지금의 기록이 미래의 자산이 된다.
Today's records become tomorrow's assets.-
로드밸런싱
로드밸런싱(Load Balancing)
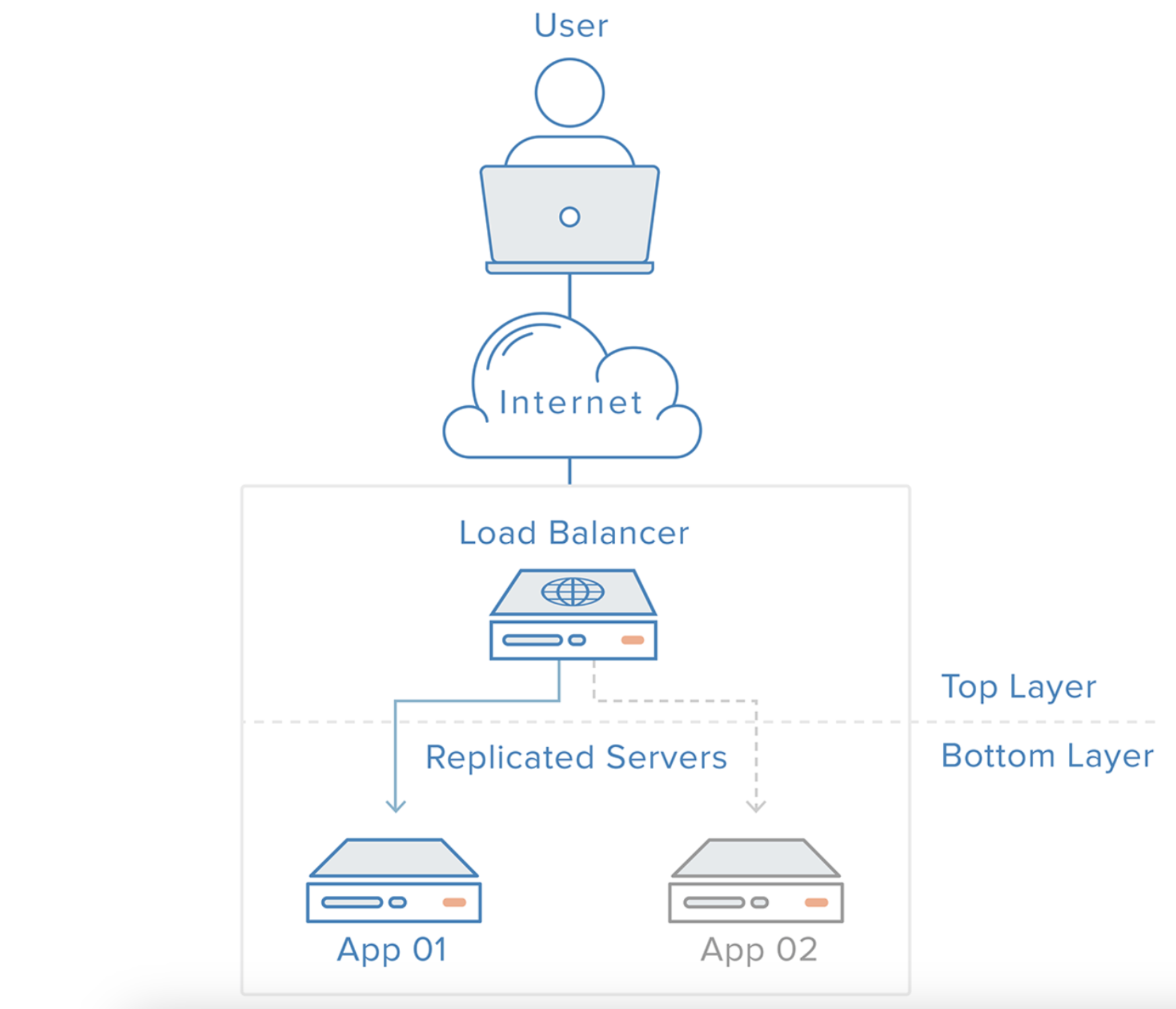
로드밸런싱은 서버에 가해지는 부하(=로드)를 분산(=밸런싱)해주는 장치 또는 기술을 말한다.
-
클라이언트와 서버풀 사이에 위치하며, 한 대의 서버로 부하가 집중되지 않도록 트래픽을 관리해 각각의 서버가 최적의 퍼포먼스를 보일 수 있도록 한다.
-
로드밸런싱을 해주는 소프트웨어 혹은 하드웨어 장비를 로드밸런서라고 한다.
-
로드밸런서는 VIP(Virtual IP)와 함께 구성된다.
VIP란 로드밸런싱의 대상이 되는 여러 서버들을 대표하는 가상의 IP이다. 클라이언트들을 서버에게 IP로 직접 요청 하는 것이 아니라 로드밸런서가 가지고 있는 VIP를 대상으로 요청을 한다. 그리고 로드밸런서는 설정된 부하 분산 방법에 따라 각 서버로 요청을 분산시키는 것이다.
-
로드밸런싱의 주 목적은 서버 자원 사용의 최적화, 데이터 처리량의 증가, 클라이언트와 서버 간의 응답속도 감소, 특정 서버의 과부화 방지, 안정성 및 가용성 극대화 등을 고려하여 적절히 분산처리하여 해주는 서비스이다.
로드밸런싱이 필요한 이유
-
로드밸런싱은 여러 대의 서버를 두고 서비스를 제공하는 분산 처리 시스템에서 필요한 기술이다.
-
사업의 규모가 확장되고, 클라이언트의 수가 기하 급수적으로 늘어나면서, 그에 따라 증가된 트래픽을 대처하려면 어떻게 해야할까?
Scale-up 과 Scale-out
-
Scale-up은 서버 자체의 성능을 확장하는 것을 의미한다. 서버에 CPU 또는 RAM을 추가하거나, 고성능의 부품을 교체할 때 쓰는 방법이다.- 모든 부하가 서버 한 대에 집중하기 때문에 장애시 위험하고, 데이터 역시 한 곳에서 처리하므로 데이터 갱신이 빈번하게 일어나는
데이터베이스 서버에 적합하다.
- 모든 부하가 서버 한 대에 집중하기 때문에 장애시 위험하고, 데이터 역시 한 곳에서 처리하므로 데이터 갱신이 빈번하게 일어나는
-
Scale-out은 서버를 여러 대 추가하여 시스템을 확장하는 방법이다.- 서버가 여러대가 되므로 로드밸런싱이 필수이며, 다중화를 통해 서버에서 장애가 났을 경우에도 다른 서버에서 대응이 가능하다. 하지만 모든 서버가 동일한 데이터를 가져야 하므로 데이터 변화가 적은
웹 서버에 적합하다.
- 서버가 여러대가 되므로 로드밸런싱이 필수이며, 다중화를 통해 서버에서 장애가 났을 경우에도 다른 서버에서 대응이 가능하다. 하지만 모든 서버가 동일한 데이터를 가져야 하므로 데이터 변화가 적은
-
Scale-out 장점
-
하드웨어 향상하는 비용보다 서버 한대 추가 비용이 더 적다.
-
여러 대의 Server 덕분에 무중단 서비스를 제공할 수 있다.
-
-
여러 대의 서버에게 균등하게 트래픽을 분산시켜주는 역할을 하는 것이
로드밸런서이다.
로드밸런싱 알고리즘
- 클라이언트의 요청을 특정 서버에 분배하는 로드밸런싱 기법은 여러가지 있다.
정적 부하분산(Static Load Balancing)
[1] 라운드 로빈 방식(Round Robin Method)
-
입력 받은 요청을 각각의 서버에 순차적으로 할당하는 방식이다.
-
클라이언트의 요청을 순서대로 분배하기 때문에 알고리즘이 단순하고 각 서버가 트래픽을 골고루 나눠서 처리하므로 각 서버의 처리량이 비슷한 경우에 쓰이는 기법이다.
[2] IP 해시 방식(IP Hash Method)
-
클라이언트의 IP 주소를 특정 서버로 매핑하여 요청을 처리하는 방식이다.
-
사용자의 IP를 해싱해 로드를 분배하기 때문에 클라이언트는 항상 동일한 서버로 접속하게 된다.
동적 부하분산(Dynamic Load Balancing)
[1] 가중 라운드 로빈 방식(Weighted Round Robin Method)
-
각 서버별로 가중치를 설정하고 가중치가 높은 서버에 클라이언트 요청을 우선적으로 배분하는 방식이다.
-
주로 서버의 트래픽 처리 능력이 상이한 경우 사용되는 부하 분산 방식이다.
-
예) 클라이언트의 입력이 100이고, 각 서버 A, B, C의 가중치가 2,3,5라고 가정한다면 각 서버에는 20, 30, 50의 입력이 라운드 로빈 방식으로 전달된다.
[2] 최소 연결 방식(Least Connection Method)
-
요청이 들어온 시점에 가장 적은 연결 상태를 보이는 서버에 우선적으로 트래픽을 배분하는 방식이다.
-
세션이 자주 길어지거나, 서버에 분배된 트래픽들이 일정하지 않는 경우에 사용되는 방식이다.
[3] 최소 응답 시간 방식(Least Response Time)
-
클라이언트 요청을 전달하기 전에 각 서버에 응답을 요청하고 응답 시간이 가장 짧은 서버에 클라이언트 요청을 전달하는 방식이다.
-
각 서버의 성능이 상이한 경우에 사용되는 방식이다.
로드밸런싱의 주요 기능
-
NAT(Network Address Translation) : 사설 IP 주소를 공인 IP 주소로 바꾸는 데 사용하는 통신망의 주소 변조기이다.
-
Tunneling : 인터넷상에서 눈에 보이지 않는 통로를 만들어 통신할 수 있게 하는 개념이다. 데이터를 캡슐화해서 연결된 상호 간에만 캡슐화된 패킷을 구별해 캡슐화를 해제할 수 있다.
-
DSR(Dynamic Source Routing protocol) : 로드밸런서 사용시 서버에서 클라이언트로 되돌아가는 경우 목적지 주소를 스위치의 IP 주소가 아닌 클라이언트 IP 주소로 전달해서 네트워크 스위치를 거치지 않고 바로 클라이언트를 찾아가는 개념이다.
로드밸런싱의 종류
-
L2 : Mac주소를 바탕으로 로드밸런싱을 한다.
-
L3 : IP주소를 바탕으로 로드밸런싱을 한다.
-
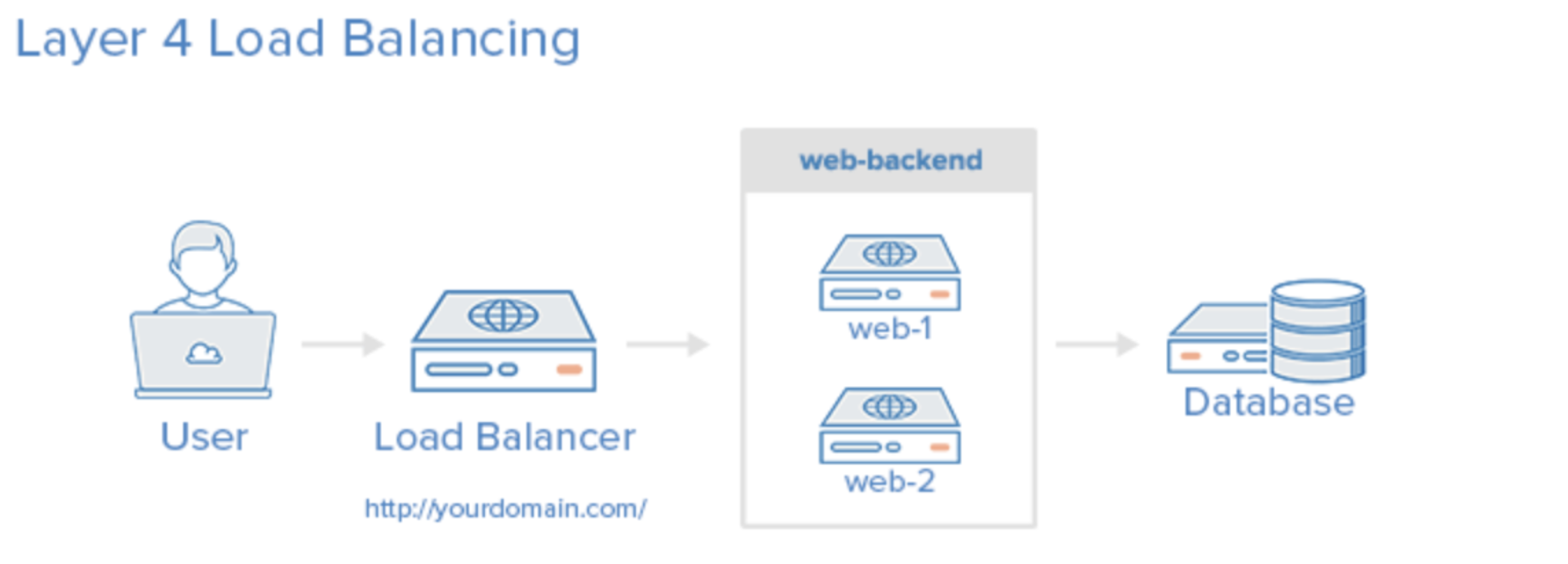
L4 : 전송계층(Transport Layer)에서 로드밸런싱을 한다. (TCP, UDP 포트 정보를 바탕으로 한다)
-
장점 : 데이터 안을 들여다보지 않고 패킷 레벨에서만 로드를 분산하기 때문에 속도가 빠르고 효율이 높다. L7 로드밸런서보다 가격이 저렴하다.
-
단점 : 패킷의 내용을 살펴볼 수 없기 때문에 섬세한 라우팅이 불가능하다. 사용자의 IP가 자주 바뀐다면 연속적인 서비스를 제공하기 어렵다.
-
-
L7 : 응용계층(Application Layer)에서 로드밸런싱을 한다. (TCP/UDP뿐만 아니라 HTTP, HTTPS, FTP의 파일명, 쿠키 정보를 바탕으로 한다)
-
장점 : 상위 계층에서 로드를 분산하기 때문에 더 섬세한 라우팅이 가능하며 캐싱 기능을 제공한다. 비정상적인 트래픽을 사전에 필터링 할 수 있어서 서비스 안정성이 높다.
-
단점 : 패킷의 내용을 복호화해야 하기에 L4 로드밸런서보다 더 높은 비용을 지불해야 한다.(가격이 더 비싸다) 그리고 클라이언트가 로드밸런서와 인증서를 공유해야하므로 해커가 로드밸런서를 통해서 클라이언트 데이터에 접근할 가능성이 있어서 보안상 위험성이 존재한다.
-
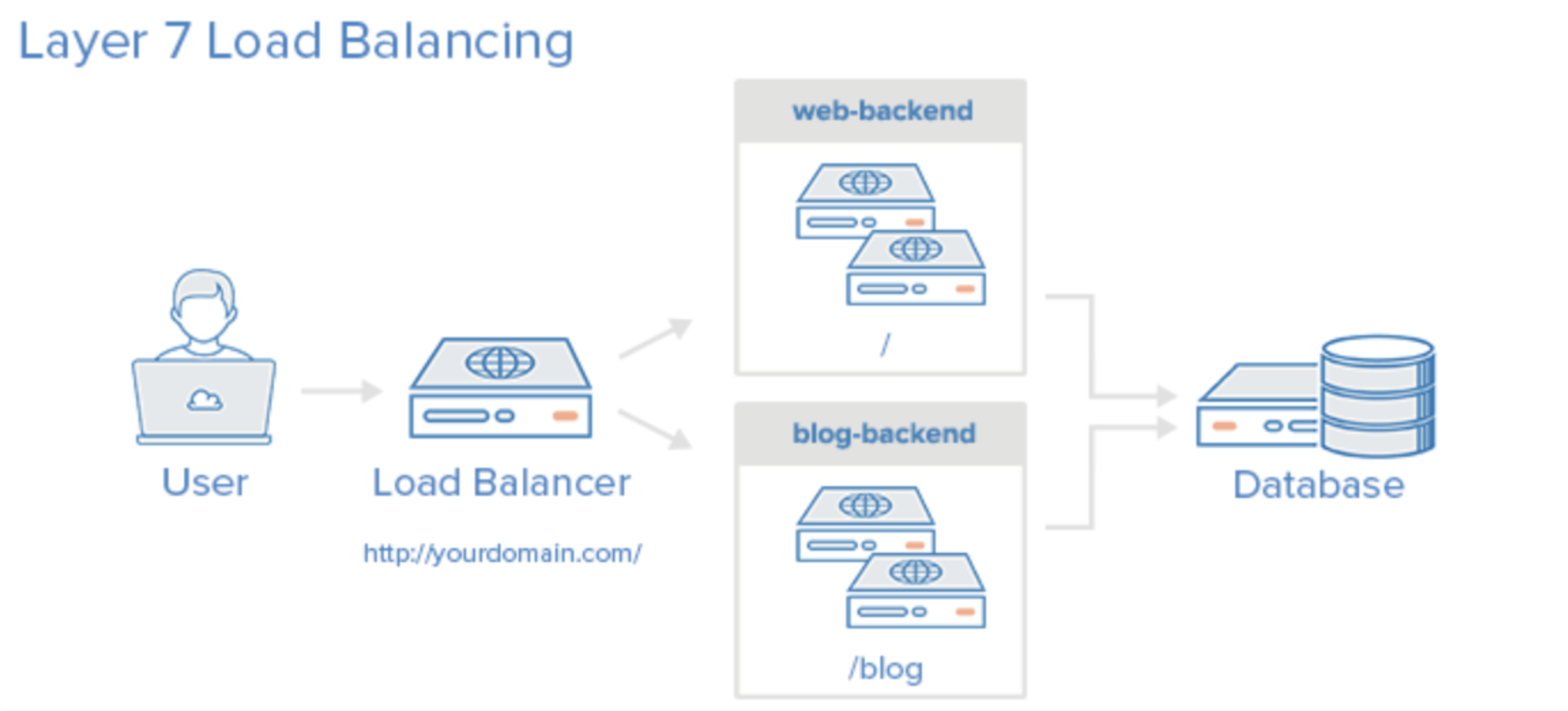
- 참고로, 4 ~ 7 계층은 하위 계층의 기능을 포함한다.
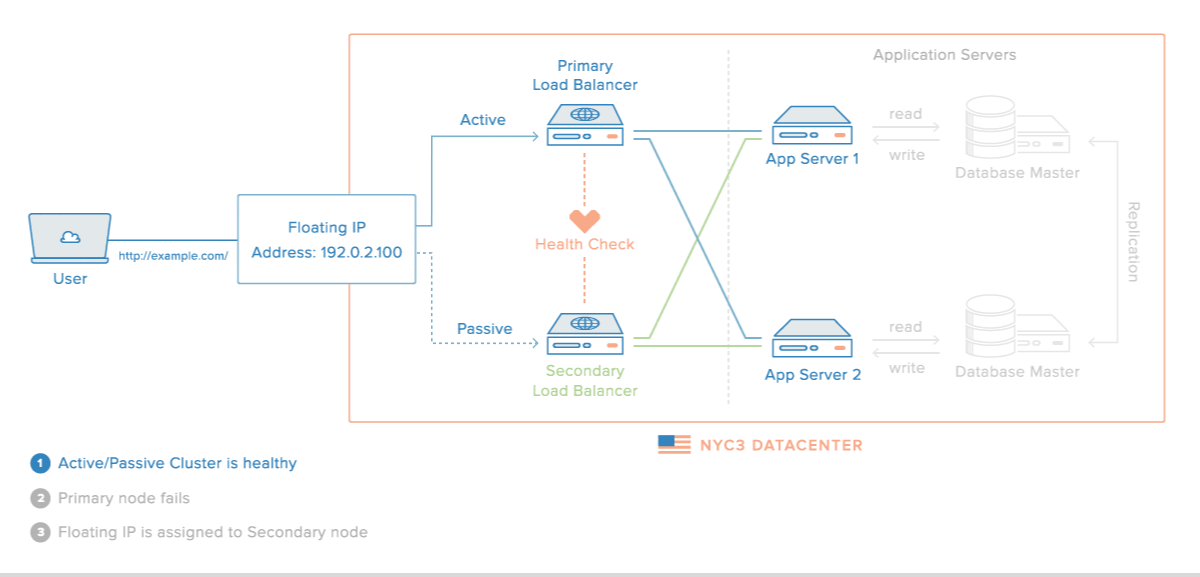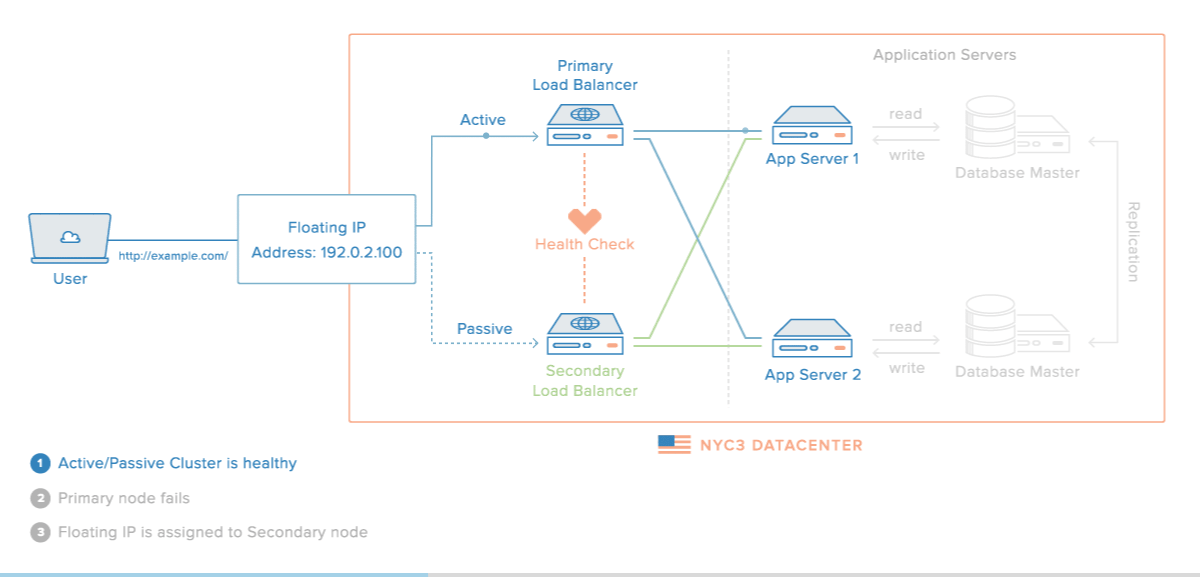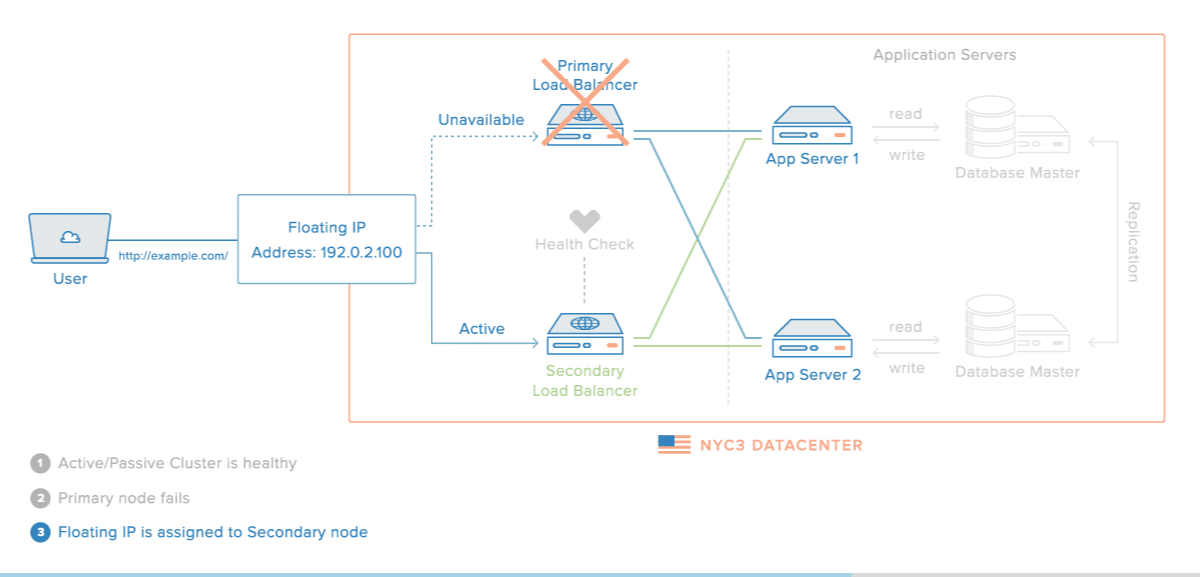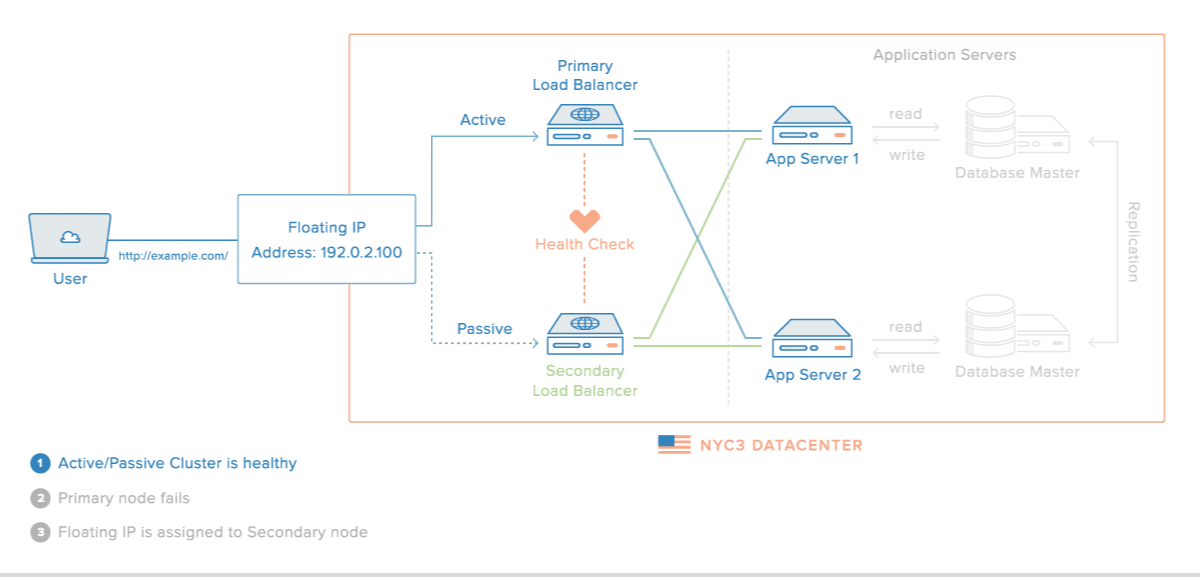
로드밸런싱 장애 대비
- 로드밸런서를 이중화하여 장애를 대비할 수 있다.
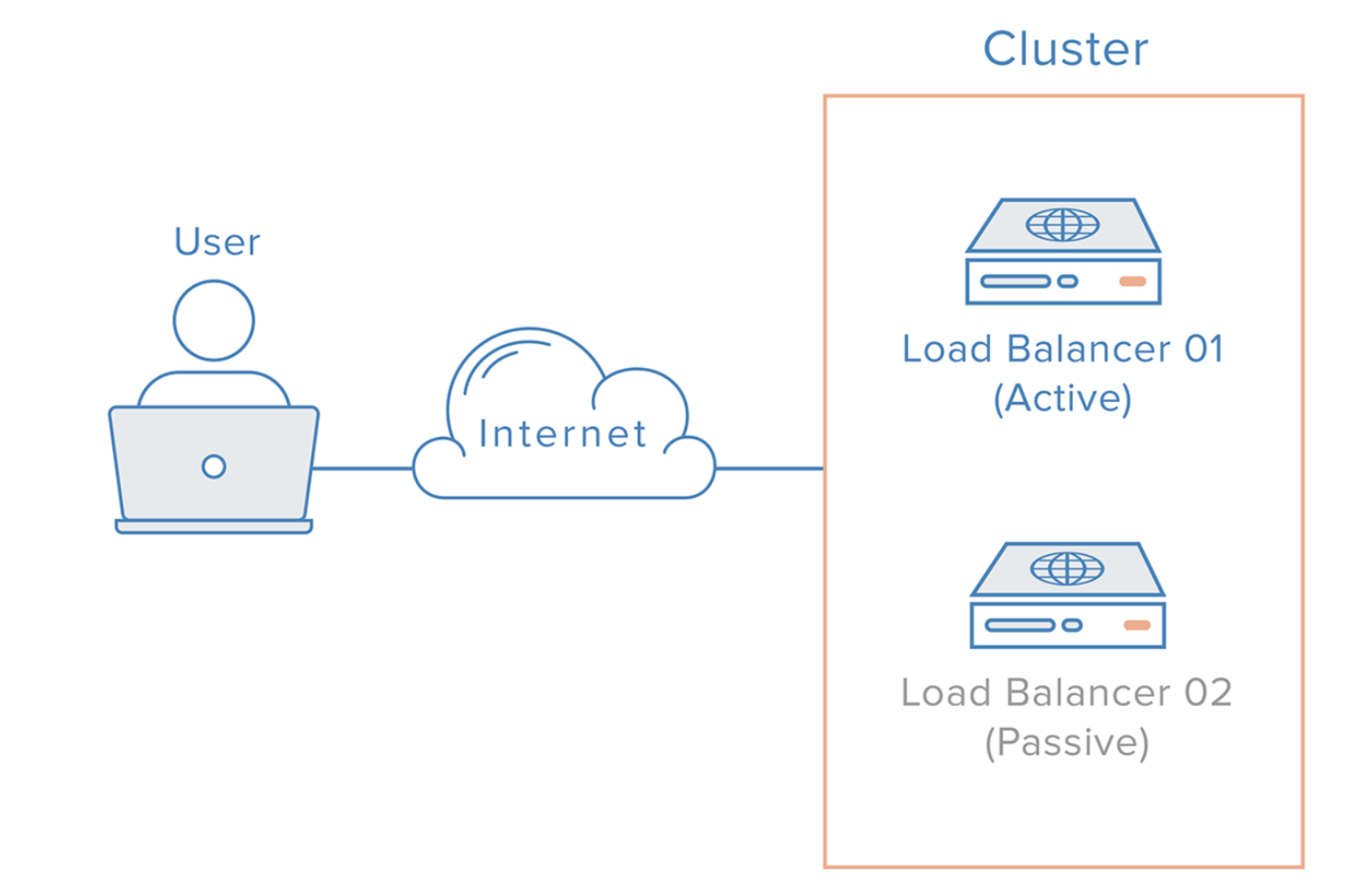
장애가 났을 경우의 시나리오
-
이중화된 로드밸런서들은 서로 Health Check를 한다.
-
메인 로드밸런서가 동작하지 않으면 가상 IP(VIP, Virtual IP)는 여분의 로드밸런서로 변경된다.
-
여분의 로드밸런서로 운영하게 된다.
-
프락시 서버
프락시 서버(Proxy Server)
프락시 서버는 클라이언트와 서버 사이에 위치하여 그들 사이의 HTTP 메시지를 정리하는 웹 중개자 역할을 한다.
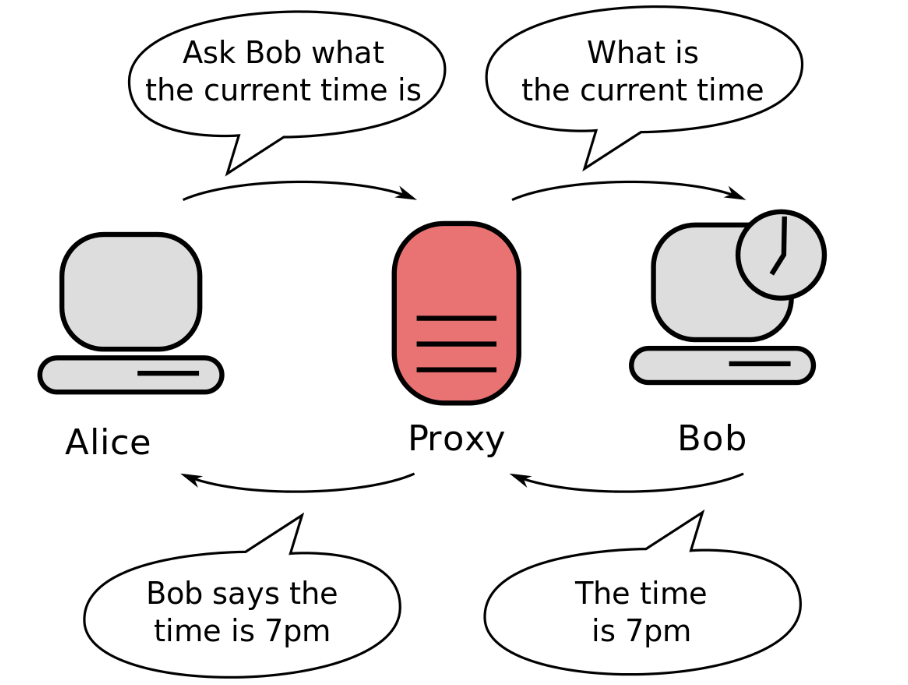
프락시 서버 동작 원리
-
요청 : 사용자가 웹 브라우저에서 도메인을 입력한다.
-
전달 : 사용자가 요청한 것을 캐시 역할을 하는 프록시 서버로 전달한다.
-
확인 : 프록시 서버 내에 도메인 홈페이지의 페이지를 가지고 있는지 확인한다.
-
가지고 있는 경우 - 홈페이지가 있는 서버에게 자신이 가진 페이지가 최신 버전인지 확인하고 필요한 경우 갱신할 부분만 가져온다.
-
가지고 있지 않는 경우 - 홈페이지가 있는 서버와 연결하여 페이지를 가져온다.
프락시 서버 vs 게이트웨이
-
프락시는 같은 프로토콜을 사용하는 둘 이상의 애플리케이션을 연결하고,게이트웨이는 서로 다른 프로토콜을 사용하는 둘 이상을 연결하며, 클라이언트와 서버가 서로 다른 프로토콜로 통신하더라도 서로 간의 트랜잭션을 완료할 수 있도록 도와준다. -
하지만 실무에서는 프락시와 게이트웨이의 경계가 불분명하다.
-
프락시는 브라우자와 서버가 다른 버전의 HTTP를 구현하는 경우 또는상용 프락시는 SSL 보안 프로토콜, SOCKS 방화벽, FTP 접근, 웹 기반 애플리케이션을 지원하는 경우 등 게이트웨이 기능을 구현하는 경우도 있으므로 사실상 차이를 논하기 모호하다.
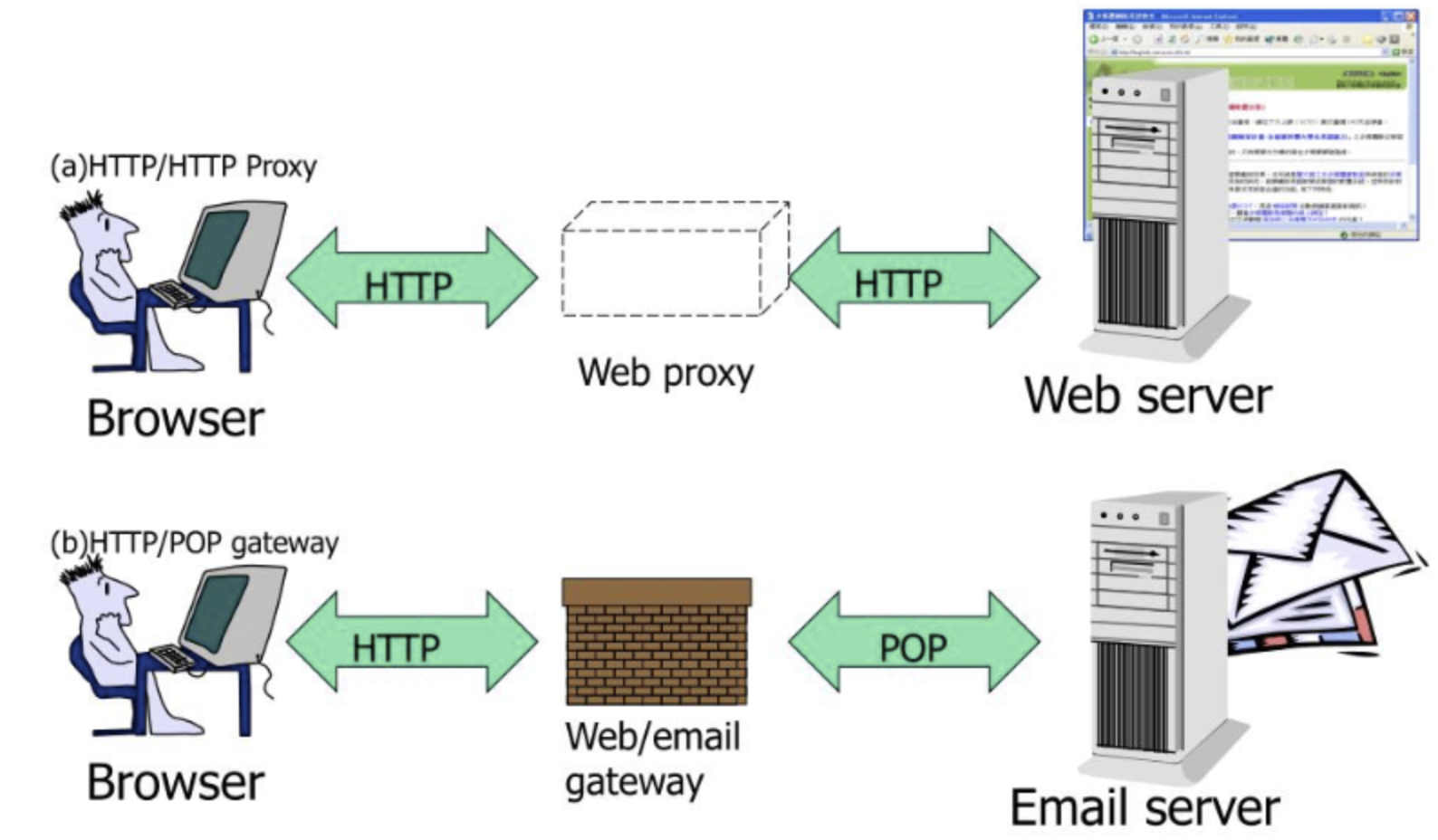
프락시 서버는 왜 필요할까?
-
프락시 서버는 실용적이고 유용한 서비스를 제공한다.
-
보안을 개선하고 성능을 향상하며, 비용을 절약해주고 트래픽 감시 및 수정이 가능하다.(모든 HTTP 트래픽에 접근이 가능하다)
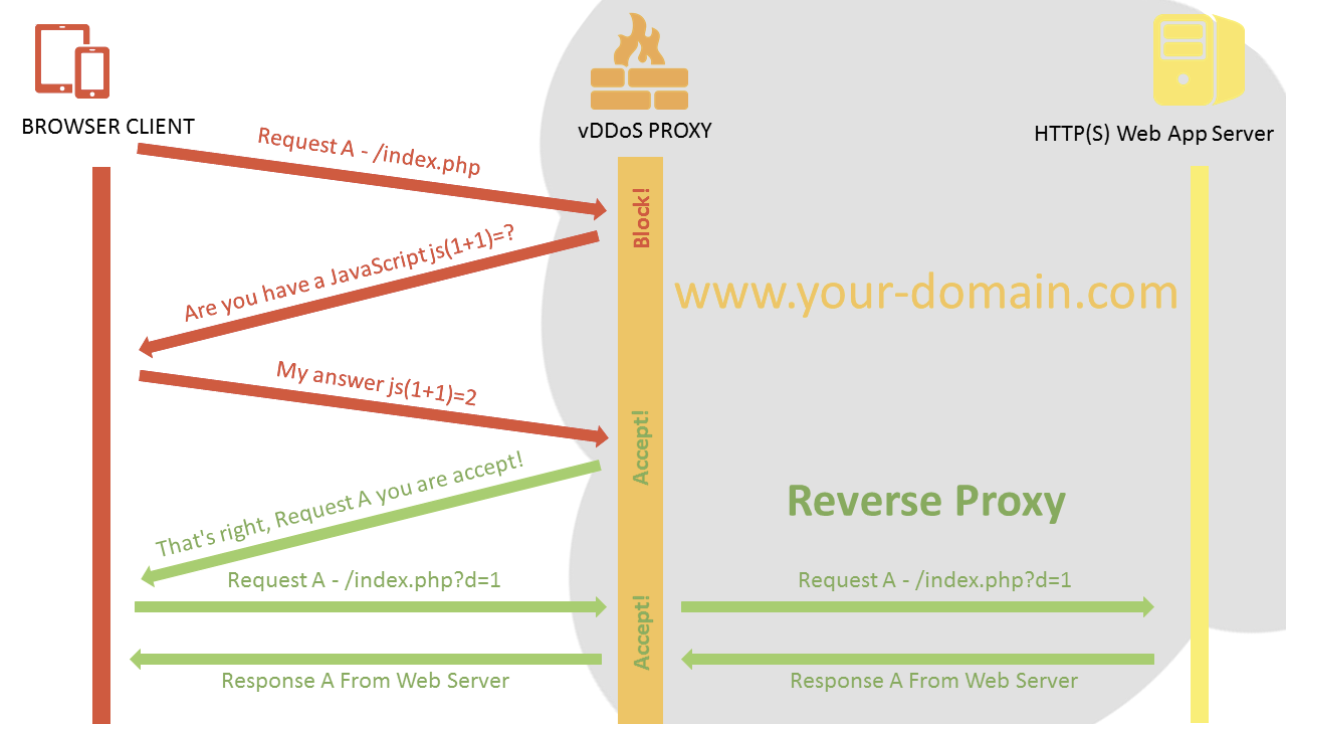
-
위 그림에서 알 수 있듯이 프락시를 통해 필터링(제어) 를 중앙 집권적으로 해결할 수 있다.
-
프락시 서버는 어린이 필터, 문서 접근 제어, 보안 방화벽, 웹 캐시, 대리 프락시(리버스 프락시), 콘텐츠 라우터, 트랜스코더, 익명화 프락시 등에서 사용된다.
-
프락시 서버를 사용하지 않으면, 서버의 주소가 쉽게 노출되고, 다른 익명의 사용자가 서버로 접근하기가 쉽다.
-
이러한 문제점을 보완하기 위해 프락시 서버를 사용하여 중간에 경유하게 되면 서버의 IP를 숨기는 것이 가능하다.
-
프락시 서버를 방화벽으로 사용하기도 한다(프락시 방화벽)
방화벽
-
방화벽(firewall)은 보안 규칙에 기반하여 들어오고 나가는 네트워크 트래픽을 모니터링하고 제어하는 네트워크 보안 시스템이다. 신뢰할 수 있는 내부 네트워크와 신뢰할 수 없는 외부 네트워크 간의 장벽을 구성한다. -
프락시 방화벽은 세션에 포함되어 있는 정보의 유해성을 검사하는 역할로, 방화벽에서 세션을 종료하고 새로운 세션을 형성하는 방식이다.-
출발지에서 목적지로 가는 세션을 가로채서 두 가지 세션으로 만든다(출발지에서 방화벽까지의 세션, 방화벽에서 목적지까지의 세션)
-
하나의 세션에서 다른 세션 정보를 넘겨주기 전에 검사를 수행하는 형식이다.
-
패킷 필터에 비해 많은 부하를 주어서 속도가 느리지만, 더 많은 검사 기능을 제공하고 프로토콜 변경 등 추가적인 수행이 가능하다.
-
웹 캐시
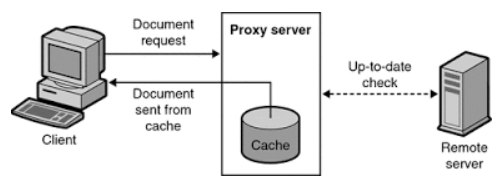
-
프락시 캐시는 문서의 로컬 사본을 관리하고 해당 문서에 대한 요청이 오면 빠르게 제공하여, 느리고 비싼 인터넷 커뮤니케이션을 줄여준다. (전송시간 절약, 외부트래픽 감소)
-
웹 서버보다 웹 캐싱 프락시가 가깝다면 클라이언트는 가까운 웹 캐시의 문서에 접근한다.
프락시 종류
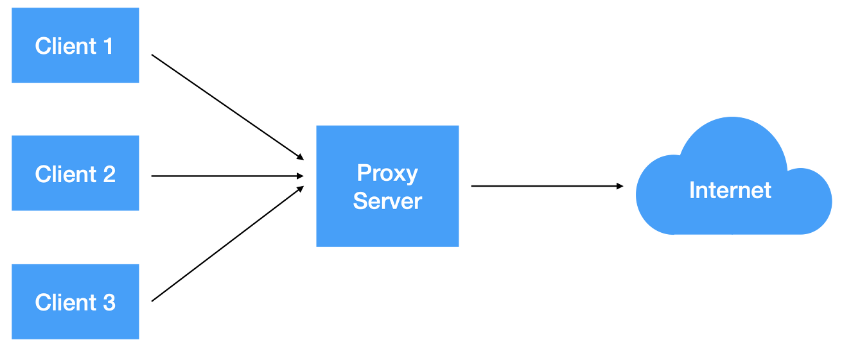
Forward 프락시
-
포워딩 프락시(Forwarding Proxy)를 일반적으로 프락시라고 부른다.
-
클라이언트가 인터넷에 직접 접근하는 것이 아닌, 포워딩 프락시 서버가 클라이언트의 요청을 받고 인터넷에 연결한 이후에 그 결과를 클라이언트에게 응답한다.
-
예) 팬시(사용자)가
google.com에 연결하고자 할 때, 프락시 서버가 팬시의 요청을 받아google.com에 연결하고 그 결과를 팬시에게 응답한다는 것이다. -
포워딩 프락시는 캐시 기능이 있으므로 자주 사용하는 컨텐츠라면 성능을 향상시킬 수 있고, 정해진 사이트만 연결하게 설정하는 등 웹 사용 환경을 제한할 수 있으므로 보안이 매우 중요한 기업환경에서 많이 사용한다.
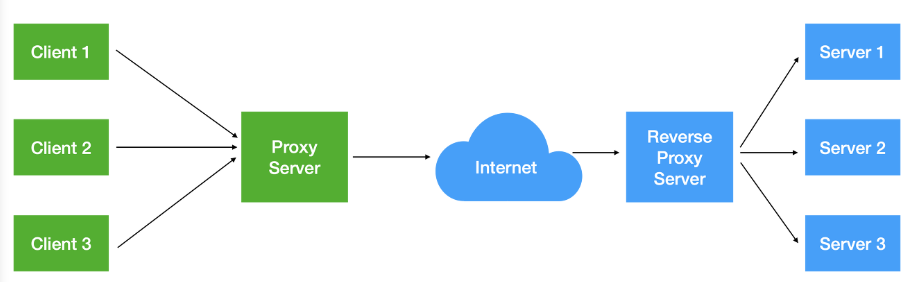
Reverse 프락시
-
리버스 프락시는 포워딩 프락시가 서버쪽에도 존재한다고 생각하면 된다. -
클라이언트가 인터넷에 데이터를 요청하면 리버스 프락시가 이 요청을 받아 내부 서버에서 데이터를 받은 후 클라이언트에게 응답한다.
-
클라이언트는 내부 서버에 대한 정보를 알 필요 없이 리버스 프락시에게 요청하면 된다.
-
내부 서버가 직접 서비스를 제공할 순 있지만, 리버스 프락시를 사용하는 이유은 보안 때문이다.
-
기업의 네트워크 환경에서는
DMZ라 불리는 내부 네트워크와 외부 네트워크 사이에 위치한 구간이 존재한다. -
이 구간에 보통 메일 서버, 웹 서버, FTP 서버 등 외부 서비스를 제공하는 서버가 위치한다.
-
내부 서버(WAS)에 직접 접근하게 되면 DB에 접근이 가능하므로 해킹 문제가 발생할 우려가 있다. -
리버스 프락시 서버를
DMZ에 두고 실제 서버는 내부망에 위치 시켜서 서비스 하는 것이 일반적이고 보안상 안전하다.
-
-
내부 서버를 설정하게 되면 로드 밸런싱이나 서버 확장에 유리한다.
-
SSL 암호화에 좋다. 원래 서버가 클라이언트와 통신을 할 때 SSL(or TSL)로 암호화, 복호화를 하면서 비용이 많이 들게 된다. 하지만
리버스 프락시를 사용하면 들어오는 요청을 모두 복호화로 하고 나가는 응답을 암호화해주기 때문에 클라이언트와 안전한 통신을 할 수 있으며 본래의 비용보다 줄일 수 있다.
-
[데이터베이스개론] 관계 데이터 모델의 개념
이 글의 정보들은
데이터베이스 개론과면접을 위한 CS 전공지식 노트교재를 공부하면서 정리한 내용을 토대로 작성하였습니다.데이터베이스의 기본
-
데이터베이스는 일정한 규칙, 혹은 규약을 통해 구조화되어 저장되는 데이터의 모음이다.
-
해당 데이터베이스를 제어, 관리하는 통합 시스템을
DBMS라고 하며, 데이터베이스 안에 있는 데이터들을 특정 DBMS 마다 정의된 쿼리 언어를 통해 삽입, 삭제, 수정, 조회 등을 수행할 수 있다. -
또한 데이터베이스는 실시간 접근과 동시 공유가 가능하다.
엔티티
-
엔티티(entity)는 사람, 장소, 물건, 사건, 개념 등 여러 개의 속성을 지닌 명사를 의미한다.
-
예를 들어 회원이라는 엔티티가 있다고 하면, 회원은 이름, 아이디, 주소, 전화번호의 속성을 갖는다.
-
물론 이보다 더 많은 속성이 있을 수 있지만 서비스의 요구 사항에 맞춰 속성이 정해진다.
릴레이션
-
릴레이션은 데이터베이스에서 정보를 구분하여 저장하는 기본 단위이다.
-
엔티티에 관한 데이터를 데이터베이스는 릴레이션 하나에 담아서 관리한다.
관계 데이터 모델의 기본 용어
-
일반적으로 관계 데이터 모델에서는 하나의 개체에 관한 데이터를 릴레이션(relation) 하나에 담아 데이터베이스를 저장한다.
-
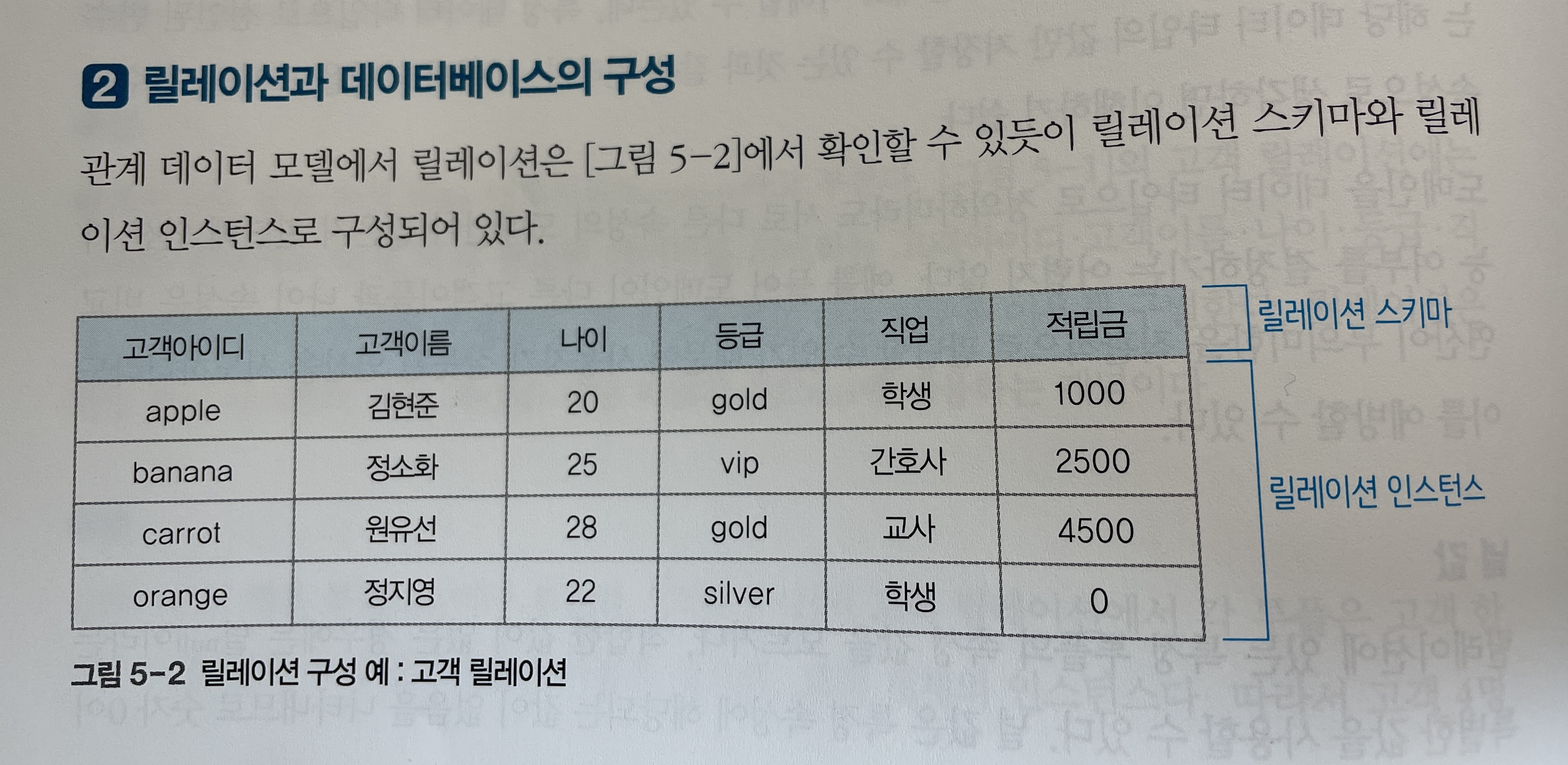
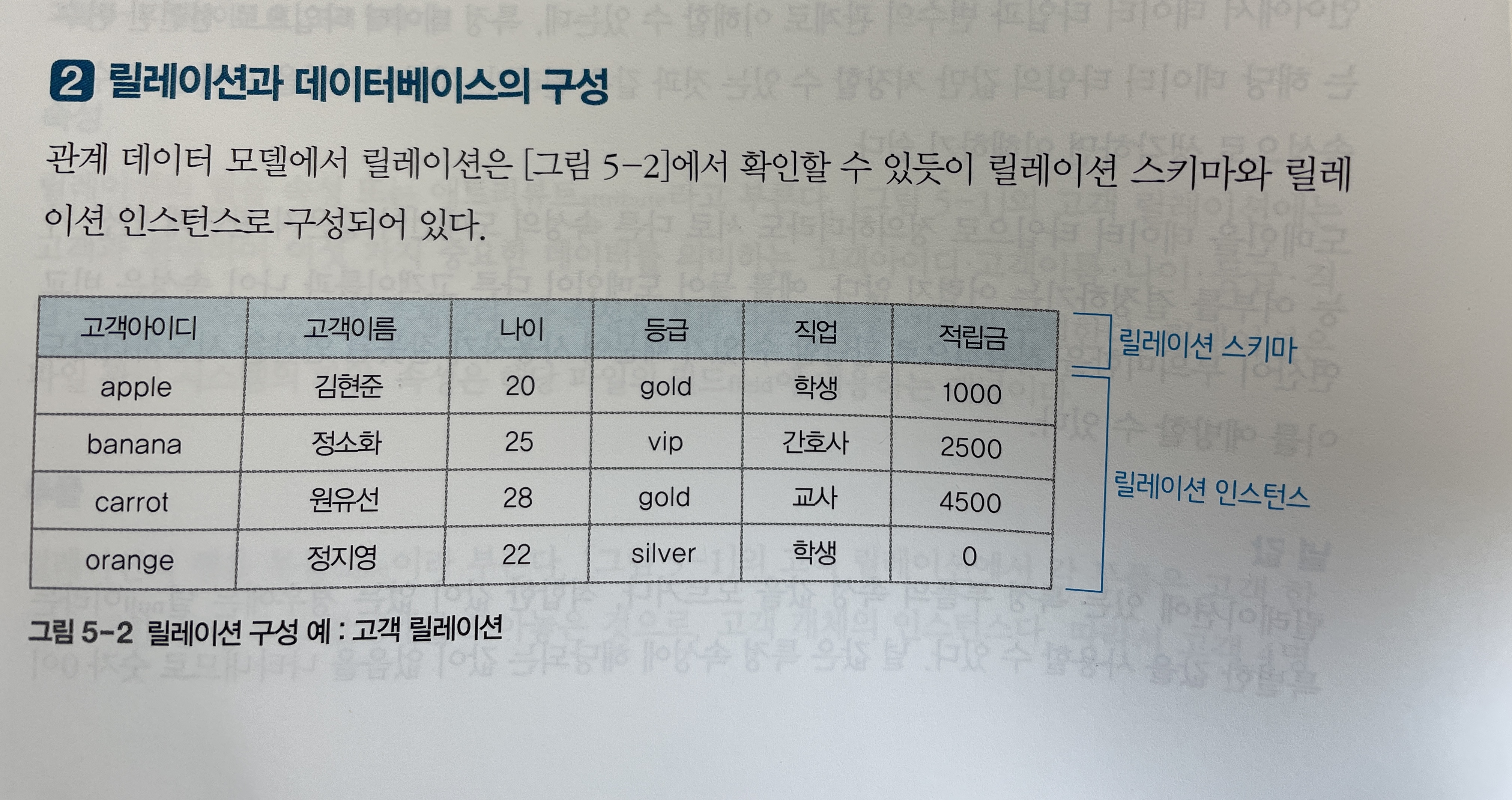
[그림 5-1]은 인터넷 쇼핑몰을 위한 데이터베이스에서 고객 개체를 표현한 고객 릴레이션의 예다. 해당 예시를 통해 릴레이션과 관련된 용어를 하나씩 알아보자.
속성
-
릴레이션의 열을 속성(or attribute)라고 부른다. [그림 5-1]의 고객 릴레이션에는 고객아이디, 고객이름, 나이, 등급, 직업, 적립금이라는 6개의 속성이 존재한다.
-
릴레이션은 파일 관리시스템의 파일, 속성은 해당 파일의 필드에 대응하는 개념이다.
튜플
-
릴레이션의 행을 튜플(or tuple)이라고 부른다. [그림 5-1]에서 고객 4명에 대한 데이터를 저장하고 있는 고객 릴레이션에는 4개의 튜플 또는 4개의 고객 개체 인스턴스가 존재한다.
-
튜플은 파일 관리 시스템 관점에서 해당 파일의 레코드에 대응하는 개념이다.
도메인
-
속성 하나가 가질 수 있는 모든 값의 집합을 해당 속성의 도메인(domain)이라 한다.
-
[그림 5-1]의 고객 릴레이션에서 등급 속성의 값으로 vip, gold, silver, bronze 중 하나만 허용된다면, 네 가지 값을 모아 놓은 것이 등급 속성의 도메인이 된다.
-
매번 모든 값을 일일이 나열하여 도메인을 정의하기가 어렵기 때문에, 일반적으로 속성의 특성을 고려한 데이터 타입으로 정의한다.
-
CHAR(20), INT 같이 특정 데이터 타입으로 선언된 변수는 해당 데이터 타입의 값만 저장할 수 있는 것과 같은 원리다.
-
데이터 타입을 도메인, 변수를 속성으로 생각하면 이해하기 쉽다.
널값
-
릴레이션에 있는 특정 튜플의 속성 값을 모르거나, 적합한 값이 없는 경우에는 널(null)이라는 특별한 값을 사용할 수 있다.
-
널 값은 특정 속성에 해당하는 값이 없음을 나타내므로 숫자 0 혹은 공백 문자와는 다르다.
-
널 값은 데이터베이스 관리 시스템마다 내부적으로 표시하는 기호가 다르다.
차수
-
하나의 릴레이션에서 속성의 전체 개수를 릴레이션의 차수(degree)라고 한다.
-
예를 들어 [그림 5-1]의 고객 릴레이션은 차수는 6이다.
-
모든 릴레이션은 최소 1 이상의 차수를 유지해야 한다.
-
릴레이션의 차수는 일반적으로 자주 변하지 않는다는 정적인 특징이 있다.
카디널리티
-
하나의 릴레이션에서 튜플의 전체 개수를 카디널리티(cardinality)라고 한다.
-
예를 들어 [그림 5-1]의 고객 릴레이션의 카디널리티는 4이다.
-
튜플이 없는 릴레이션이 존재할 수도 있다.
-
새로운 튜플이 계속 삽입되거나 기존 튜플이 삭제될 수 있으므로 릴레이션의 카디널리티는 일반적으로 자주 변한다는 동적인 특징이 있다.
릴레이션과 데이터베이스의 구성
- 관계 데이터 모델에서 릴레이션은 [그림 5-2]와 같이
릴레이션 스키마와릴레이션 인스턴스로 구성되어 있다.
릴레이션 스키마
-
릴레이션 스키마는 릴레이션의 이름과 릴레이션에 포함된 모든 속성의 이름으로 정의하는 릴레이션의 논리적 구조다.
-
일반적으로 다음과 같은 형태로 쉽게 표현한다.
릴레이션 이름(속성이름1, 속성이름2, …, 속성이름 n)
-
[그림 5-2]의 고객 릴레이션에서 릴레이션 스키마는
고객(고객아이디, 고객이름, 나이, 등급, 직업, 적립금)이다. -
릴레이션 스키마는
릴레이션 내포라고도 부른다.
릴레이션 인스턴스
-
릴레이션 인스턴스는 어느 한 시점에 릴레이션에 존재하는 튜플들의 집합이다.
-
[그림 5-2]의 고객 릴레이션에서
4개의 튜플로 구성된 릴레이션 인스턴스를 확인할 수 있다. -
릴레이션 인스턴스는 간단히
릴레이션이라 부르기도 하고릴레이션 외연이라고도 부른다.
데이터베이스 스키마와 데이터베이스 인스턴스
-
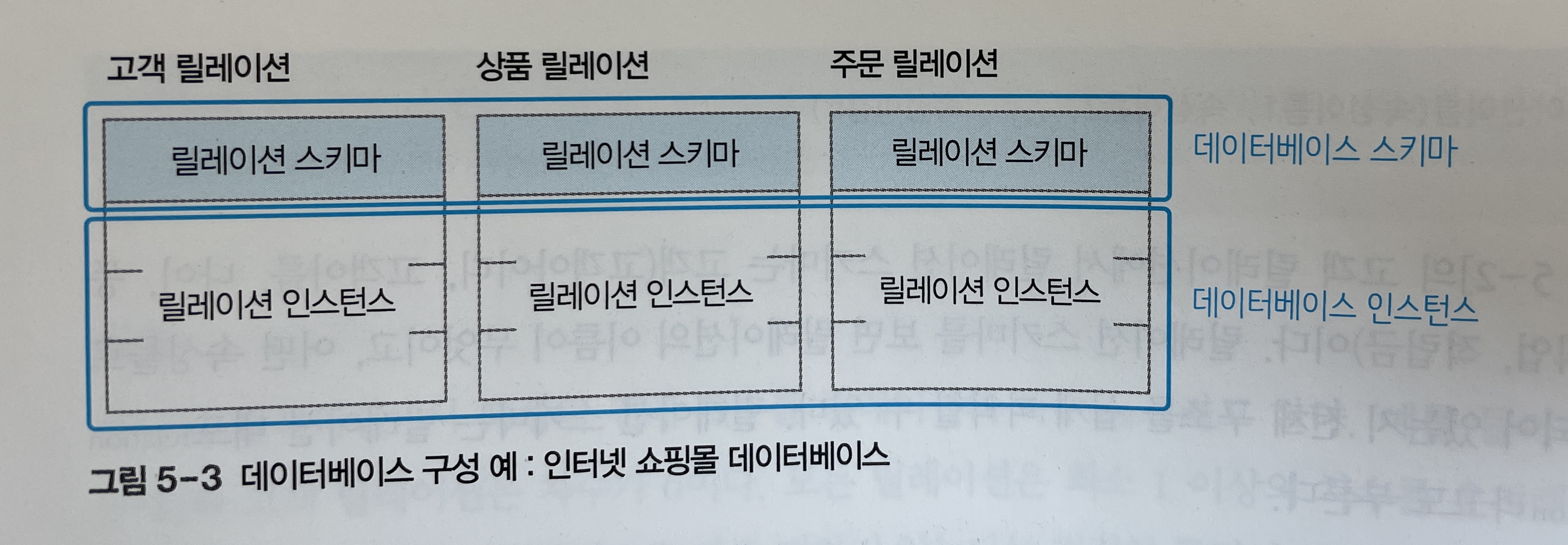
일반적으로 데이터베이스는 릴레이션이 여러 개로 구성된다.
-
[그림 5-3]와 같이 인터넷 쇼핑몰 데이터베이스는 여러 릴레이션으로 구성되어 있다.
-
데이터베이스 스키마는 데이터베이스를 구성하는 릴레이션들의 스키마를 모아놓은 것이다. -
데이터베이스 인스턴스는 어느 한 시점에서 데이터베이스에 저장된 데이터 내용의 전체 집합을 의미한다.
릴레이션의 특성
-
관계 데이터 모델의 릴레이션에는 4가지 중요한 특성이 있다.
-
기본적으로 이 4가지 특성을 만족해야 테이블이 릴레이션으로 인정받을 수 있다.
-
튜플의 유일성 : 하나의 릴레이션에는 동일한 튜플이 존재할 수 없다.
-
튜플의 무순서 : 하나의 릴레이션에서 튜플 사이의 순서는 무의미하다.
-
속성의 무순서 : 하나의 릴레이션에서 속성 사이의 순서는 무의미하다.
-
속성의 원자성 : 속성 값으로 원자 값만 사용할 수 있다. (
원자 값이란 더는 분해할 수 없는 하나의 값을 의미한다)
-
-
[데이터베이스개론] 관계 데이터 모델의 개념 - Key의 종류
이 글의 정보들은
데이터베이스 개론과면접을 위한 CS 전공지식 노트교재를 공부하면서 정리한 내용을 토대로 작성하였습니다.Key의 종류
-
key는 테이블 간의 관계를 조금 더 명확하게 하고, 관계 데이터 모델에서 중요한 제약조건을 정의한다.또한 튜플을 처리하는 데 중요한 역할을 하므로 키의 개념을 정확히 이해할 필요가 있다.
-
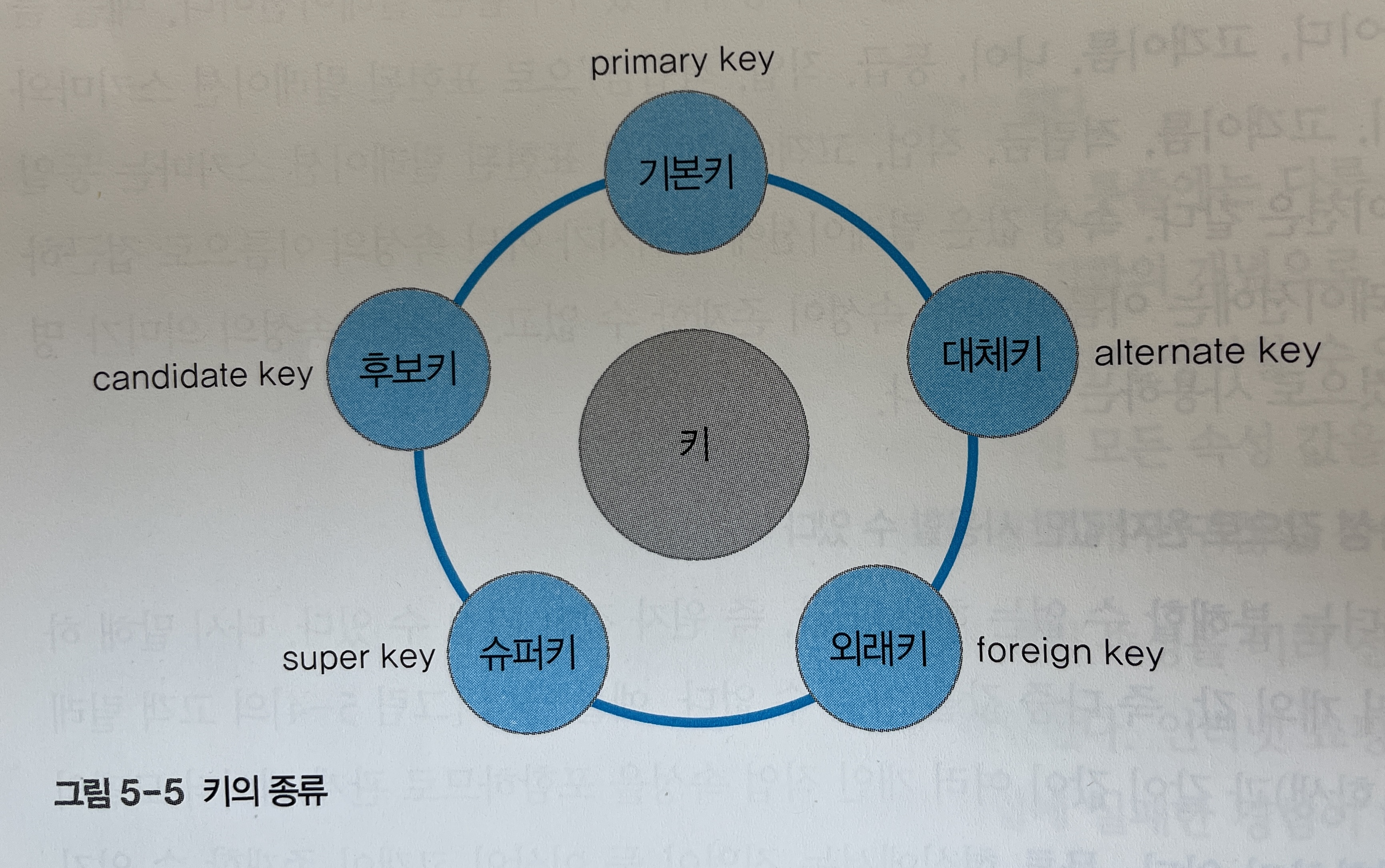
관계 데이터 모델에서는 키를 다음과 같이
슈퍼키,후보키,기본키,대체키,외래키의 다섯 가지로 분류할 수 있다.
슈퍼키
슈퍼키는 유일성의 특성을 만족하는 속성 또는 속성들의 집합이다.유일성은 키가 갖추어야 하는 기본 특성으로, 키 값이 같은 튜플은 존재할 수 없다.
-
예를 들어 [그림 5-2]의 고객 릴레이션에서
고객아이디속성은 모든 고객 튜플마다 값이 다르고 이를 통해 다른 튜플과 유일하게 구별할 수 있으므로 슈퍼키가 될 수 있다. -
그러나 다른 속성(나이, 등급, 직업, 적립금)은 값이 같은 고객이 있을 수 있으므로 유일성을 만족시키지 못해 슈퍼키가 될 수 없다.
-
고객 아이디속성만으로도 모든 튜플을 구별할 수 있기 때문에 고객 아이디를 포함하는 속성 집합은 모두 슈퍼키가 될 수 있다.
후보키
-
후보키는 유일성과 최소성을 만족하는 속성 또는 속성들의 집합이다.최소성은 꼭 필요한 최소한의 속성들로만 키를 구성하는 특성이다. 그러므로 하나의 속성으로 구성된 키는 당연히 최소성을 만족한다. -
슈퍼키 중에서 최소성을 만족하는 것이 후보키가 된다. [그림 5-2]의
고객아이디속성은 단독으로 고객 튜플을 유일하게 구별할 수 있으므로 후보키가 될 수 있다. -
후보키를 만족하기 위해서는 새로운 튜플이 삽입되거나 기존 튜플의 속성 값이 바뀌어도 유지되어야 한다.
기본키
-
여러 후보키 중에서 기본적으로 사용할 키를 반드시 선택해야 하는데 이것이
기본키다. -
후보키가 1개일 경우에는 해당 후보키가 기본키로 선택하고, 후보키가 여러개일 경우에는 데이터베이스 사용 환경을 고려해서 적합한 것을 기본키로 선택하면 된다.
-
선택한 기본키는 [그림 5-6]과 같이 속성 이름에 밑줄을 그어 표헌한다.
-
기본키를 선택할 때 고려하면 도움이 되는 기준 몇 가지를 정리했다.
-
널 값을 가질 수 있는 속성이 포함된 후보키는 기본키로 부적합하다.
-
값이 자주 변경될 수 있는 속성이 포함된 후보키는 기본키로 부적합하다.
-
단순한 후보키를 기본키로 선택한다.
기본키 선정 과정은 대학에서 학생회장을 선발하는 과정과 유사하다. 대학에 다니는 학생들(슈퍼키) 중에서 학생회장이 될 만한 자격을 갖춘 후보 학생(후보키)을 추천한 다음, 지지를 가장 많이 받은 한 명의 학생(기본키)을 학생회장으로 임명하는 과정으로 이해하면 된다.
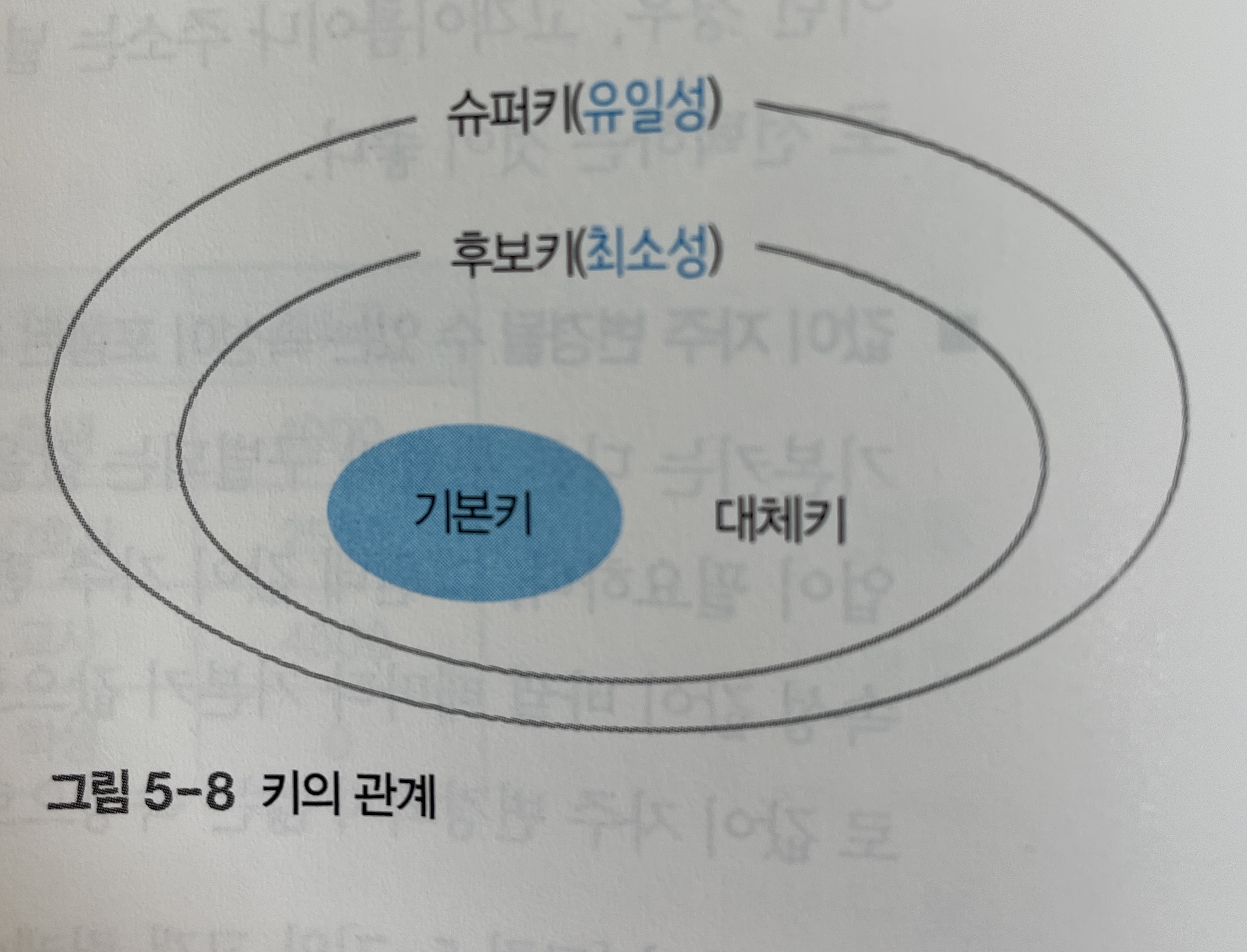
대체키
대채키는 기본키로 선택되지 못한 후보키들이다.
-
[그림 5-8]은 하나의 릴레이션에서 볼 수 있는 슈퍼키, 후보키, 기본키, 대체키의 관계를 그림으로 표현한 것이다.
-
이 외에도 다른 릴레이션과 관계에서 고려할 수 있는 외래키가 있다.
외래키
-
외래키는 어떤 릴레이션에 소속된 속성 또는 속성 집합이 다른 릴레이션의 기본키가 되는 키다. -
다시 말해 다른 릴레이션의 기본키를 그대로 참조하는 속성의 집합이 외래키다.
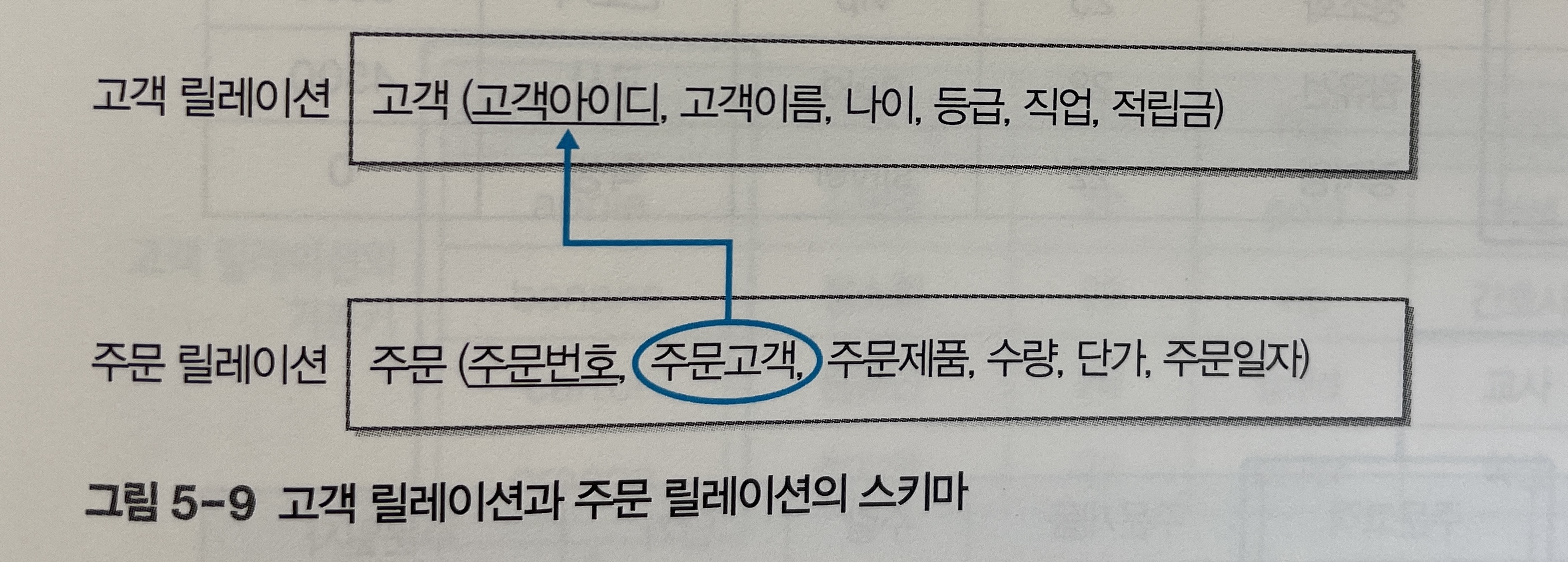
외래키가 다른 테이블의 대체키를 참조하는 것도 가능하다. 기본키로 선택받지 못했지만 유일성과 최소성을 만족하는 대체키를 참조하더라도 **관련 있는 튜플을 구분할 수 있기 때문**이다.- 외래키의 개념과 필요성을 파악하기 위해 인터넷 쇼핑몰을 위한 데이터베이스에서 고객 릴레이션과 주문 릴레이션의 관계를 생각해보자.
-
[그림 5-9]에서 고객 릴레이션은 속성이 6개이고,
고객 아이디속성이 기본키다. 주문 릴레이션은 속성이 6개이고,주문번호속성이 기본키다. -
여기서 주문 릴레이션의 주문고객 속성이 고객 릴레이션의 기본키인
고객 아이디속성을 참조하면주문고객속성을 외래키라고 한다.
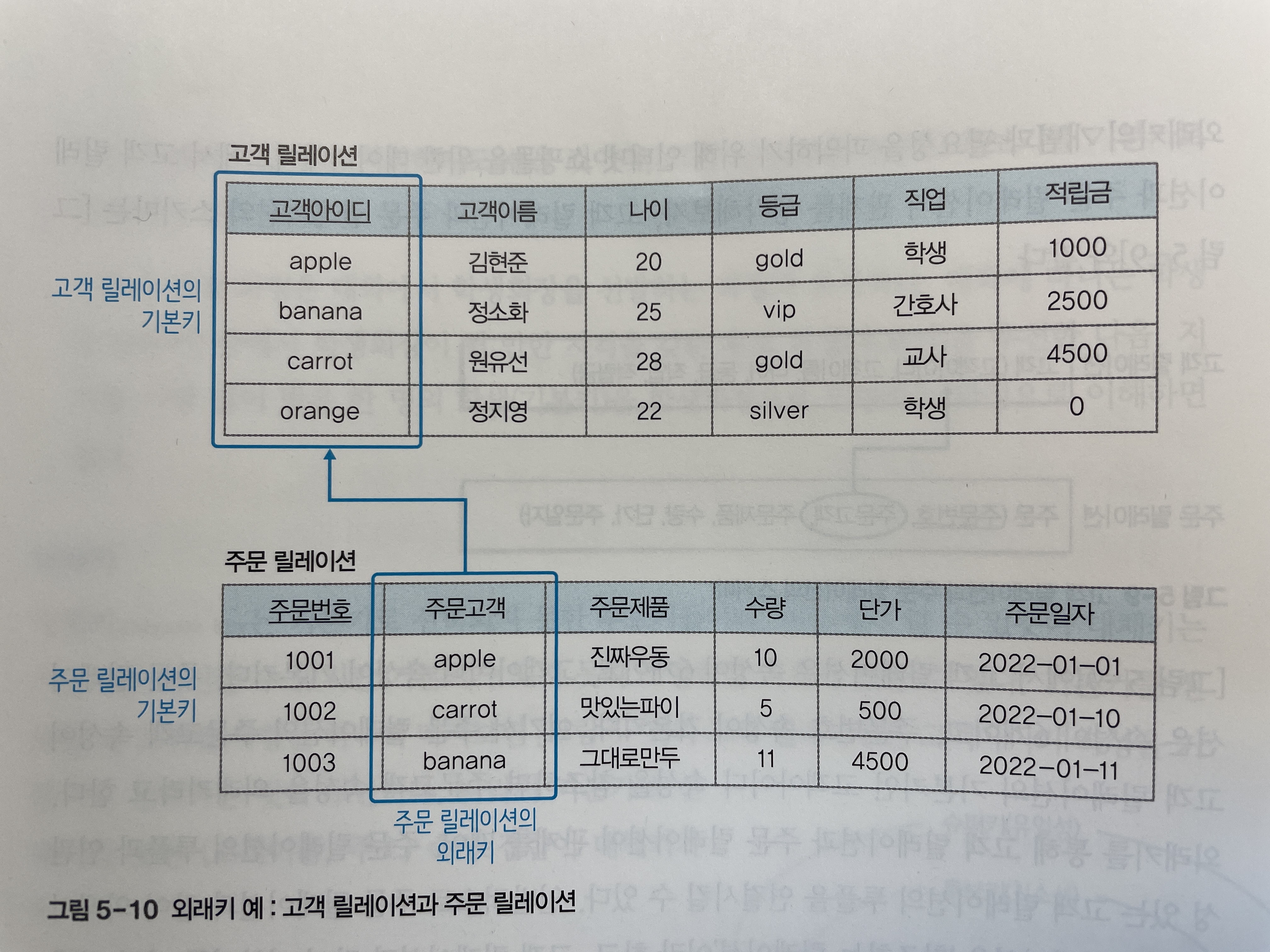
- [그림 5-10]와 같이 외래키는 반드시 다른 릴레이션의 기본키를 참조해야 하며 외래키의 도메인은 참조되는 기본키와 같게 정의되어야 한다.
Reference
-
-
[Programmers] 43165. 타켓 넘버(dfs)
성능 요약
- 메모리: 78 MB, 시간: 0.31 ms - Answer Code1(2023.02.13)
구분
코딩테스트 연습 > 깊이/너비 우선 탐색(DFS/BFS)
Answer Code(2023.02.13)
class Solution { int [] numbers; int target; int answer; void dfs(int index, int sum) { //1. 탈출 조건 if(index == numbers.length) { if(sum == target) answer++; return; } //2. 수행 동작 dfs(index + 1, sum + numbers[index]); dfs(index + 1, sum - numbers[index]); } public int solution(int[] numbers, int target) { answer = 0; this.numbers = numbers; this.target = target; dfs(0, 0); return answer; } }Answer Code1 - 문제 풀이
-
수행 동작 : 인덱스 값은 현재 인덱스에 하나를 더하거나 뺀 값으로 넘겨주면 된다. => index + 1 또는 index - 1
-
왜냐하면 경우의 수가 2가지(+ 또는 -)이기 때문이다.
-
sum 에는 numbers[index]를 더하거나 빼주면 된다. (즉 여테까지 만들어진 누적합에 현재 index 번째 숫자를 더해서 다음 dfs 함수를 call 해주는 의미)
-
-
탈출 조건 : 재귀함수는 영원하게 불러주기 때문에, 탈출 조건은 현재 재귀함수가 call된 인덱스(depth 길이)가 numbers.length만큼 되면 빠져나오기로 한다.
- 마지막 노드까지 탐색했을 때(index와 numbers 배열의 길이가 같은 경우), target과 sum의 값이 일치하면 answer 값을 증가시키고 탈출한다.
- DevHistory 4
- Essay 1
- Java 10
- Spring 15
- SpringBoot 17
- JPA 13
- MySQL 3
- Flyway 1
- Kafka 8
- Technology 22
- GoodCode 7
- Side_Project 20
- Retrospective 4
- AlgorithmSkill 3
- LeetCode 2
- Algorithm 70
- SQL 9
- OS 14
- Database 8
- Network 7
- HTTP 7
- DataStructure 5
- Linux 4
- Woowacourse 4
- Git 9
- AssertJ 1
- IntelliJ 5
- Probability-Statistics 5
- Electronic-Finance 13
- Business-Statistics 13
- Competition 1
- Book 6
- Workout 7
- E.T.C 8