지금의 기록이 미래의 자산이 된다.
Today's records become tomorrow's assets.-
19. TLB(Translation Lookaside Buffers)
- Prologue
- TLB (Translation Lookaside Buffers)
- TLB entry (TLB 안에는 무엇이 있을까?)
- Example: Accessing An Array
- Locality
- Effective Access Time(EAT)
- TLB Issue: Context Switching
- To Solve Problem
- Another Case
- TLB Replacement Policy
- 예상 질문
이 글의 사진과 내용은 공룡책 과 컴퓨터학부 수업인 운영체제 강의자료를 기반으로 작성했습니다.
Prologue
-
Paging 기법을 사용하여 메모리 가상화를 지원한다면 오버 헤드가 발생한다.
-
[1] Page Table에 한번 접근하고, [2] Page Table을 기반으로 실제 메모리에 접근하기 때문에 메모리 낭비가 발생하는 문제점이 있다.
-
즉, Paging 기법은 메모리 낭비가 발생하고, 느리기 때문에 이를 좀 더 빠르게 만들기 위해
TLB가 나오게 되었다.
TLB (Translation Lookaside Buffers)
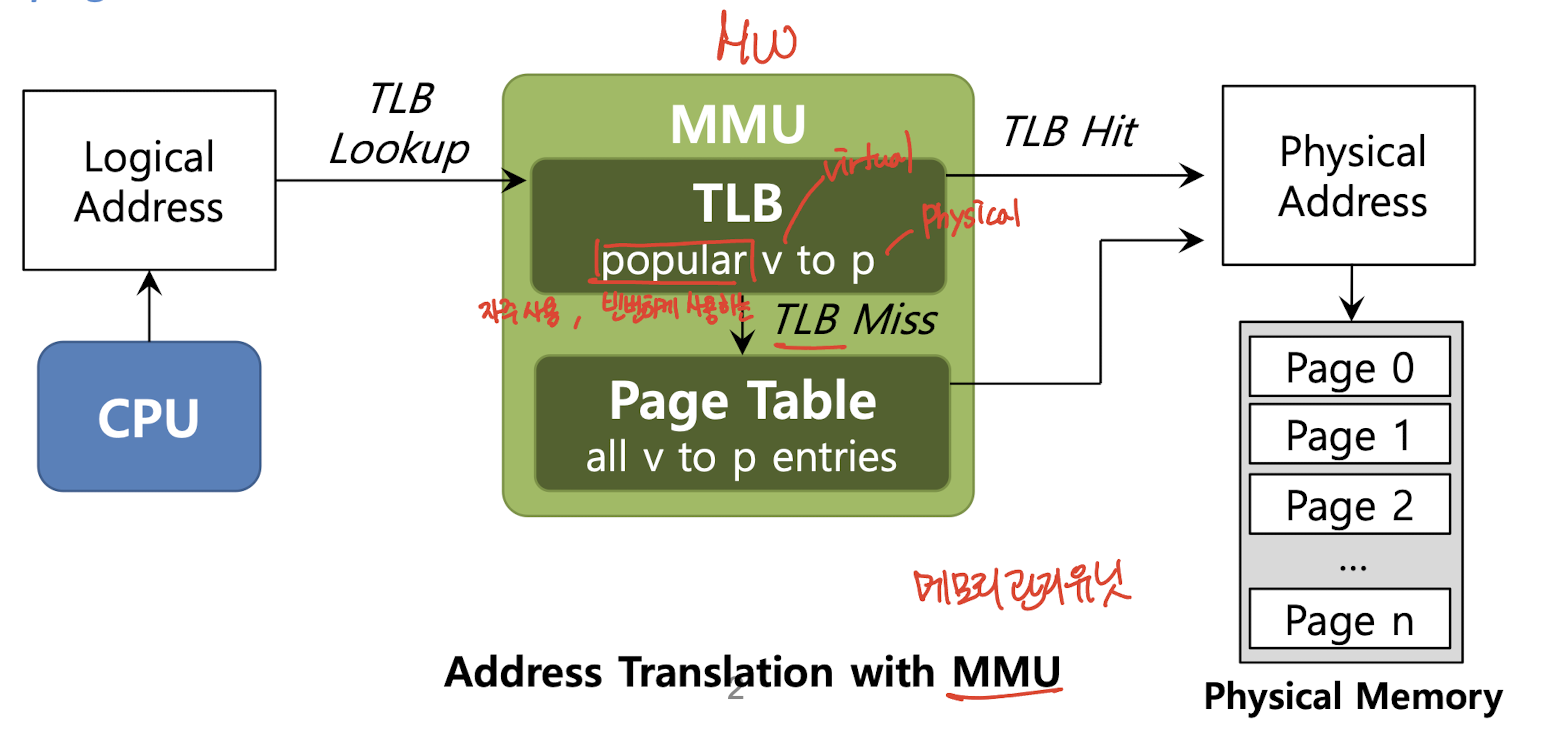
TLB는 Memory-Management Unit(MMU)의 일부분이자, 주소 변환의 하드웨어 캐시이다.
-
TLB에는 자주 사용하는 VPN(virtual page number)와 PFN(physical frame number) 정보가 쌍으로 존재하며 이를 사용해 가상 주소를 실제 주소로 변환하도록 도와주는 Hardware cache이다.
-
이를 사용해 CPU가 Paging 기법으로 주소 변환을 할 때 Page Table이 아닌 TLB에 접근하는데, CPU가 원하는 VPN과 PFN의 정보가 TLB에 있다면, 해당 정보로 빠르게 주소변환을 할 수 있다.
-
즉, 해당 정보를 Page Table 없이 TLB로 가져오기 때문에 주소 변환이 빠르게 수행하는 장점이 있다.
-
하지만, 해당 정보가 TLB에 없다면 어쩔 수 없이 Page Table에서 가져오는 단점이 있다.
-
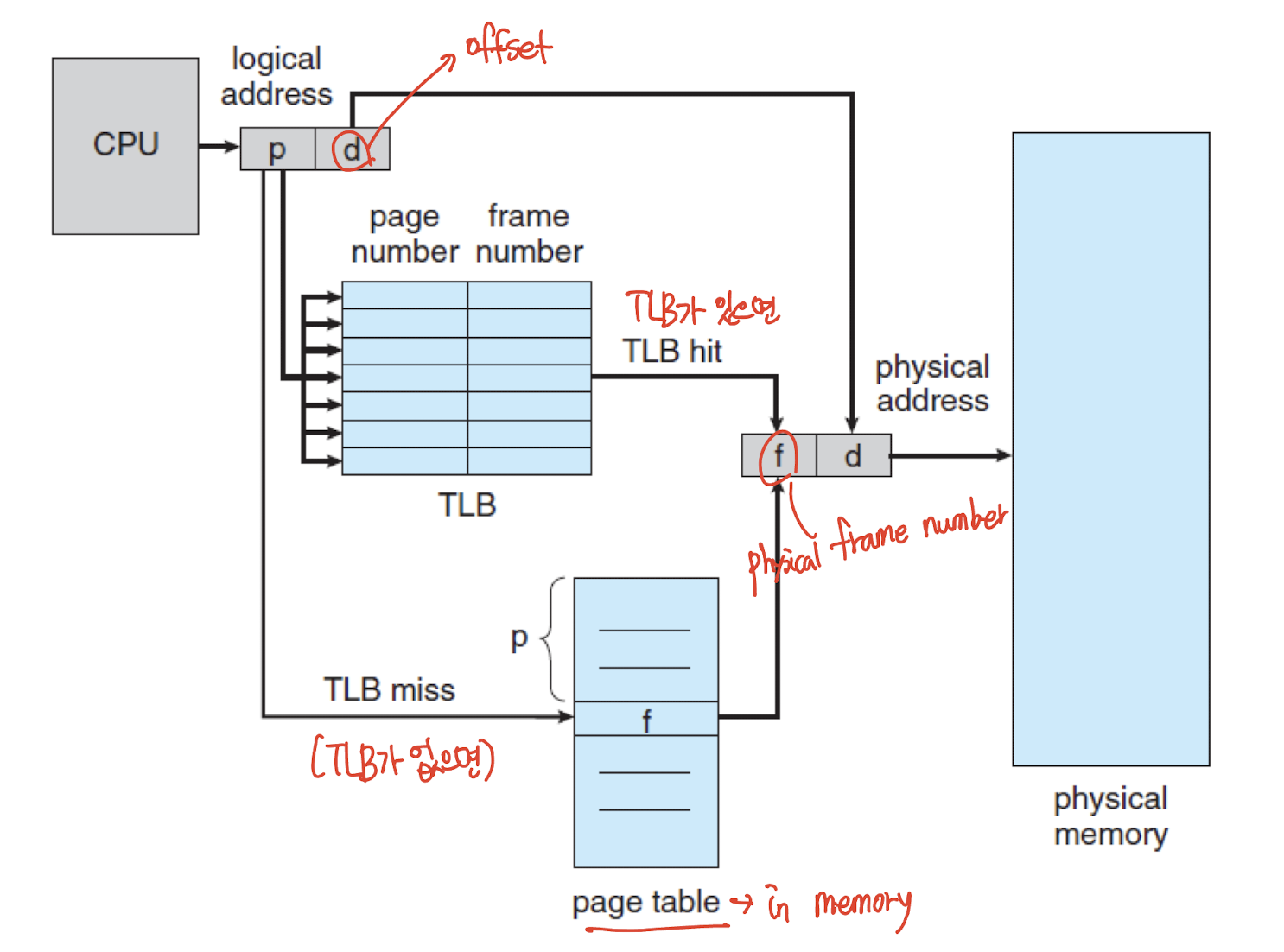
위의 그림은 TLB를 사용한 Paging Hardware 예시이다.
-
TLB hit(= TLB가 있으면) Page Table 거쳐갈 필요 없이 가상 주소를 실제 주소로 변환한다. -
TLB miss(= TLB가 없으면) Memory에 있는 Page Table에서 가상 주소에 해당하는 정보를 가져와서 실제 주소로 변환한다.
TLB entry (TLB 안에는 무엇이 있을까?)
-
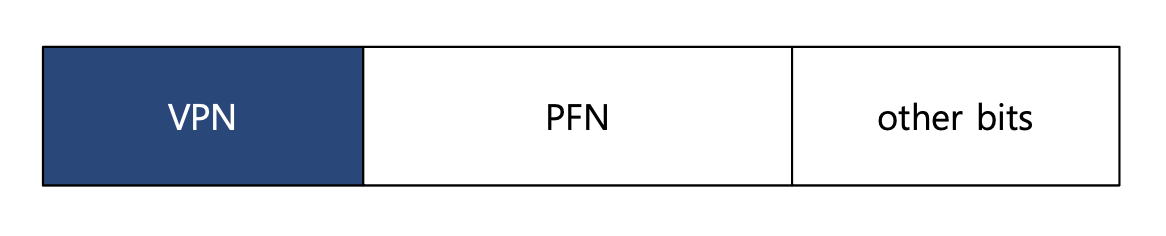
TLB는 Full Associative method에 의해 관리된다.
-
일반적인 TLB는 32, 64 또는 128개의 항목을 가질 수 있다.
-
하드웨어는 전체 TLB를 병렬로 검색하여 원하는 변환을 찾습니다
-
Other bits : valid bits , protection bits, address-space identifier, dirty bit
-
-
정리하자면, 자주 사용하는 TLB에는 VPN(virtual page number)과 PFN(Page Frame Number) 정보가 쌍으로 존재하며, 이를 사용해 주소 변환을 하도록 도와주는 Hardware Cache이다.
Appendix: Cache
-
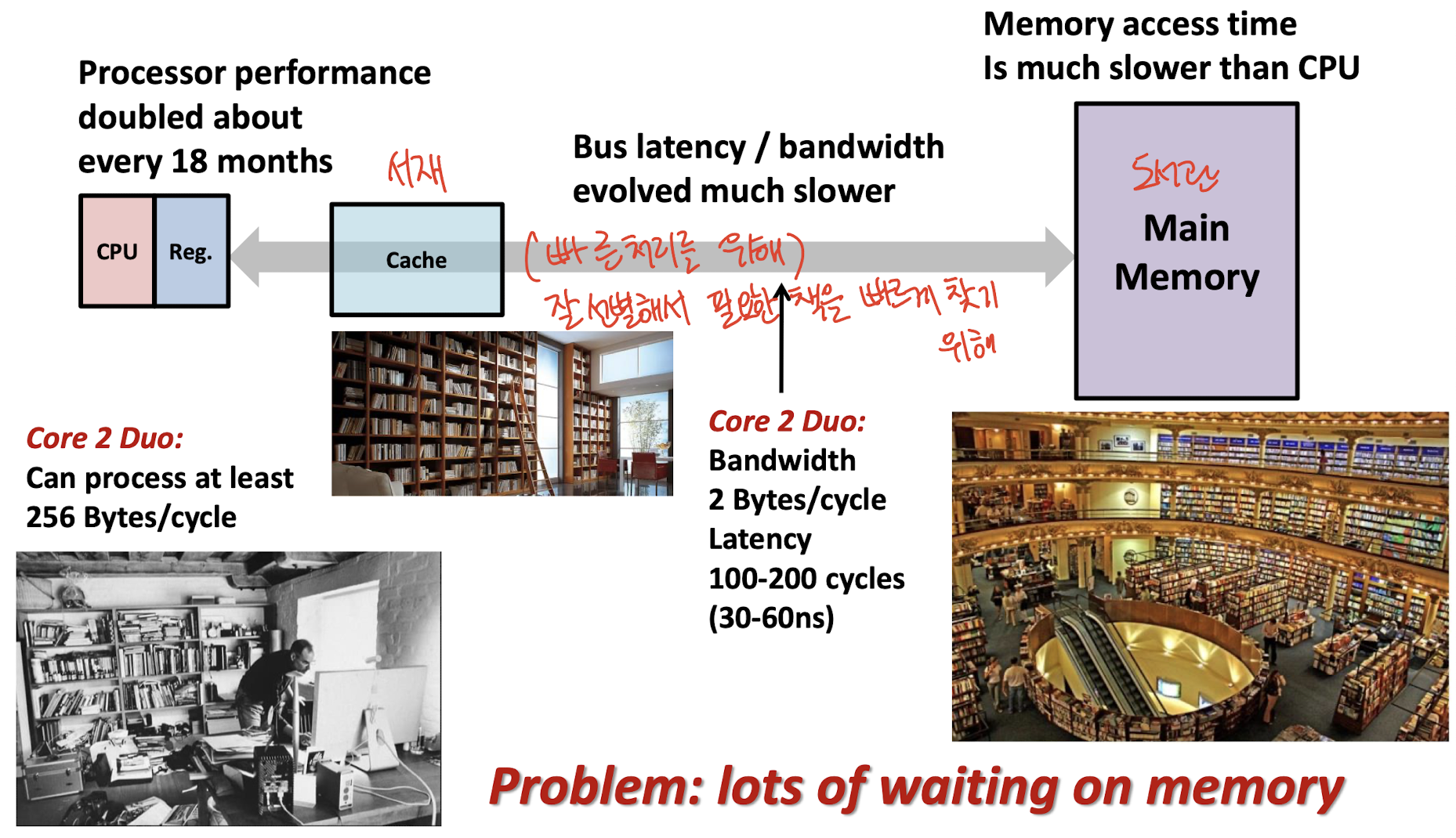
Cache는 임시로 쓰이는 버퍼(buffer) 메모리이다.
-
빈번하게 사용하는 데이터들을 하위 메모리보다 빠른 공간에 임시로 넣어두고, 필요할 때마다 바로 쓸 수 있도록 하기 위해 생겨난 기술이자, 구조이자 장치라고 할 수 있다.
-
메모리가 다른 I/O 장치보다는 빠르지만, Process의 속도보다는 많이 느리다. 그래서 전체적인 시스템 성능을 높이기 위해서 메모리에서 데이터를 읽어오는 속도를 빠르게 하기 위해
Cache(캐시)가 등장한 것이다.
-
예로 들자면,
팬시가 “Operating Systems Three Easy Pieces” 이라는 운영체제 책을 빌리려고 학교 도서관(Main Memory)에 갔다. -
하지만, 운영체제 책뿐만 아니라 다른 책들도 빌릴 때마다 도서관을 이용하게 되는데, 문제는 도서관까지 가고, 원하는 책을 찾는데 시간이 너무 오래 걸린다는 점이다.
-
이러한 점을 해결하기 위해 IT 학부에서는 컴퓨터학부생들의 시간 효율성을 위해 IT 융복합관(5호관) 지하 1층에 서재(Cache)를 만들었다.
-
서재(Cache)를 만든 이후부터
팬시는 컴퓨터학부와 관련된 책을 IT 융복합관 지하에 있는 서재(Cache)에 가서 빌림으로써 도서관(Main Memory)에서 빌리는 시간보다 더 효율적이고 빠르게 해결했다.
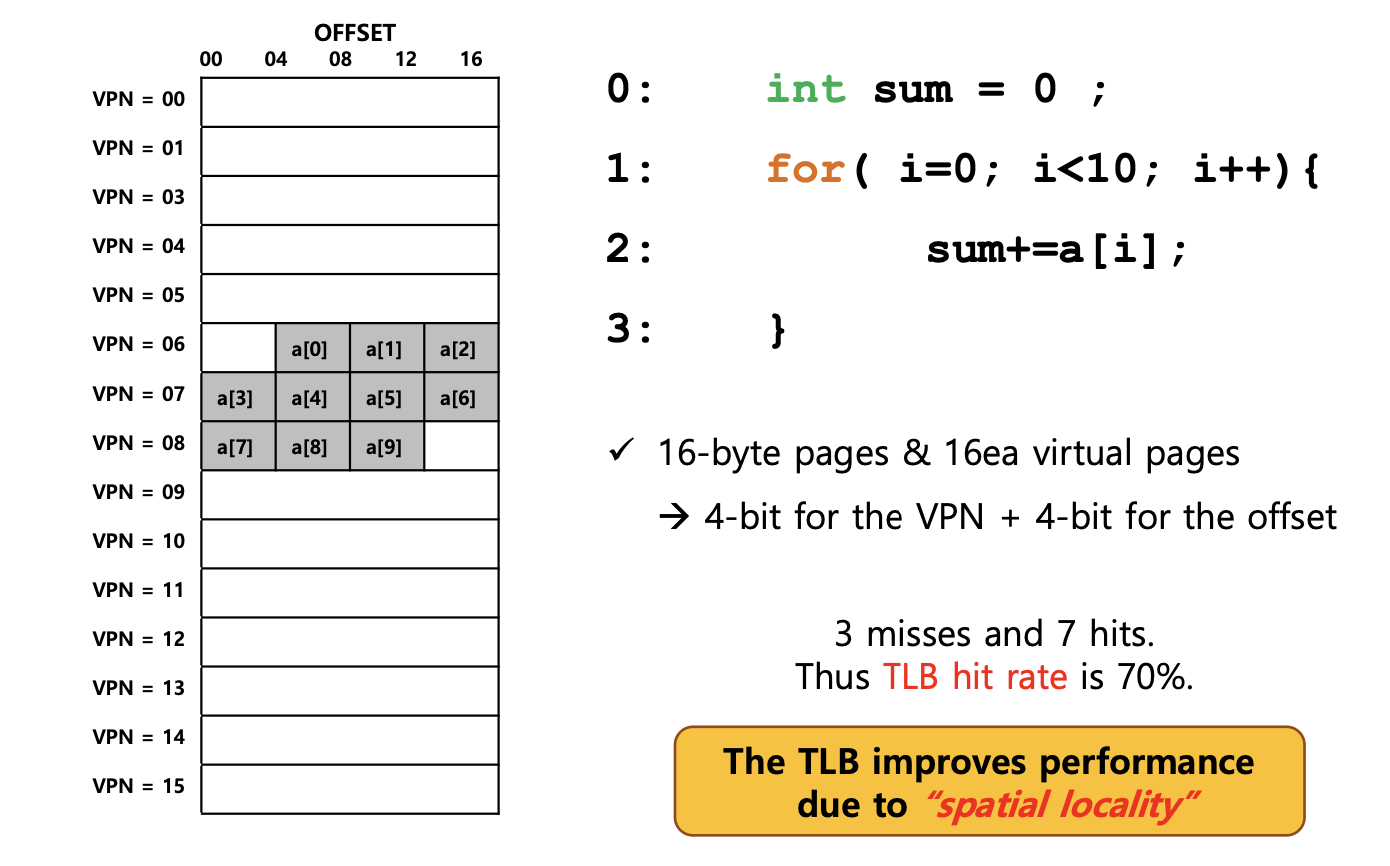
Example: Accessing An Array
- TLB가 메모리 성능을 어떻게 향상시키는 지 다음 예시를 가져와 봤다.
-
가정) Page의 크기는 16-byte이며 가상 주소 공간의 크기를 8-bit(2^8=196byte)라고 가정한다.
-
가상 주소 공간에 존재하는 Page 수는 16개(가상 주소 공간의 크기 / Page의 크기)가 된다.
-
int 자료형이 4byte이므로 for문에 적용하면 총 배열의 크기는 40byte이다. (배열이 가상 주소 공간 100에서 시작하면 Page Table이 왼쪽 그림과 같이 그려진다)
-
for문을 돌리고, [1] a[0]이 요청이 오면 VPN = 6(a[0] ~ a[2])이 전부 올라간다.
-
a[3]이 요청이 오면 VPN = 6에 없으므로
miss가 되고, VPN = 7(a[3] ~ a[6])에 올라간다. -
결론적으로 3개의 miss와 7개의 hit이 생겼고, 그러므로 TLB hit rate = 70% 이라는 결론이 나왔다.
-
3개의
miss는 a[0], a[3], a[7]이며, 7개의hit은 a[1], a[2], a[4], a[5], a[6], a[8], a[9]이다.-
a 배열에 요청이 올 때 해당하는 값이 VPN에 없으면 miss가 발생하고, 한 번 접근한 뒤에 다시 a 배열에 요청이 오면 이미 TLB에 변환 정보가 존재하기 때문에 hit으로 처리된다.
-
여기서는 page의 크기가 16byte이므로 hit rate가 70%라는 값이 나왔지만, 배열의 요소 개수가 이 보다 더 많이 증가한다면, 100%에 가깝게 될 것이다.
-
-
TLB에서 주소변환이 성공한 것을
TLB Hit이라고 한다. -
TLB가 없는 상황에서는 총 10번의 반복이 발생하고, 반복할 때 마다 page table에 접근하여 주소 변환을 해줘야 한다.
-
하지만, 위의 그림처럼 TLB가 있는 상황에서는 a 배열에 대한 10번의 접근 중 3번의 TLB miss만 발생했기 때문에, 3번만 page table에 접근하여 주소 변환을 해주면 된다.
-
TLB는
Spatial Locality(공간 지역성)로 인해, 성능을 향상시킨다.
Locality
-
Temporal Locality(시간 지역성)란 최근에 접근한 데이터에 접근할 가능성이 높다는 의미이다. 주로 반복문에서 확인할 수 있다.하드웨어에서는 cache(캐시)라는 작고 빠른 메모리에 정보를 저장하여 지역성을 활용하다.
캐시의 크기가 작기 때문에 빠르게 메모리에 정보를 저장하는 것이지, 만약에 캐시의 크기가 커진다면 빠르게 될 수 없다.
-
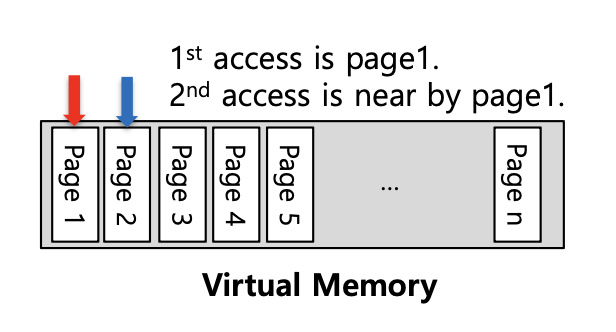
Spatial Locality(공간 지역성)란 어떤 요소에 접근한 상황이라면 그 주변의 요소들에 접근할 가능성이 높다는 의미이다.배열과 같은 데이터에 접근할 때 순차적으로 접근(연속적인 접근)하게 되므로 apple 이라는 요소에 접근한 상황이라면 다음에 접근할 때에는 apple 주변의 요소들에 접근할 가능성이 높다는 것이다.
Effective Access Time(EAT)
-
실제 메모리에 접근하는 시간(EAT)를 구하는 방법에 대해 알아보자.
-
다음 예시를 가정해보자.
-
TLB hit ratio $\alpha$ = 80%
-
TLB search : 20 ns (TLB에서 해당 정보를 찾는 시간)
-
Memory access : 100 ns (메모리에 한번 접근하여 데이터를 가져오는 시간)
-
-
EAT= 0.80 x (20 + 100) + 0.20 x (20 + 100 + 100) = 140 ns-
(20 + 100): TLB Hit이 된 경우 TLB에 가서 메모리가 접근한 시간을 의미한다.(TLB가 있는 경우) -
(20 + 100 + 100): TLB search + Page table에 접근한 시간 + Memory access 합한 값을 의미한다. (TLB가 없는 경우)
-
-
ns 로 표기하는 것이 중요하고 잊지 말자.
TLB Issue: Context Switching
- TLB를 사용할 때 Context Switching이 발생한다면 어떻게 되는지 다음 예시를 통해 알아보자.
-
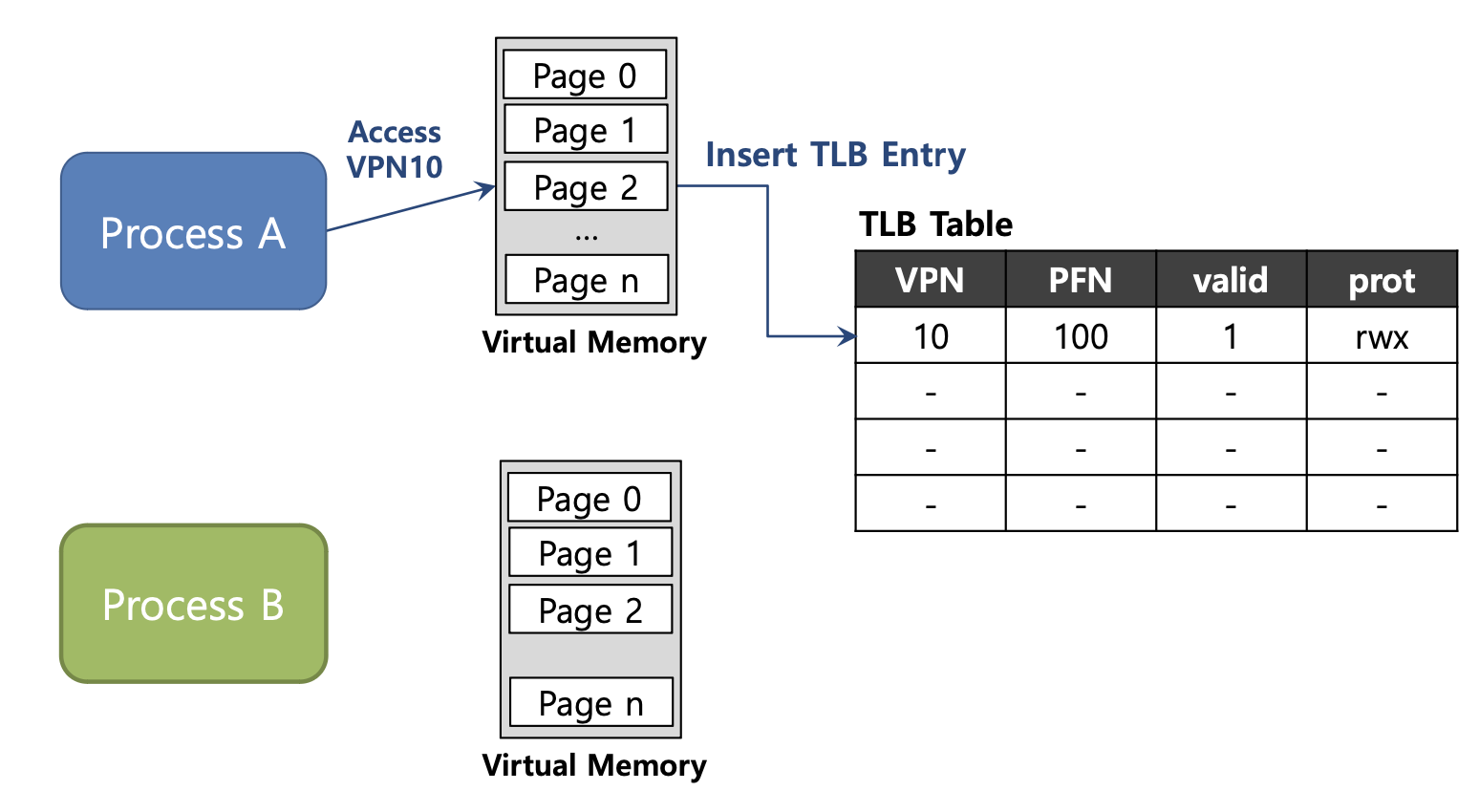
Process A의 VPN 10에 대한 주소 변환 정보가 TLB에 저장되어 있다. -
참고로 Process마다 각자의 Virtual Memory를 가지고 있다.
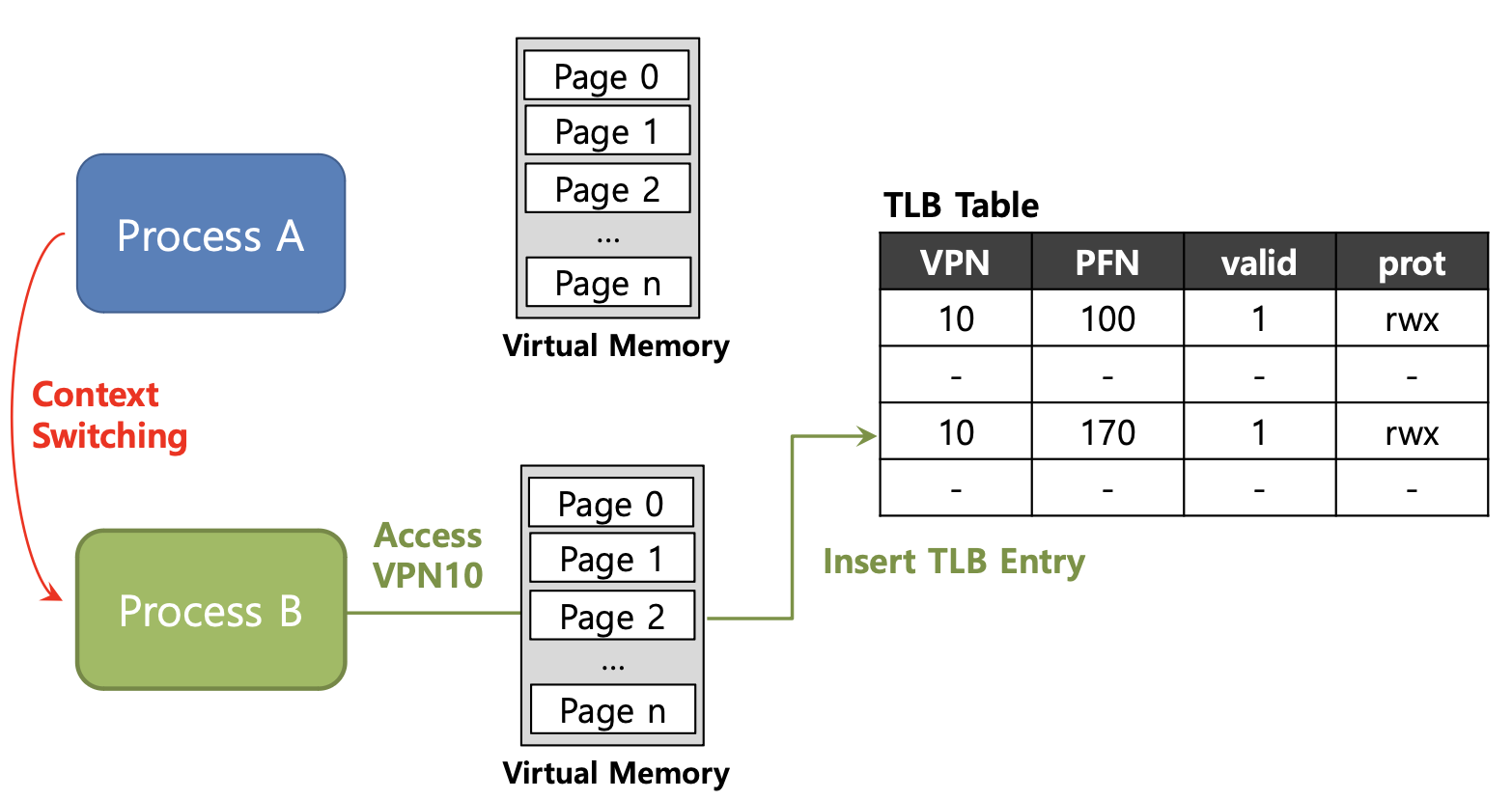
-
이때 Context Switching이 발생하여
Process B로 넘어가게 되는데, Process B 역시 VPN 10에 대한 주소 변환 정보가 TLB에 저장되어 있다. -
이런 경우 Process A, B 둘다 VPN은 10으로 동일하지만 PFN은 서로 다른 것을 확인할 수 있다.
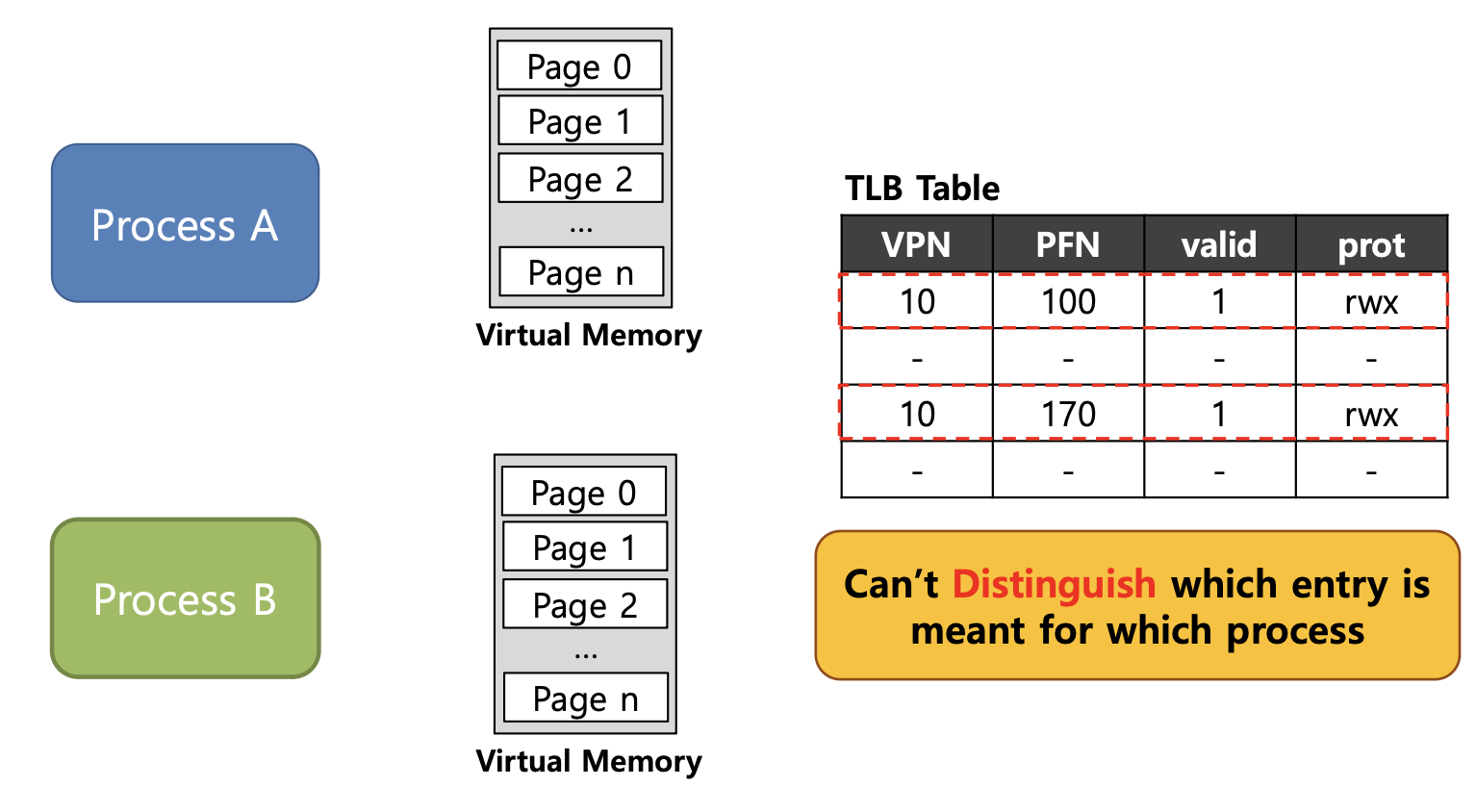
-
하지만 위와 같이 TLB에 정보를 저장하게 되면 어떤 정보가 어떤 Process의 정보인지 알 수가 없다.
-
Process에서 서로의 주소 공간이 아닌 곳에 접근을 하게 될 경우 문제가 발생하므로 이를 해결할 방법이 필요하다.
To Solve Problem
- 위의 문제를 해결하기 위해 하드웨어의 도움을 받아 TLB에서
ASID(address space identifier)라는 정보를 추가하여 문제를 해결하는 것이다.
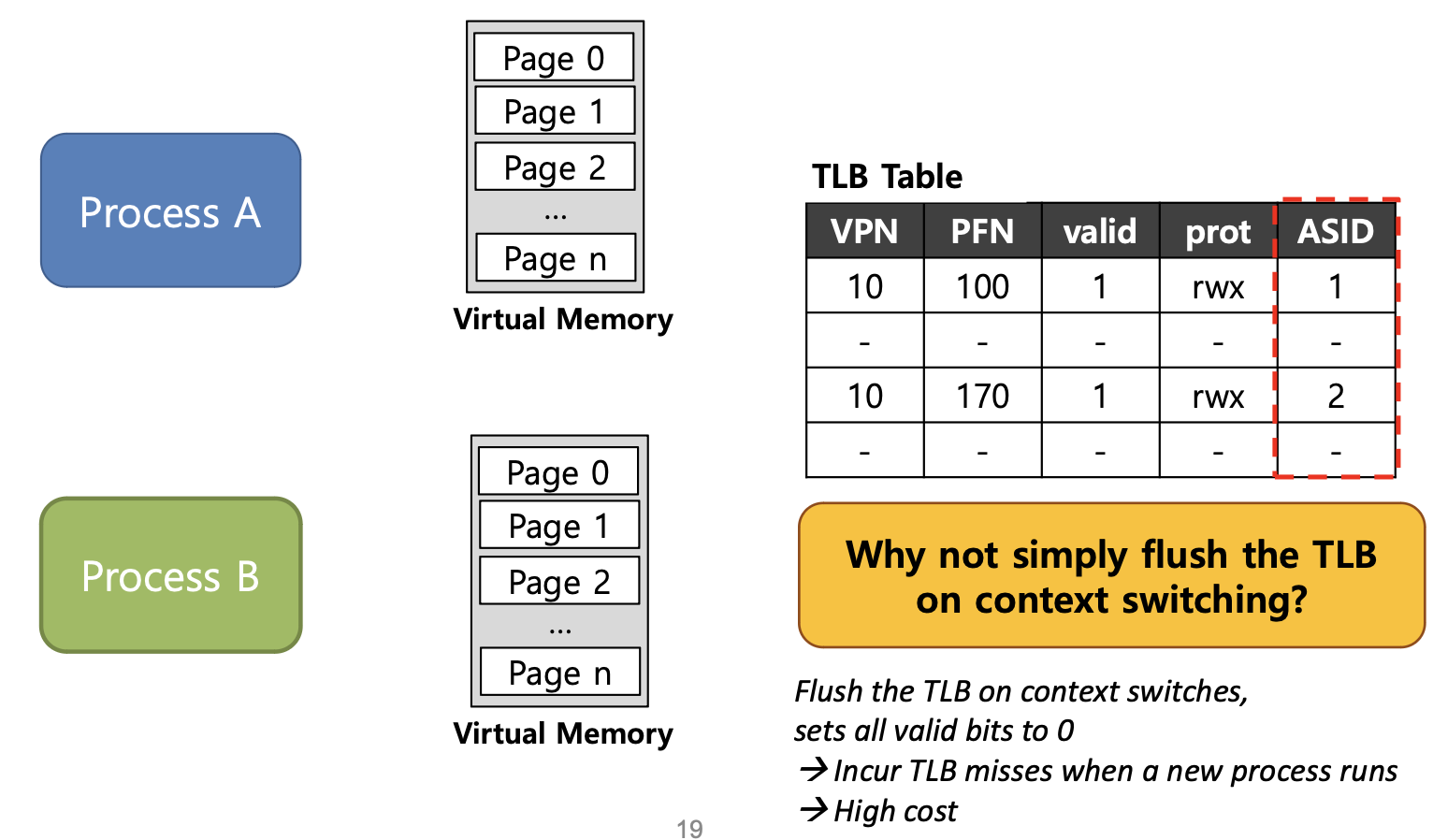
-
어떤 프로세스의 정보인지 구별하기 위해 TLB에서
ASID를 제공한다. -
이를 통해 프로세스마다 다른 ASID 정보를 저장하여 주소 변환을 성공적으로 수행할 수 있도록 한다.
Another Case
- 위에서는 VPN이 동일한 예시를 봤고, 이번에는 PFN이 동일한 경우에 대해서 알아보자.
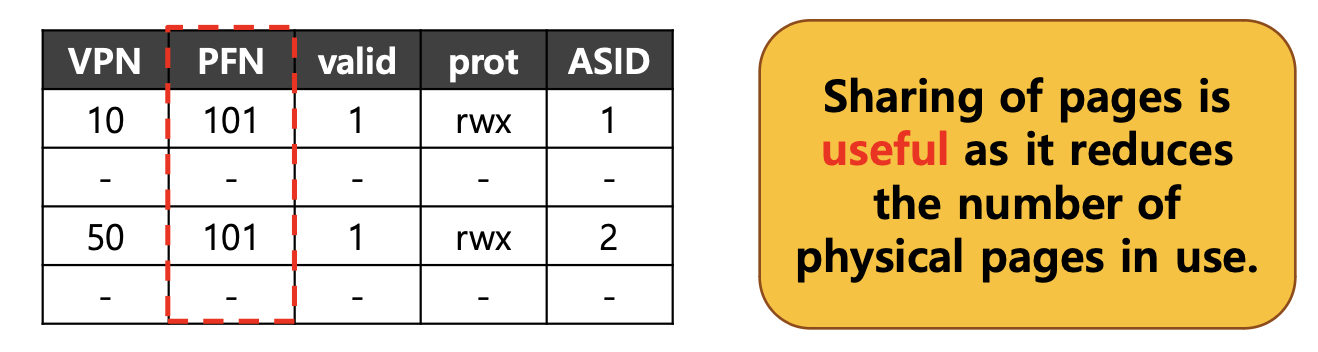
-
위의 예시를 가정해보면 Process 1은 Process 2와 같은 PFN 값이 101로 동일하다.
- Process1의 VPN은 10이고, Process2의 VPN은 50이다.
-
두 개의 Process가 PFN 값이 같으므로 Page를 공유할 수 있다.
-
그러면 메모리의 사용을 줄일 수 있으므로 메모리의 공간을 이전보다 더 확보할 수 있게 된다.
-
하지만, 어떤 프로세스인지 구별을 확인하기 위해
ASID값도 같이 저장한다.
TLB Replacement Policy
-
TLB에 저장 가능한 공간이 꽉 찼을 경우 새로운 프로세스가 실행된다면, 어떤 프로세스를 빼고 새로운 것을 넣어야 하는지에 대해 알아보자.
-
우선, 목표는 TLB miss rate를 최소화 하는 것이다. (TLB hit rate를 향상시키는 것과 같은 말이다)
-
전형적으로 2가지 간단한 접근 방법이 있다. (LRU, Random policy)
-
LRU(Least-recently-used) : 최근에 사용하지 않는(예전에 사용하고 지금은 사용하지 않는) Process를 내보내는 방법이다.- LRU는 위에서 설명한
Temporal Locality의 장점을 이용한다.
- LRU는 위에서 설명한
-
Random policy: 이름 그대로 랜덤하게 제거하는 방법이다.
Example: LRU
- LRU 접근 방법을 이용하여 TLB miss rate를 최소화하는 과정을 알아보자.
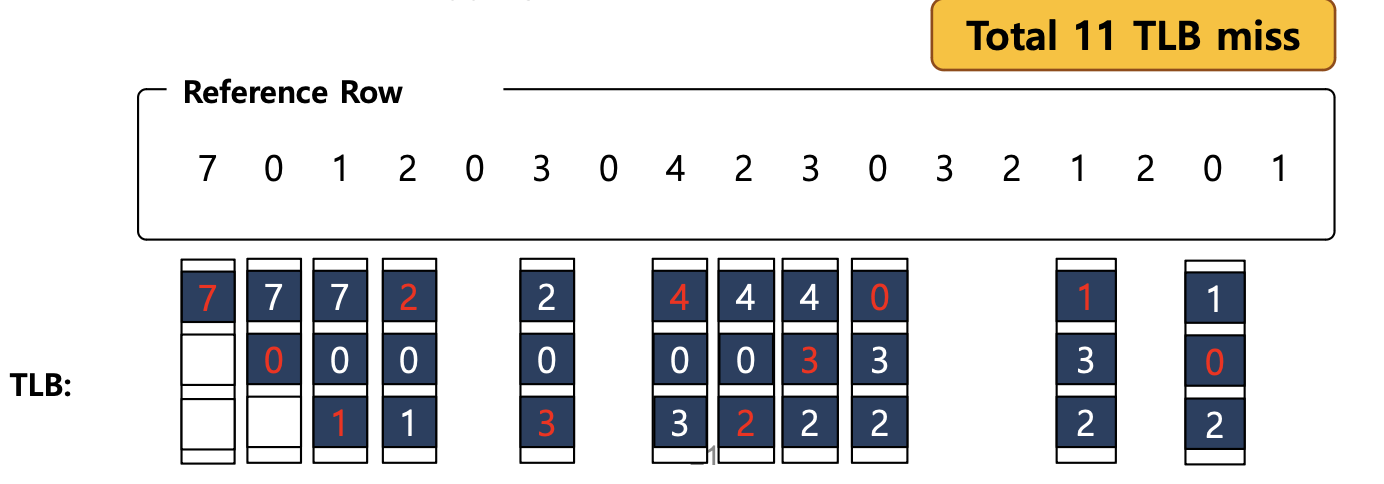
-
Reference Row : 주어진 새로운 숫자(프로세스)가 순차적으로 실행한다는 것을 의미한다.
-
4번째에 숫자 ‘2’라는 새로운 프로세스가 발생했을 때, 가장 오래 사용하지 않았던 숫자 ‘7’를 빼고 ‘2’를 넣는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
-
이처럼 최근에 가장 사용하지 않았던 프로세스를 내보내고, 그 자리에 새로운 프로세스가 들어온다.
-
18번 중에 11번의 miss가 발생했기 때문에, 결론적으로
TLB miss ratio= 11/18 = 0.61 = 61% 값을 확인할 수 있다.
예상 질문
-
TLB가 나오게 된 배경은 무엇이고, TLB 개념에 대해 설명해주세요.
-
TLB가 메모리 성능을 어떻게 향상시키는지
TLB hit rate와Spatial Locality개념과 연관지어 설명해주세요. -
TLB를 사용할 때
Context Switching이 발생한다면 어떻게 해결하는 지 설명해주세요. (2가지 해결방안) -
TLB에 저장 가능한 공간이 꽉 찼을 경우 새로운 프로세스가 실행된다면, 어떤 프로세스를 빼고 새로운 것을 넣어야 하는지 과정에 대해 설명해주세요. (TLB Replacement policy)
-
GitHub Blog에 댓글 기능 추가(utterances)
해당 글은 Jekyll 기반 GitHub Blog 중심으로 작성한 내용입니다.
Prologue
-
블로그를 운영한 지 이제 24일이 지났을 쯤에, 내 GitHub Blog에 수정할 부분이 뭐가 있는지 자세히 확인해봤다.
-
기존에 댓글 기능을 Disqus을 사용했는데, 몇 가지 단점들이 보이기 시작했다.
-
무료 라이센스로 사용하는 경우 광고가 붙어서 다른 사용자가 보기 불편하다는 생각이 들었다.
-
Disqus 자체가 무겁다는 얘기가 주변 개발자들로부터 전해들었다.
-
댓글을 입력하려면 Disqus 자체 회원가입을 해야 하거나, 깃허브 계정이 아닌 페이스북, 트위터, 구글 계정으로 로그인 해야하는 불편함이 있었다.
-
내 GitHub Blog 에만 존재할 수도 있는데, 스크롤을 맨마지막까지 내리면 해당 댓글 창이 사라지는 것을 확인했다.
- 따라서 나는 ‘Disqus 보다 더 좋은 댓글 기능이 뭐가 있을까?’라는 생각으로 구글링을 한 결과,
utterances라는 것을 발견하게 되었다.
Utterances

-
GitHub issues를 기반으로 하는 가벼운 댓글 위젯이다.
-
블로그 댓글, 위키(wiki) 페이지 등에 해당 위젯을 사용할 수 있다.
(해당 앱에 대한 자세한 설명은 여기에 가보시면 확인할 수 있습니다)
- 내가 위에서 적어두었던 Disqus 의 단점 4가지를 모두 보완할 수 있기 때문에 댓글 기능을 해당 위젯으로 변경하기로 했다.
Install(설치)
- Github -> GitHub App에서 utterances 페이지로 이동한다.
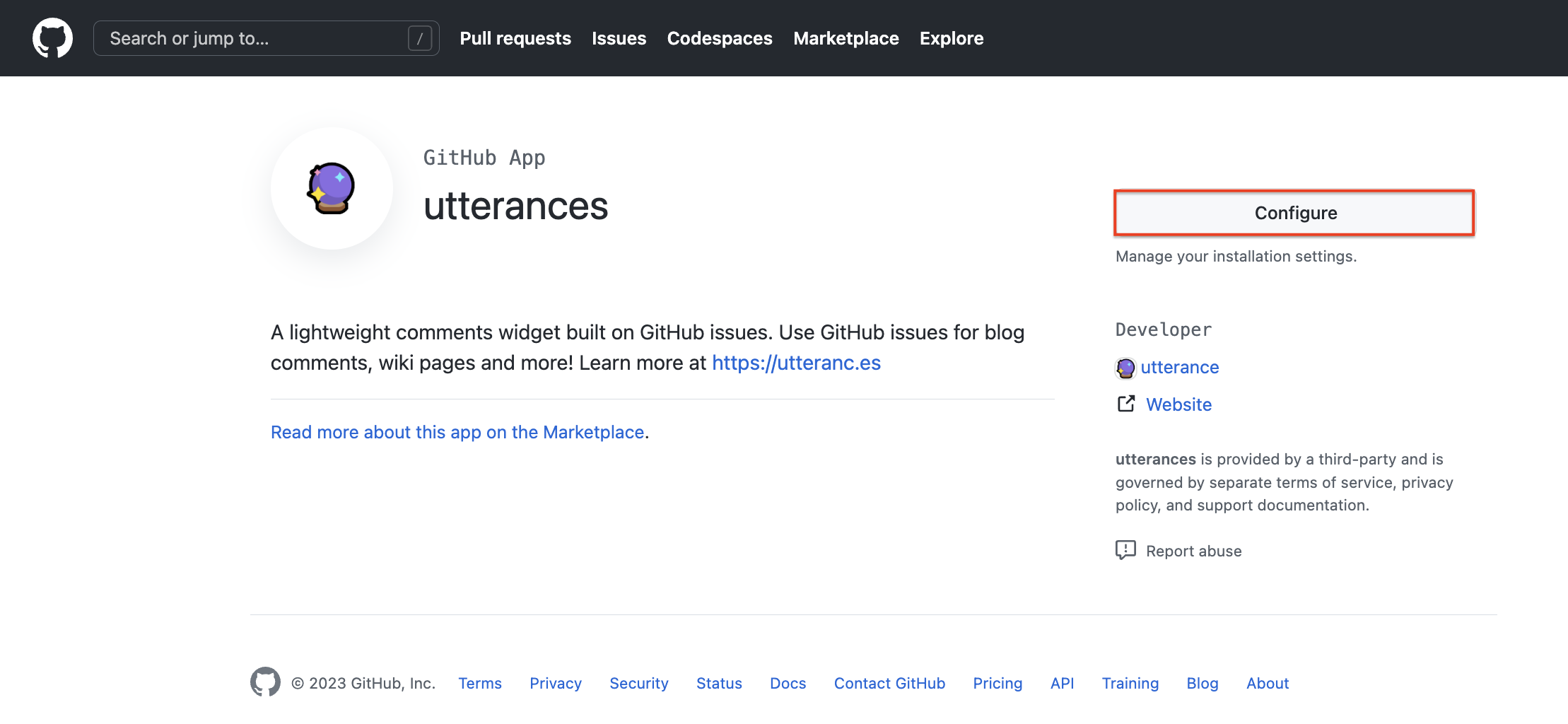
-
이미 설치된 경우
Configure버튼으로 보이는데, 설치되지 않았다면Install버튼이 보일 것이다. -
해당
Install버튼을 클릭하면 repository(저장소)를 선택하는 화면이 나오는데, GitHub Blog repository(저장소)를 선택하면 된다. -
그리고 아래의
Install버튼을 클릭하여 설치를 완료한다.
Setting(설정)
- 설치가 완료되면 설정 페이지로 이동하는데, 해당 페이지에서 저장소에 대한 설정을 한다.
repo
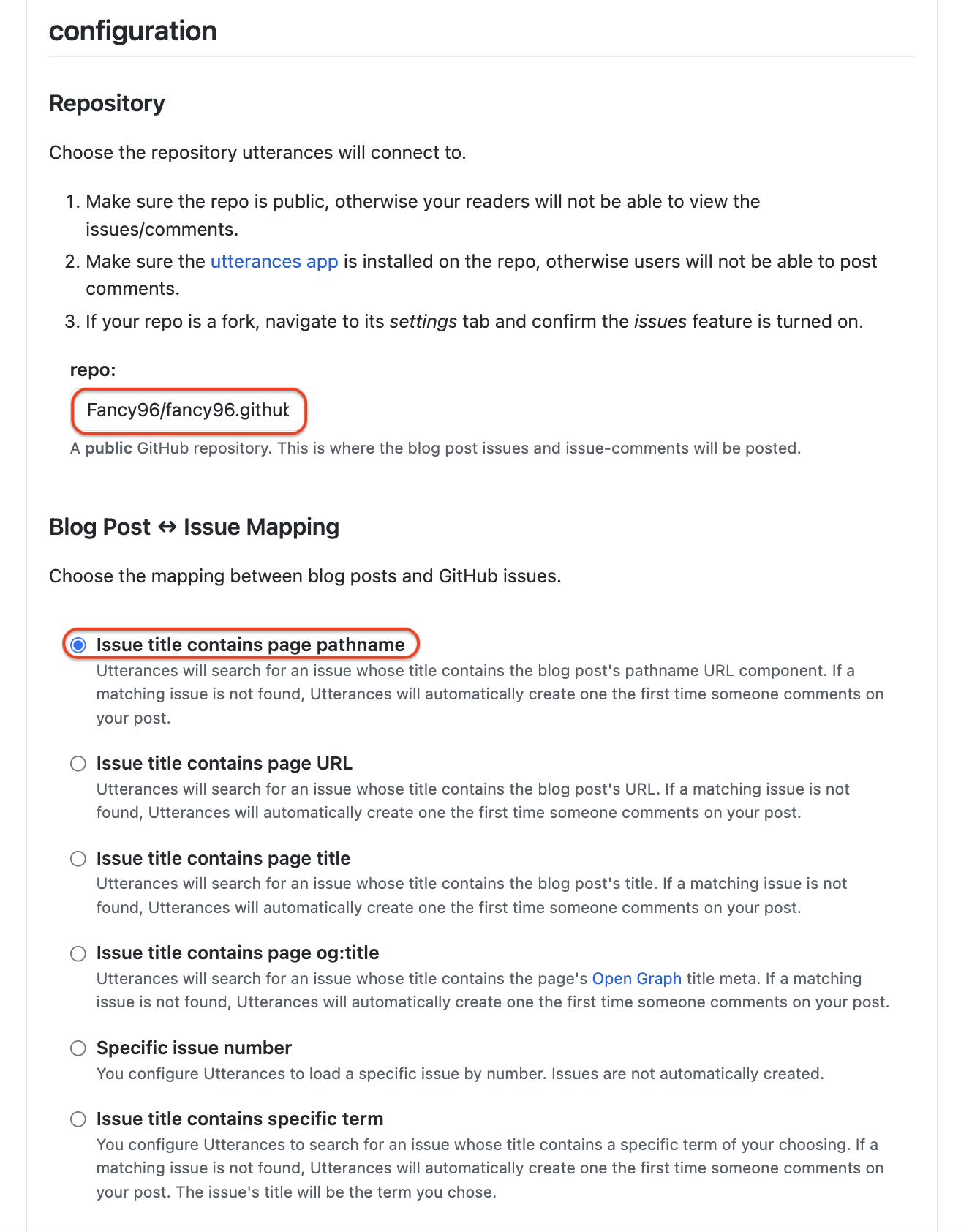
-
repo:아래 입력 칸에는 본인의 “Github-ID/GitBlog-repository name”을 입력하면 된다. -
예) devfancy/devfancy.github.io
Blog Post ↔️ Issue Mapping
-
Blog Post ↔️ Issue Mapping밑에는 블로그 Posts와 깃허브 Issues를 연동하기 위해 선택하는 항목들이다. -
누군가가 나의 Post에 댓글을 입력하면 해당 Post의 제목과 경로(URL)를 Issues에 표기하기 위해 첫 번째 부분을 선택했다.
Issue Label
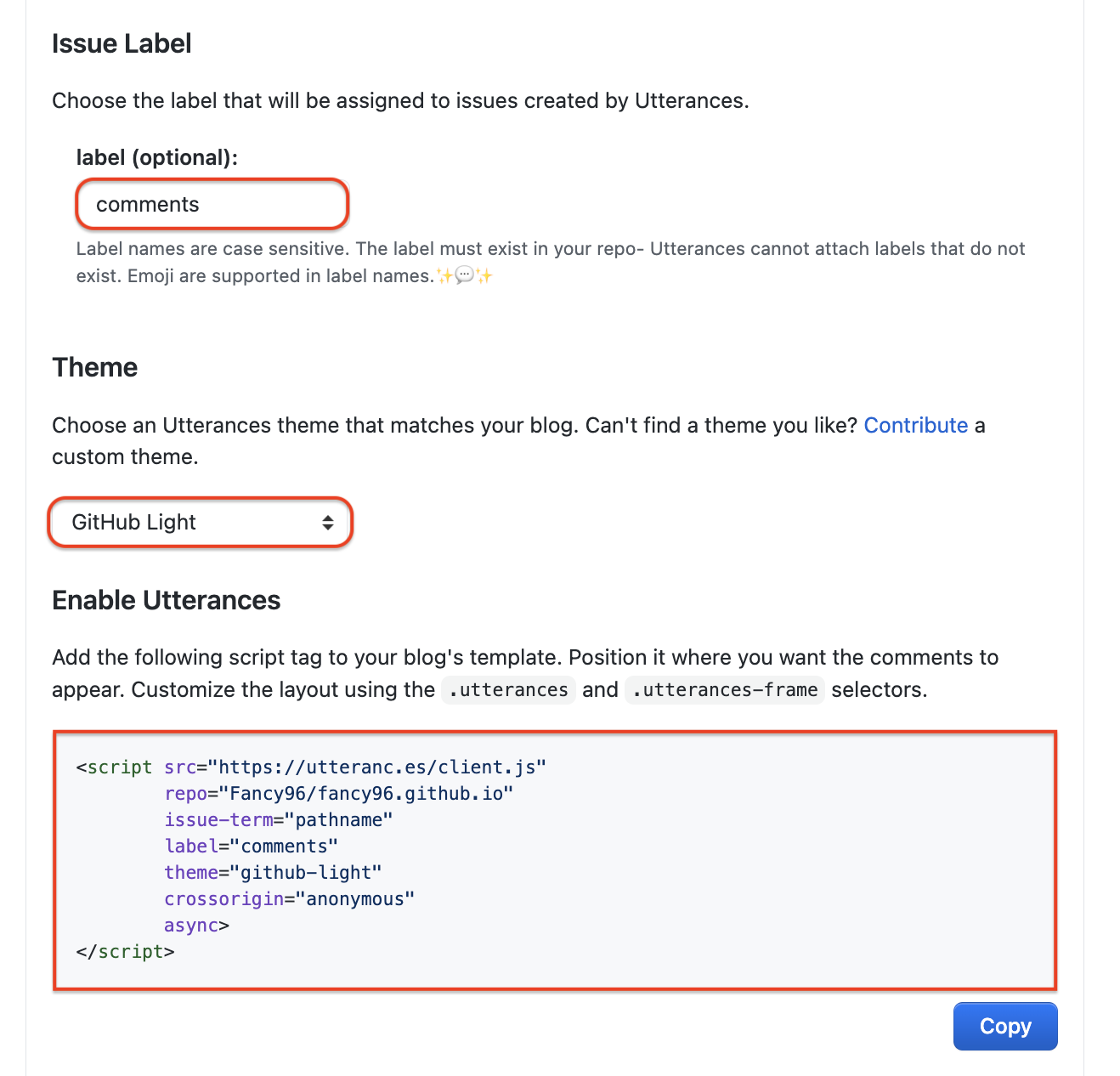
Issue Label에는 밑에 나와있는 설명대로 Issue 부분에 Label 이름을 정하는 건데, 선택 사항이므로 안해도 상관 없다.
Theme
-
Theme에는 댓글에 대한 배경 색상을 정하는 부분이다. 어두운 색상 / 밝은 색상 / 그외 다양한 색상 이 있기 때문에, 본인이 원하는 색상을 선택하면 된다. -
나는 밝은 색상을 선택했다.
Enable Utterances
-
Enable Utterances의 의미는 나의 블로그 탬플릿에 해당utterances를 적용하는 부분이다. -
구글링을 한 결과, 대부분 본인의 GitHub Blog 폴더의
_layout/post.html혹은_includes/comments.html에 해당 스크립트를 추가하였다. -
나는 내 GitHub Blog 구조상 더 적절한
_includes/comments.html에 추가하였다.(본인의 GitHub Blog 구조에 맞게 추가하는 것이 중요하다)
-
기존에 나는 disqus 를 적용하였기 때문에 해당 부분을 주석처리하고 그 밑에
utterances부분을 추가하였다.
<!-- --> <!-- utterances comment --> <script src="https://utteranc.es/client.js" repo="devfancy/devfancy.github.io" issue-term="pathname" label="comments" theme="github-light" crossorigin="anonymous" async> </script>GitHub repository 반영
-
이제 GitHub repository에
utterances을 반영(적용) 하면 끝이다. -
Git Desktop이 설치가 이미 되었다면, 커밋 내용을 입력하고 push 하면 된다.
-
Git Desktop이 설치 되지 않았다면,
IntelliJ - 본인의 GitHub Blog 폴더 열기 - 터미널 열기하고 다음 명령어를 입력하면 된다. (Git 명령어 직접 입력)
-
-
[Programmers] 12941. 최솟값 만들기
성능 요약
메모리: 메모리: 52 MB, 시간: 1.57 ms - Answer Code1
구분
코딩테스트 연습 > 연습문제
Answer Code1(23.02.04)
import java.util.Arrays; class Solution { public int solution(int []A, int []B) { int answer = 0; // 기본 정렬 조건 : 오름차순 Arrays.sort(A); Arrays.sort(B); for(int i = 0; i < A.length; i++) { answer += A[i] * B[B.length - 1 - i]; } return answer; } }문제 풀이
-
양쪽에서 각각 한개의 숫자를 뽑아 곱한 값을 누적하였을 때 한 쪽의 최댓값과 다른 쪽의 최솟값을 곱하는 경우 누적값을 최소로 구할 수 있다
-
정렬을 하기 위해서는
import java.util.Arrays;선언해야 한다. -
Arrays.sort(): 기본 정렬 조건이 오름차순 이다.
-
-
따라서 A와 B 배열을 정렬하여 한 쪽의 최댓값과 다른 쪽의 최솟값을 곱해 누적하면 최소값을 구할 수 있다
Review
-
최솟값을 구하는 조건을 바로 떠올리지 않아서 시간이 좀 걸렸지만, 조건만 알 수 있으면 바로 풀 수 있는 문제였다.
-
최솟값을 구하는 조건에 대해서 잘 기억해두자.
-
-
[Programmers] 12909. 올바른 괄호
성능 요약
-
메모리: 52.8 MB, 시간: 19.78 ms - Answer Code1
-
메모리: 53.1 MB, 시간: 7.90 ms - Answer Code2
구분
코딩테스트 연습 > 스택/큐
Answer Code1(23.02.04)
import java.util.*; class Solution { boolean solution(String s) { // [1] 정답을 저장할 변수로 answer와 stack을 선언 boolean answer = true; Stack <Character> stack = new Stack<>(); // 반복문을 이용하여 문자열을 앞에서부터 비교 for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) { char c = s.charAt(i); // [2] 문자를 비교할 때 `(` 일 경우 스택에 push if(c == '(') { stack.push(c); } // [3] `)`일 경우 if( c == ')') { // stack의 크기가 0이면 false 반환 if(stack.size() == 0) { answer = false; } // stack의 크기가 0이 아니라면 `(`가 있다는 의미이므로 스택에 pop else { stack.pop(); } } } // [4] 문자열을 끝까지 확인한 이후에 스택의 크기가 0이면 true 반환 if(stack.size() != 0) { answer = false; } return answer; } }Answer Code1 - 문제 풀이
-
스택을 이용하여 괄호가 짝을 이룬다면 스택을 제거한다.
-
문자열을 끝까지 검사했을 때 스택의 크기가 0이면 올바른 괄호이므로 true를 반환하고, 그렇지 않으면 false를 반환한다.
-
[1] 정답을 저장할 변수로 answer와 stack을 선언하고, 반복문을 이용하여 문자열을 앞에서부터 비교한다.
-
[2] 문자를 비교할 때
(일 경우 스택에 push 한다. -
[3]
)일 경우 이때, stack의 크기가 0이 아니라면 스택에 pop 한다.- stack의 크기가 0이 아니라면
(가 있다는 의미이고, 스택의 크기가 0이라면(가 없으므로 짝을 이룰 수 없다.
- stack의 크기가 0이 아니라면
-
[4] 문자열을 끝까지 확인한 이후에 스택의 크기가 0이면 true, 아니면 false를 return 한다.
Answer Code2(23.02.04)
class Solution { boolean solution(String s) { boolean answer = false; int count = 0; for(int i = 0; i<s.length();i++){ if(s.charAt(i) == '('){ count++; } if(s.charAt(i) == ')'){ count--; } if(count < 0){ break; } } if(count == 0){ answer = true; } return answer; } }Review
-
(2번째 풀이) 다른 사람의 풀이를 가져와봤는데, 스택을 사용안하면서 count 변수를 사용하여 깔끔하게 풀이했다.
-
그 결과 1번째 풀이보다 시간적인 측면에서 3배 가까이 시간을 절약하는 것을 볼 수 있었다.
-
스택을 사용한다고 해서 좋은 정답은 아니라는 것을 알 수 있었다.
-
-
[Programmers] 12951. JadenCase 문자열 만들기
성능 요약
메모리: 86.2 MB, 시간: 4.88 ms - Answer Code1
구분
코딩테스트 연습 > 연습문제
Answer Code1(23.02.03)
import java.util.*; class Solution { public String solution(String str) { String answer = ""; // 1. 공백을 기준으로 문자열을 잘라서 String 배열에 저장 String [] strArr = str.split(" "); // 2. 잘린 String 배열을 순서대로 처리 for(int i = 0; i < strArr.length; i++) { String now = strArr[i]; // 문자열의 길이가 0이면 " " 추가 if(strArr[i].length() == 0) { answer += " "; } // 문자열의 길이가 있다면 else { // 첫번째 문자는 소문자 -> 대문자로 변환 answer += now.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase(); // 나머지 문자는 대문자 -> 소문자로 변환 answer += now.substring(1, now.length()).toLowerCase(); // 단어 사이에 공백을 위해 마지막에 `" "`을 추가 answer += " "; } } // 3. 입력 받은 문자열의 맨 마지막이 " "이라면(기존에 있었던 공백이면), 바로 answer 반환 if(str.substring(str.length()-1, str.length()).equals(" ")) { return answer; } // 4. 입력 받은 문자열의 맨 마지막이 `" "`이 아니라면 해당 부분을 제거하고 반환 return answer.substring(0, answer.length()-1); } }Answer Code1 - 문제풀이
-
기존 문자열 이름인 str 을
split(" ")을 사용하여 공백을 기준으로 잘라서 String 배열에 저장한다. -
잘린 String 배열을 순서대로 처리한다.
-
첫 번째 문자와 나머지 문자를 나눈다 -> substring()
-
첫 번째만 대문자로, 나머지는 소문자로 변환한다.
-
toUpperCase() : 소문자 -> 대문자
-
toLowerCase() : 대문자 -> 소문자
-
-
단어 사이에 공백을 위해 마지막에
" "을 추가한다.
-
-
입력 받은 문자열의 맨 마지막이
" "이라면(기존에 있었던 공백이면), 바로 answer을 반환한다.(마지막 공백을 지우지 않는다) -
입력 받은 문자열의 맨 마지막이
" "이 아니라면 해당 부분을 제거하고 반환한다.
Review
-
첫 번째 부분과 나머지 부분을 구분하는 경우에는
substring()을 사용하자. -
소문자와 대문자간 변환할 때 쓰이는
toUpperCase(),toLowerCase()에 대해 다시 공부하게 되었고, -
(중요) 문제풀이 - 3번째 조건 부분이 없으면 테스트케이스 부분이 실패로 되버렸다.
- 문제에 대한 설명 부분을 놓치지 말고, 완벽히 이해해야 한다는 것을 일깨워줬다.
-
- DevHistory 4
- Essay 1
- Java 10
- Spring 15
- SpringBoot 17
- JPA 13
- MySQL 3
- Flyway 1
- Kafka 8
- Technology 22
- GoodCode 7
- Side_Project 20
- Retrospective 4
- AlgorithmSkill 3
- LeetCode 2
- Algorithm 70
- SQL 9
- OS 14
- Database 8
- Network 7
- HTTP 7
- DataStructure 5
- Linux 4
- Woowacourse 4
- Git 9
- AssertJ 1
- IntelliJ 5
- Probability-Statistics 5
- Electronic-Finance 13
- Business-Statistics 13
- Competition 1
- Book 6
- Workout 7
- E.T.C 8