지금의 기록이 미래의 자산이 된다.
Today's records become tomorrow's assets.-
[BE] 2주차 미션 회고 (숫자 야구 게임)

- 이 글은 프리코스 과정 이후에 한번 더 복습한 과정을 담긴 내용이며, 기존에 제출했던 코드와 다를 수 있습니다.
-
[Git] 다른 사람 혹은 나의 repository에 있는 branch 복사하는 방법
Motivation
-
우아한테크코스 프리코스 미션들을 복습하고 있었다.
-
그러던 와중에, 해당 미션들을 저장하는 branch를 실수로
main에 저장하고 있었다. -
그래서 이전에 만든 repository 기존 branch을 새로운 repository(저장소)를 만들어서 새 branch에 가져오기(복사하기)로 했다.
-
즉, old repository의 branch -> new repository의 branch로 복사하는 것이다.
-
(기존 branch
main-> 새 branchfancy-log2으로 복사하기)
Assumption(가정)
-
기존 repository명을
old-java-bridge-review이고, branch명은main이다. -
새로운 repository명을
new-java-bridge-review이고, 새 branch명은fancy-log2이다. -
나는 내 기존 repository에 있는 branch를 가져오는 걸로 했다. (상대방 repository에서 가져오는 방식도 같다)
-
나는 IntelliJ에서 제공하는 terminal에서 작업했다.
- repository명 : new-java-bridge-review
-
기존 branch를 복사하기 위해서는 새 branch(fancy-log2)에서 작업해야 한다.
-
따라서, 새 branch인
fancy-log2를 먼저 추가해준다.
local(로컬) branch 추가
-
상대방(혹은 나)의 repository에 있는 기존 branch를 저장하는 새 branch를 추가한다.
-
나는
new-java-bridge-reviewrepository에서 새 branch명fancy-log2를 만든다.
git checkout -b [새 브랜치명]
-
위의 코드를 해석하면,
-
새로운 branch를 만들고 나서 동시에 새로운 branch에 이동이 된다는 의미다.
branch 복사하기
1. 상대방(혹은 나의) git repository 주소 복사하기
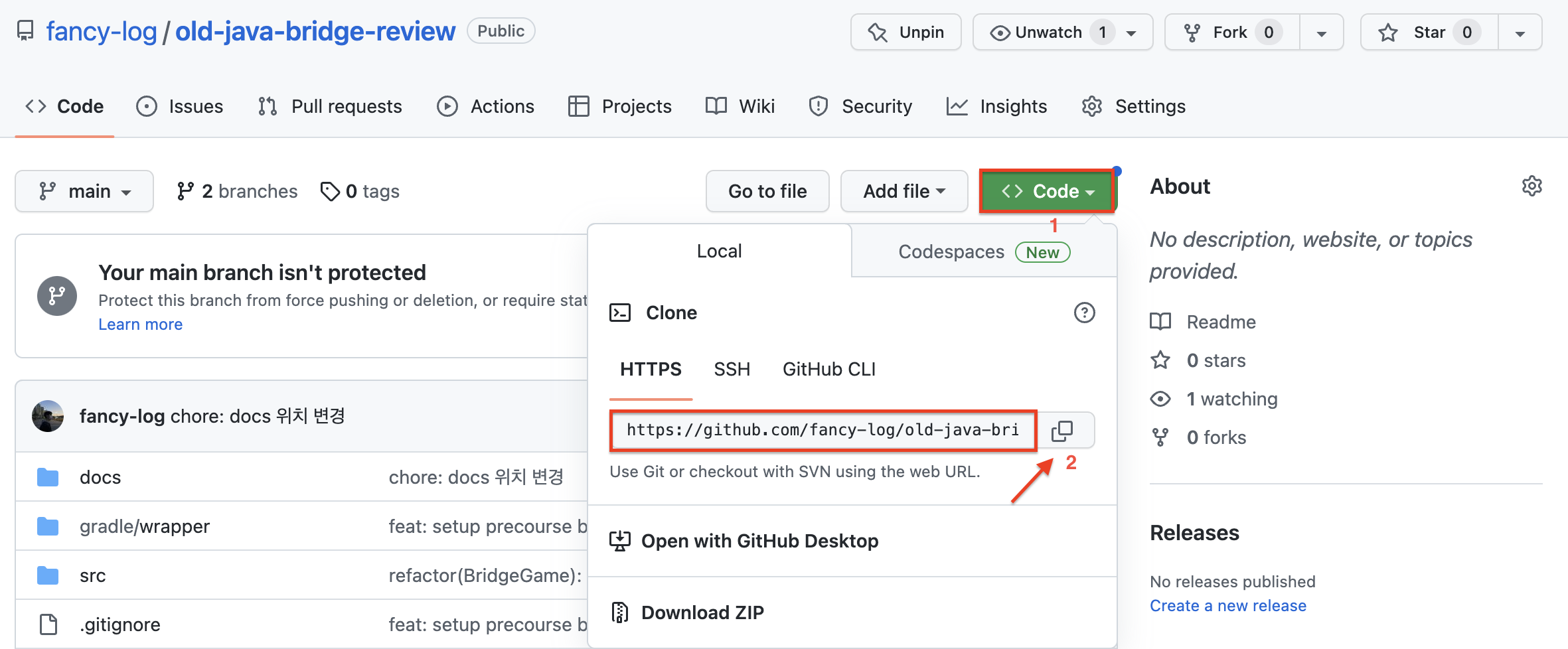
2. remote 추가
- terminal에서 상대방(혹은 나)의 git repository 링크를 저장하기 위해 새 remote명에 추가한다.
깃 레포지토리 링크->리모트명에 저장git remote add <리모트명> <깃 레포지토리 링크>git remote add fancy-log2-remote http://github.com/fancy-log/old-java-bridge-review.git
- IntelliJ 하단에 있는는
Git을 클릭하면 위와 같이 remote명fancy-log2-remote가 추가된 것을 볼 수 있다.
3. 가져오고자 하는 브랜치 pull
git pull <remote명> <remote의 branch명>
-
위의 코드를 해석하면,
-
2번에서 git repository 링크를 저장한
-
리모트명에 있는 branch(main)를
new-java-bridge-reviewrepository의 branchfancy-log2에 저장한다는 의미이다. -
그러면 기존 repository 있던 branch(main) 안에 있는 코드와 히스토리가 새 repository branch(fancy-log2)에 복사된다.
-
[추가 설명]
-
git pull 을 해주면 현재 사용하고 있는 branch(fancy-log2) 에 remote 되어 있는 특정 branch를 pull 해오게 된다.
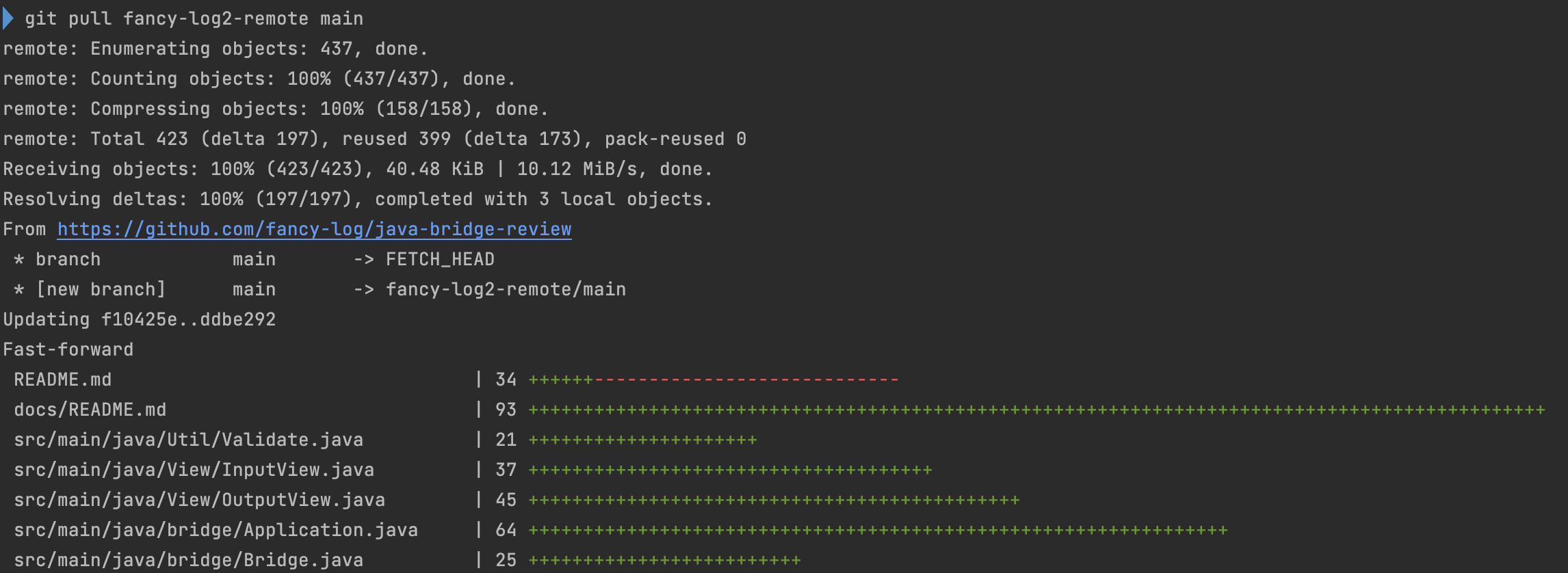
- git pull을 해주면 다음과 같이 실행이 된다.
결과
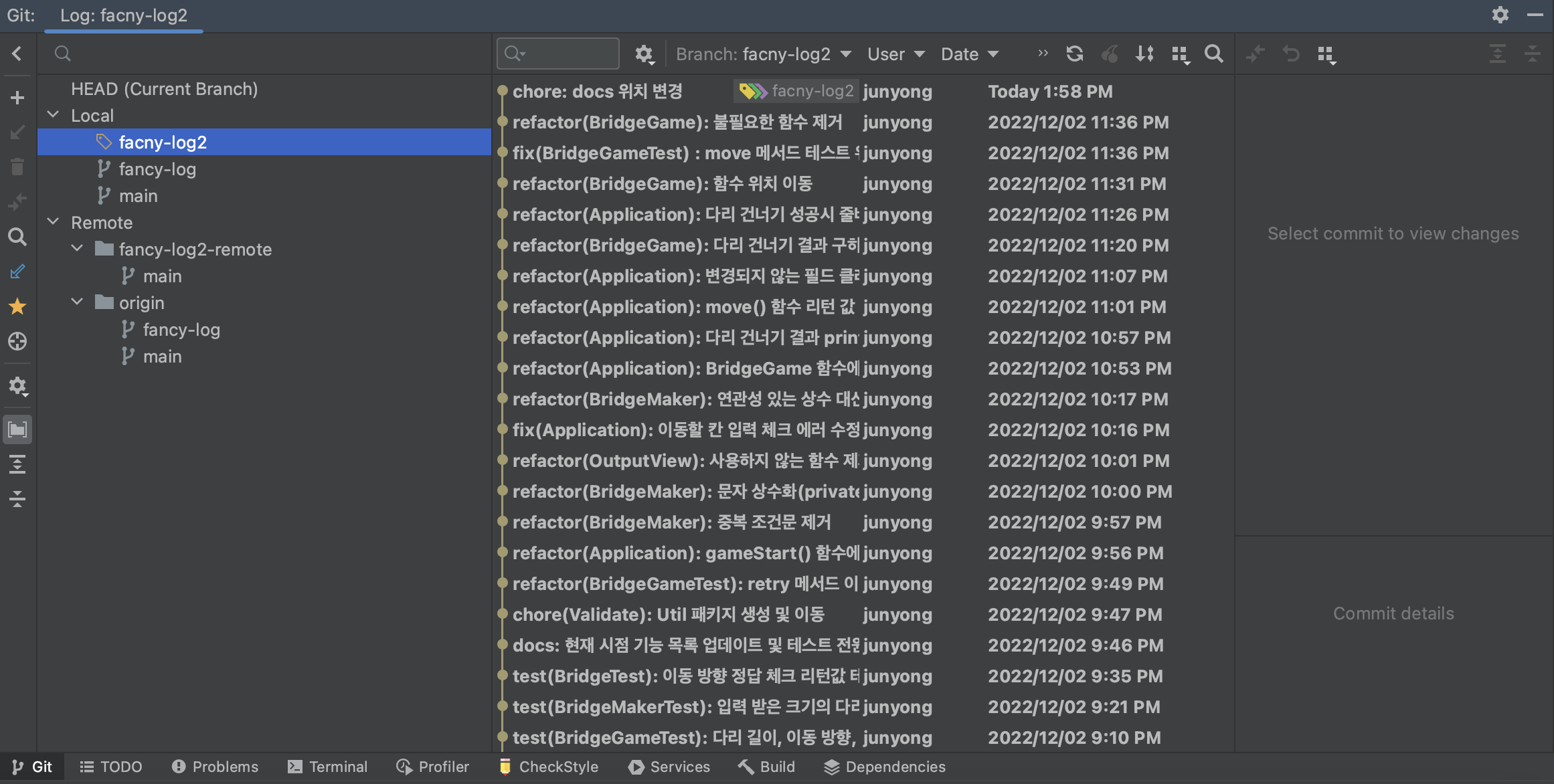
- 그리고 IntelliJ 하단
Git을 클릭하고 해당 branchfancy-log2를 클릭하면 커밋 내용과 코드가 복사되었다는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
-
-
[Git] fork 해온 repository 잔디 심는 방법
fork 해온 repository 잔디 심는 방법
- 잔디를 심기 위해서는 아래의 요건들이 충족되어야 한다.
GitHub 계정과 commit 이메일 계정이 동일하거나
commit이 Fork한 repository가 아닌 나만의 repository에서 이루어져야 한다
순서
- fork 없이 repository를 나의 깃허브로 복사해오도록 할 것이다.
[1] 일단 내 git hub에 새로운 레파지토리를 만든다.
[2] terminal을 연다.
[3] 복사하고자 하는 repository를 bare clone한다.
$ git clone –bare https://github.com/exampleuser/old-repository.git
- 터미널에 git clone –bare를 입력하고 그 뒤에 복사해온 주소를 붙여넣기한다.
[4] 새로운 레파지토리로 Mirror-push
$ cd old-repository.git
$ git push –mirror https://github.com/exampleuser/new-repository.git
- cd 명령어를 이용해 새로운 레파지토리로 이동한뒤👉 3번에서 한 것과 같이 새로운 레파지토리 주소를 복사한뒤, git push –mirror 뒤에 붙여넣으면 Mirror-push가 된다.
[5] 처음에 임시로 생성했던 local repository를 삭제
$ cd ..
$ rm -rf old-repository.git
참고
fork 해온 repository 잔디 심는 방법 : repository 복사해오기 duplicate the repository
-
리스트 내 요소 중복 체크(유효성 검사)
- 해당 미션에서 예외 처리 목록에서 서로 다른 숫자가 아닌 경우 예외 처리를 해줘야만 했다.
Set 이용
-
Set : 중복을 허용하지 않은 자료구조이다.
-
리스트를 Set으로 변환해서 크기를 비교한다.
-
크기가 달라졌으면 리스트에 중복된 요소가 있었다는 것을 의미한다.
@DisplayName("중복인지 확인") @Test void DuplicateTest() { List<Integer> userDuplicate = Arrays.asList(1,1,2,3,4,5); // Set 으로 변환 Set<Integer> userNoDuplicate = new HashSet<>(userDuplicate); if(userNoDuplicate.size() != userDuplicate.size()) { System.out.println("중복된 요소가 있습니다."); System.out.println("전체 개수는 " + userDuplicate.size()); // 6개 System.out.println("중복되지 않은 개수는 " + userNoDuplicate.size()); // 5개 } }
-
throw와 throws 차이
- throw와 throws차이를 짚고 가기 이전에, try-catch 문에 대한 개념을 먼저 알고 가자.
try-catch 문
try { 예외가 발생할 가능성이 있는 실행문 }catch (Exception 클래스명 e){ 예외 처리문 }-
try 블록에 실제 실행되어야 하는 코드가 들어가며 Exception이 발생할 가능성이 있는 코드가 들어간다.
-
catch 블록에는 Exception이 발생하면 실행되는 코드가 들어갑니다. 즉 예외 처리를 하는 코드다.
throw 와 throws 차이
throw
-
throw: 개발자가 의도적으로 예외를 발생시키는 것이다. -
throw라는 키워드를 이용하며, 주로 비즈니스 로직을 구현하는 과정 중 컴파일에는 문제가 없지만 해당 비즈니스 로직이 개발자가 의도한 대로 통과하지 못했을 경우 고의로 예외를 발생시켜야 할 때 사용한다.
-
다음 예시는 숫자가 아닌 경우 혹은 3미만 20 초과인 경우 예외를 발생시키는 경우다.
-
여기서 min은 3, max는 20을 의미한다.
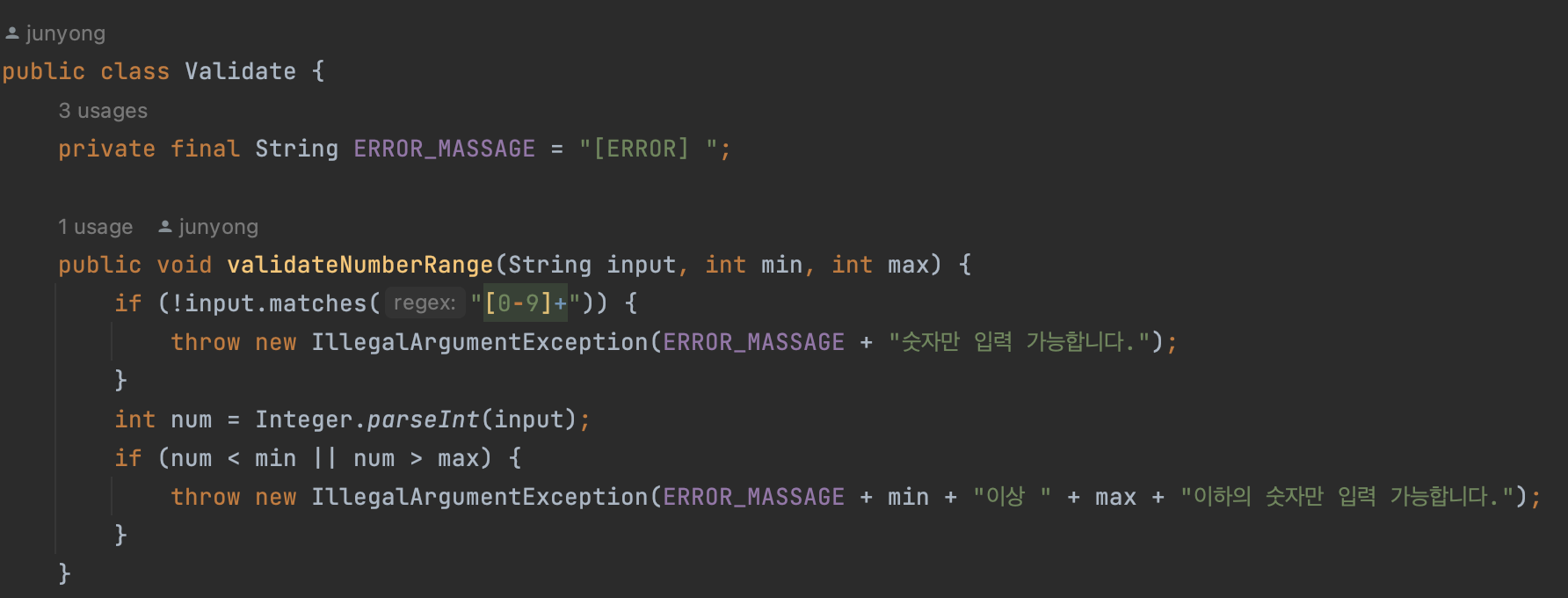
-
예외가 발생하면, IllegalArgumentException()으로 처리된다.
-
IllegalArgumentException(): 적합하지 않거나(illegal) 적절하지 못한(inappropriate) 인자를 메서드에 넘겨주었을 때 발생합니다. -
이처럼
throw키워드를 사용하면 개발자의 판단에 따라 강제로 예외를 발생시킬 수 있다.
throws
-
throws: 메서드 내에서 예외 처리를 하지 않고 해당 메서드를 사용한 곳에서 예외 처리를 하도록 예외를 다른 곳으로 던지는 것이다. -
즉, 예외를 전가시키는 것이다.
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { int a = 2; int b = 0; try { divide(a,b); } catch (ArithmeticException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static int divide(int a, int b) throws ArithmeticException { if (b == 0) { throw new ArithmeticException("0으로 나눌 수 없습니다."); } return a / b; } }-
여기서 divide 메서드는 예외를 자신이 처리하지 않고 throws 키워드를 통해 자신을 호출한 main 메서드에게 책임을 전가했다.
-
이 divide 메서드를 호출한 main 메서드에서 try catch 문을 통해 예외 처리를 진행했다.
정리하자면,
throw는 강제로 예외를 발생시키는 것이며, 개발자의 의도에 따라 강제로 예외를 발생시킬 수 있고, throws는 자신을 호출한 메서드에게 책임을 전가하여 호출한 메서드에서 예외 처리를 하도록 강요하는 것이다.
- throw를 사용하는 이유는 예외가 발생할 수 있는 코드가 있다는 것을 인지시키고 예외 처리를 강요하며, 여러 가지 발생 가능한 예외들을 호출한 메서드에서 한 번에 처리할 수 있게 하는 장점이 있다.
- DevHistory 4
- Essay 1
- Java 10
- Spring 15
- SpringBoot 17
- JPA 13
- MySQL 3
- Flyway 1
- Kafka 8
- Technology 22
- GoodCode 7
- Side_Project 20
- Retrospective 4
- AlgorithmSkill 3
- LeetCode 2
- Algorithm 70
- SQL 9
- OS 14
- Database 8
- Network 7
- HTTP 7
- DataStructure 5
- Linux 4
- Woowacourse 4
- Git 9
- AssertJ 1
- IntelliJ 5
- Probability-Statistics 5
- Electronic-Finance 13
- Business-Statistics 13
- Competition 1
- Book 6
- Workout 7
- E.T.C 8