sh ''' rm -rf node_modules tar -cvf dist.tar dist ''' } } } stage('Frontend Deploy') { steps { sshagent(credentials: ['from-jenkins-to-aws-nginx-ec2-access-key']) { sh ''' ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=yes ubuntu@172.31.34.44 uptime scp /var/jenkins_home/workspace/Goodfriends-pipeline/frontend/dist.tar ubuntu@172.31.34.44:/home/ubuntu ssh -t ubuntu@172.31.34.44 chmod +x ./deploy.sh ssh -t ubuntu@172.31.34.44 ./deploy.sh ''' } } post { success { slackSend ( channel: '#jenkins', color: '#00FF00', message: "프론트엔드 배포 성공! 🚀" ) } failure { slackSend ( channel: '#jenkins', color: '#FF0000', message: "프론트엔드 배포 실패 🥲" ) } } } stage('Backend secret file download') { steps { script { withCredentials([ file(credentialsId: 'secret-application-yml', variable: 'YML'), file(credentialsId: 'secret-application-db-yml', variable: 'DbYML'), file(credentialsId: 'secret-application-oauth-yml', variable: 'OauthYML'), file(credentialsId: 'secret-application-sms-yml', variable: 'SmsYML') ]) { sh 'cp $YML backend/src/main/resources/application.yml' sh 'cp $DbYML backend/src/main/resources/application-db.yml' sh 'cp $OauthYML backend/src/main/resources/application-oauth.yml' sh 'cp $SmsYML backend/src/main/resources/application-sms.yml' } } } } stage('Backend Build') { steps { dir('backend') { sh 'chmod +x ./gradlew' sh './gradlew clean build' } } } stage('Backend Deploy') { steps { sshagent(credentials: ['from-jenkins-to-aws-backend-ec2-access-key']) { sh ''' ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=yes ubuntu@172.31.39.91 uptime scp /var/jenkins_home/workspace/Goodfriends-pipeline/backend/build/libs/goodfriends-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar ubuntu@172.31.39.91:/home/ubuntu ssh -t ubuntu@172.31.34.44 chmod +x ./deploy.sh ssh -t ubuntu@172.31.39.91 ./deploy.sh ''' } } post { success { slackSend ( channel: '#jenkins', color: '#00FF00', message: "백엔드 배포 성공! 🚀" ) } failure { slackSend ( channel: '#jenkins', color: '#FF0000', message: "백엔드 배포 실패 🥲" ) } } } } }기존 백엔드 파이프라인을 포함하여 프론트엔드 파이프라인 스크립트를 작성했습니다.
이렇게 파이프라인을 작성한 뒤에 배포를 실행하면 아래와 같이 정상적으로 빌드 및 배포가 완료된 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
2023.08.26(이전)
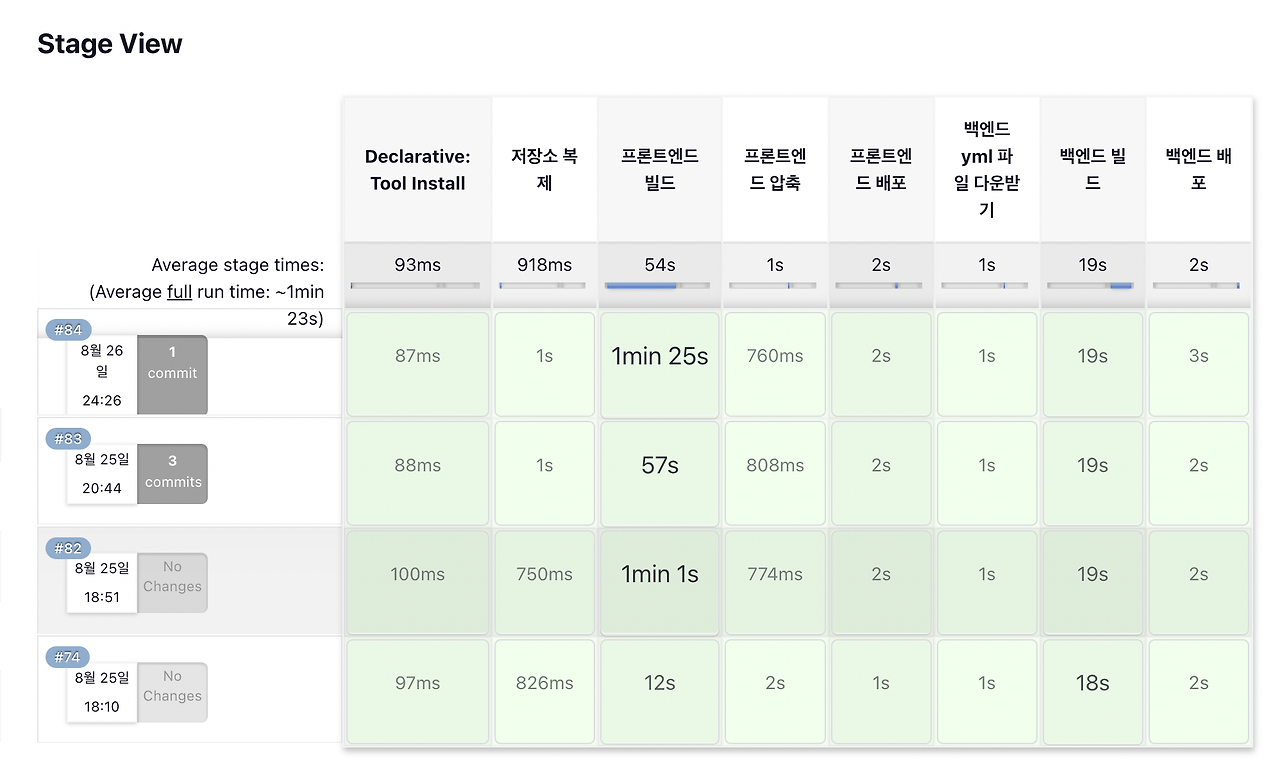
2023.10.14(최근)
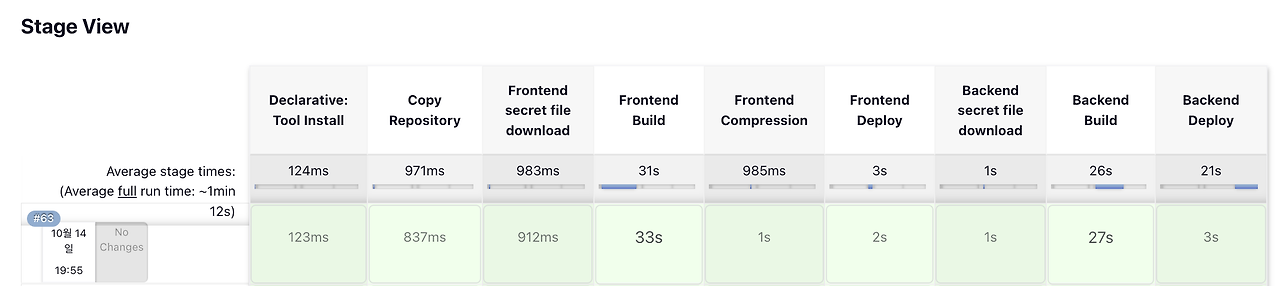
위의 pipeline에 맞게 수정된 jenkins 부분입니다! (9월 말에 우리FISA로부터 지원이 끊겨서 갑작스럽게 모든 서버 구축(프론트, 백엔드, 젠킨스)을 처음부터 다시 하게 되었습니다ㅠㅠ 하지만, 다시 한번 구축하면서 복습도 할 수 있었고, 동작 원리가 머릿 속에 정리되어서 빠르게 구축하게 되었습니다! 😆)
마치며
현재 프론트엔드와 백엔드 모두 develop 브랜치에서 작업을 하다보니 둘 중 어느 한쪽의 코드만 병합(Merge)되어도 프론트엔드, 백엔드 두개의 빌드 프로세스가 실행되는 이슈가 존재합니다.
이후에는 빌드 트리거를 조금 더 세분화하여 Github의 라벨을 기반으로 트리거를 개선하려고 합니다.
긴글 읽어주셔서 감사합니다. 😌
-
[Goodfriends] 젠킨스를 사용하여 CI/CD Pipeline 구축기(백엔드편)
이 글은 우리FISA 1기 굿프렌즈팀의 기술 블로그에 게시된 글 입니다.
Intro
굿프렌즈팀의 프로젝트에서 백엔드 CI/CD 구조는 다음과 같습니다.
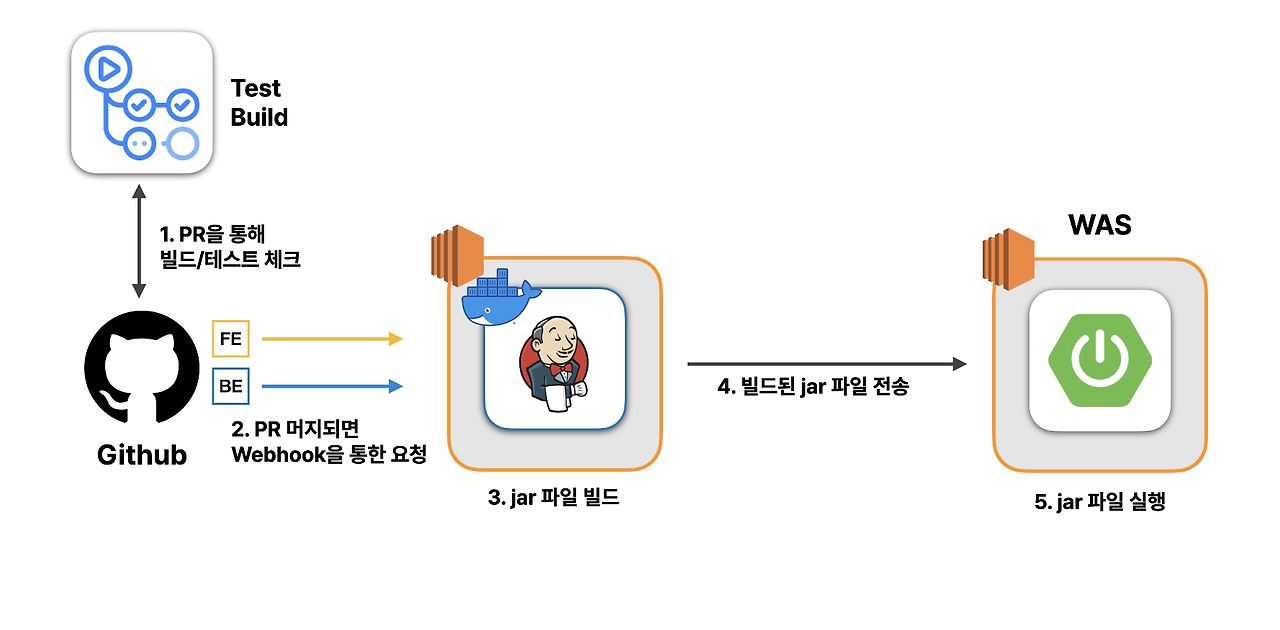
우선, 굿프렌즈의 프론트/백엔드 개발자가 기능을 개발하여 Github에 PR을 생성합니다. 이때 PR 코드가 정상적으로 빌드되고, 모든 테스트를 통과하는지 Github Actions를 사용하여 우선적으로 검사합니다. 이때, PR 브랜치의 코드가 문제가 있다면 develop 브랜치로 병합이 불가능합니다.
정상적으로 빌드가 되는 코드는 굿프렌즈 개발자들끼리 코드리뷰가 진행되고, develop 브랜치에 병합이 됩니다.
이때, Github은 굿프렌즈팀이 구축한 젠킨스 서버에
Webhook을 통해 병합 사실을 알립니다.Webhook이란, 특정한 애플리케이션이 다른 애플리케이션으로 이벤트 발생 정보를 실시간으로 제공하기 위한 방법입니다.젠킨스는 외부에 Webhook URL을 열어두고, Github으로부터 이 Webhook URL로 요청을 받아 이벤트가 발생한 즉시 그 사실을 알 수 있습니다.
[백엔드]
Webhook을 통해 신호를 받은 젠킨스는 미리 지정된 젠킨스 파이프라인 스크립트를 실행하여 스프링 부트 애플리케이션을 빌드하여 jar 파일을 생성합니다.
생성한 jar 파일은 스프링부트 애플리케이션이 실행되고 있는 EC2 인스턴스로 전송됩니다. 그리고 스프링부트 인스턴스에서 jar 파일이 실행되어 배포가 완료됩니다.
1. 젠킨스 서버에게 github 접근 권한 주기
젠킨스가 Github에서 레포지토리를 clone하기 위해서는 해당 레포지토리에 대한 접근 권한이 필요합니다.
(public repository이면 아래 과정들을 안해도 상관 없습니다)
1-1. github에서 personal access token 발급 받기
우측 상단 프로필 선택 후 하단 settings → 좌측 하단 Developer settings → Personal Access tokens → Tokens(classic) →
우측 상단에
Generate new token선택합니다.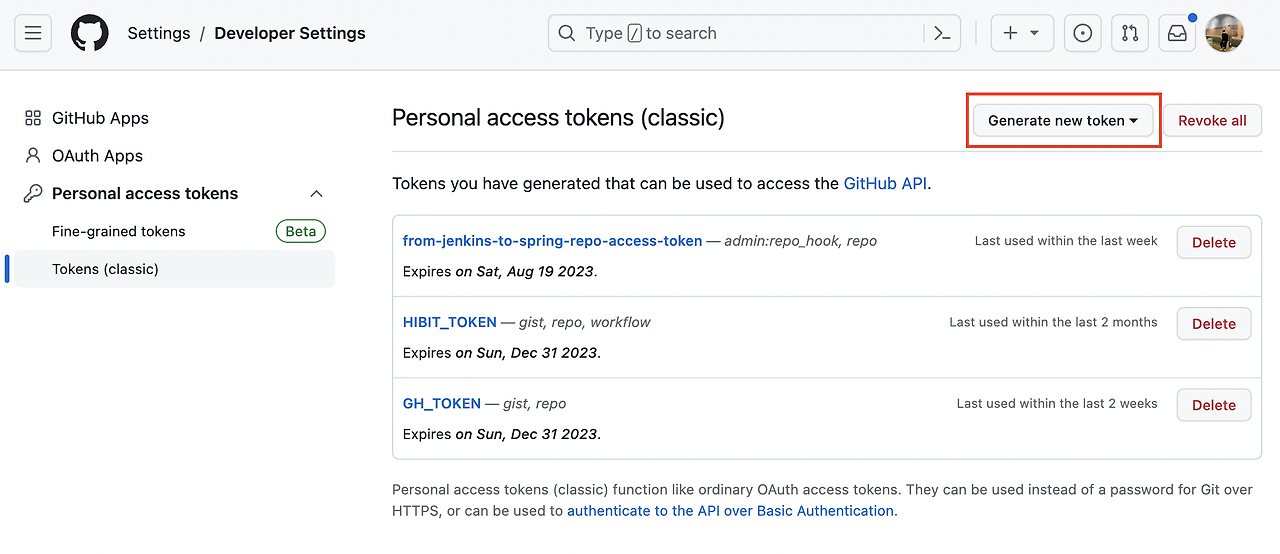
Note, Expiration, Select scopes를 아래와 같이 선택했습니다.
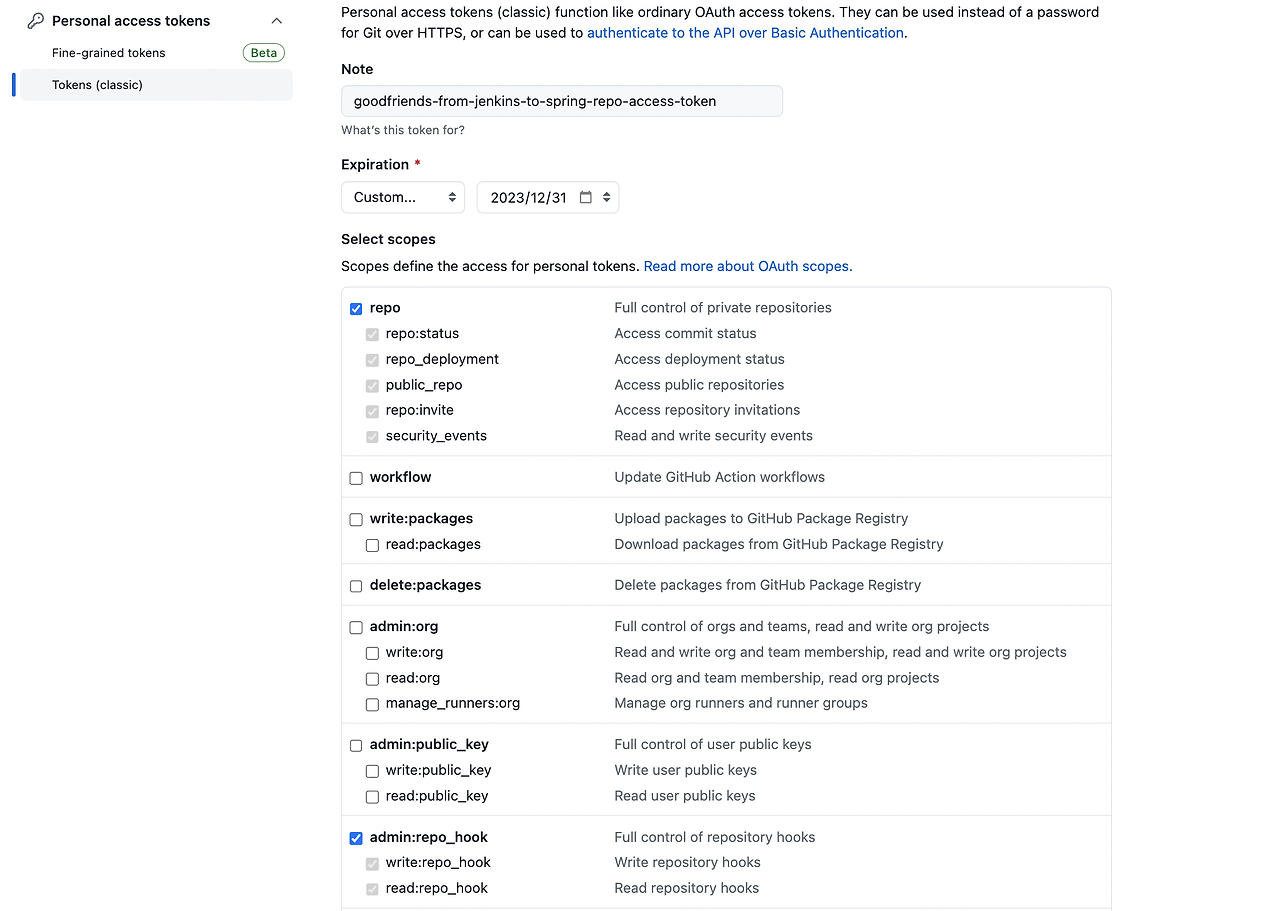
그런 다음 하단에
Generate token을 선택했습니다.가운데 부분에 체크 아이콘으로 표시된 access token 값을 복사한 뒤 따로 보관해두셔야 합니다.
(저희 굿프렌즈팀은 “goodfriends-from-jenkins-to-spring-repo-access-token.txt” 라는 파일을 생성한 뒤에 복사한 키 값을 보관했습니다)
- DevHistory 4
- Essay 1
- Java 10
- Spring 15
- SpringBoot 17
- JPA 13
- MySQL 3
- Flyway 1
- Kafka 8
- Technology 22
- GoodCode 7
- Side_Project 20
- Retrospective 4
- AlgorithmSkill 3
- LeetCode 2
- Algorithm 70
- SQL 9
- OS 14
- Database 8
- Network 7
- HTTP 7
- DataStructure 5
- Linux 4
- Woowacourse 4
- Git 9
- AssertJ 1
- IntelliJ 5
- Probability-Statistics 5
- Electronic-Finance 13
- Business-Statistics 13
- Competition 1
- Book 6
- Workout 7
- E.T.C 8