지금의 기록이 미래의 자산이 된다.
Today's records become tomorrow's assets.-
[내 코드가 그렇게 이상한가요?] 3장. 클래스 설계: 모든 것과 연결되는 설계 기반
이 글은 내 코드가 그렇게 이상한가요? 책을 읽고 정리한 내용을 바탕으로 작성하였습니다.
클래스 단위로 잘 동작하도록 설계하기
-
잘 만들어진 클래스는 다음 두 가지로 구성된다.
-
인스턴스 변수
-
인스턴스 변수에 잘못된 값이 할당되지 않게 막고, 정상적으로 조작하는 메서드
-
-
자신의 몸은 자신이 지켜야 하듯이, 클래스 스스로 자기 방어 임무를 수행할 수 있어야 소프트웨어의 품질을 높이는 데 도움이 된다.
성숙한 클래스로 성장시키는 설계 기법
-
데이터 클래스를 성숙한 클래스로 가는 과정을 알아가보자.
-
금액을 나타내는 클래스인 Money를 예시로 들면,
금액을 나타내는 클래스
import java.util.Currency; class Money { int amount; // 금액 Currency currency; // 통화 단위 }-
위의 Money 클래스는 인스턴스 변수만 갖고 있는 전형적인 데이터 클래스이다.
-
일단 인스턴스 변수를 모두 초기화하는 데 필요한 매개변수들을 받는 생성자를 만든다.
-
그리고 잘못된 값이 유입되지 못하게
유효성 검사(validation)를 생성자 내부에 정의한다.-
금액 amount: 0 이상의 정수
-
통화 currency: null 이외의 것
-
생성자에서 유효성 검사하기
import java.util.Currency; class Money { int amount; // 금액 Currency currency; // 통화 단위 Money(int amount, Currency currency) { if (amount < 0) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("금액은 0 이상의 값을 지정해 주세요."); } if (currency == null) { throw new NullPointerException("통화 단위를 지정해 주세요. "); } this.amount = amount; this.currency =currency; } }-
이렇게 하면 올바른 값만 인스턴스 변수에 저장할 수 있을 것이다.
-
위의 클래스 처럼 처리 범위를 벗어나는 조건을 메서드 가장 앞 부분에서 확인하는 코드를
가드라고 부른다. -
생성자에 가드를 배치함으로써, 잘못된 값이 전달되면 생성자에서 예외가 발생할 것이다.
계산 로직도 데이터를 가진 쪽에 구현하기
-
데이터와데이터를 조작하는 로직이 분리되어 있는 구조를 응집도가 낮은 구조라고 한다. -
이런 문제를 막기 위해서는 계산 로직도 Money 클래스 내부에 구현하면 된다.
불변 변수로 만들어서 예상하지 못한 동작 막기
-
변수의 값이 계속해서 바뀌면, 나중에 비즈니스 요구 사항이 바뀔때마다 코드를 수정하다가 의도하지 않는 값을 할당하는 예상치 못한 부수 효과가 쉽게 발생할 수도 있다.
-
이를 막으려면, 인스턴스 변수를 불변으로 만든다.
-
값을 한 번 할당하면 다시는 바꿀 수 없는 변수를
불변 변수라고 한다. -
불변 변수로 만들려면
final수식자를 사용한다.
final을 붙여 불변 변수로 만들기
import java.util.Currency; class Money { final int amount; // 금액 final Currency currency; // 통화 단위 Money(int amount, Currency currency) { if (amount < 0) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("금액은 0 이상의 값을 지정해 주세요."); } if (currency == null) { throw new NullPointerException("통화 단위를 지정해 주세요. "); } this.amount = amount; this.currency =currency; } }- 인스턴스 변수에
final수식자를 붙이면, 한 번만 할당할 수 있고 이후에는 재할당할 수 없다.
변경하고 싶다면 새로운 인스턴스 만들기
- 만약 인스턴스의 값을 변경하고 싶은 경우, 변경된 값을 가진 새로운 인스턴스를 만들어서 사용하면 된다.
import java.util.Currency; class Money { final int amount; // 금액 final Currency currency; // 통화 단위 Money add(int other) { int added = amount + other; return new Money(added, currency); } }- 이렇게 하면 불변을 유지하면서도 값을 변경할 수 있다.
메서드 매개변수와 지역 변수도 불변으로 만들기
-
값이 중간에 바뀌는 것을 방지하기 위해 기본적으로 매개변수는 변경하지 않는 것이 좋다.
(값이 중간에 바뀌면, 값의 변화를 추적하기 힘들기 때문에 버그를 발생하기도 한다)
-
매개변수에
final을 붙이면 값을 변경할 수 없게 된다. -
지역 변수도 마찬가지로 중간에 값이 변경될 수 있으므로
final을 붙여 불변으로 만든다.
import java.util.Currency; class Money { // 생략 Money add(final int other) { // 매개변수에 final 붙임 final int added = amount + other; // 지역 변수에 final 붙임 return new Money(added, currency); } }엉뚱한 값을 전달하지 않도록 하기
- 엉뚱한 값이 전달되지 않도록 하려면, Money 자료형만 매개변수로 받을 수 있게 메서드를 변경하면 된다.
import java.util.Currency; class Money { // 생략 Money add(final Money other) { // Money 자료형을 매개변수로 받음 final int added = amount + other.amount; return new Money(added, currency); } }-
기본 자료형 위주로 사용하면, 나중에 실수로 의미가 다른 값을 전달하기 쉽다.
-
반면 Money처럼 독자적인 자료형을 사용하면, 의미가 다른 값을 전달할 경우 컴파일 오류가 발생할 수 있다.
악마 퇴치 효과 검토하기
-
지금까지 악마 퇴치를 위한 객체 지향 설계의 기본을 살펴보았다.
-
Money 클래스의 소스 코드와 클래스 다이어그램을 살펴보면 아래와 같다.
관련 로직을 응집해서 코드 수정 시 버그 발생이 어려워진 Money 클래스
import java.util.Currency; class Money { final int amount; // 금액 final Currency currency; // 통화 단위 Money(int amount, Currency currency) { if (amount < 0) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("금액은 0 이상의 값을 지정해 주세요."); } if (currency == null) { throw new NullPointerException("통화 단위를 지정해 주세요. "); } this.amount = amount; this.currency =currency; } Money add(final Money other) { if(!currency.equals(other.currency)) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("통화 단위가 다릅니다."); } final int added = amount + other.amount; return new Money(added, currency); } }퇴치된 악마 - 이유
-
중복 코드 최소화 - 필요한 로직이 Money 내부 클래스에 모여있어, 다른 코드에 중복 코드를 작성할 일이 줄어듦.
-
수정 누락 최소화 - 중복 코드가 발생하지 않으므로, 수정 시 누락이 발생할 일이 줄어듦.
-
가독성 개선 - 필요한 로직이 Money 내부 클래스에 모여있어, 디버깅 또는 기능 변경시 관련 로직이 모여있어서 가독성이 높아짐.
-
쓰레기 객체 발생 X - 생성자에서 인스턴스 변수의 값을 확정함.
-
잘못된 값 X - 잘못된 값이 나오지 않도록 유효성 검사를 앞 부분에 처리하고, 인스턴스 변수에 final 수식자를 붙여 불변으로 만듦.
-
생각하지 못한 부수 효과 - final 수식자를 붙여 불변 변수로 만들었으므로, 부수 효과로부터 안전함.
-
값 전달 실수 - 매개변수를 Money 자료형으로 바꿨으므로, 다른 자료형의 값을 실수로 넣으면 컴파일 오류가 발생하도록 함.
-
이처럼
클래스 설계란 인스턴스 변수가 잘못된 상태에 빠지지 않게 하기 위한 구조를 만드는 것이라고 해도 과언이 아니다. -
Money 클래스처럼 로직이 한곳에 모여 있는 구조는 응집도가 높은 구조라고 한다.
-
또한
데이터와그 데이터를 조작하는 로직을 하나의 클래스로 묶고, 필요한 절차(메서드)만 외부에 공개하는 것을캠슐화라고 한다.
프로그램 구조의 문제 해결에 도움을 주는 디자인 패턴
-
디자인 패턴은, 응집도가 높은 구조를 만드는 등 프로그램의 구조를 개선하는 설계 방법이라고 한다. -
몇 가지 디자인 패턴을 소개하면 표 3.2와 같다.

- 이 장의 Money 클래스는 완전 생성자와 값 객체라는 두 가지 디자인 패턴을 적용한 것이다.
완전 생성자
-
완전 생성자는 잘못된 상태로부터 클래스를 보호하기 위한 디자인 패턴이다. -
다음 2가지로 설계하면 값이 모두 정상인 완전한 객체로 만들어질 것이다.
-
인스턴스 변수를 모두 초기화해야지만 객체를 생성할 수 있게, 매개변수를 가진 생성자를 만든다.
-
생성자 내부에 가드를 사용해서 잘못된 값이 들어오지 않게 만든다.
-
값 객체
-
값 객체란 값을 클래스(자료형)을 나타내는 디자인 패턴이다. -
예를 들어 금액을 단순한 int 자료형의 지역 변수 또는 매개변수로 사용하면, 금액 계산 로직이 이곳저곳에 분산될 것이다.
-
추가로 주문 수, 할인 포인트까지 int 자료형으로 사용한다면, 실수로 의미가 다른 값들이 섞일 수도 있다.
-
이러한 상황을 막으려면, 값을 클래스로 정의하면 된다.
-
금액을 더하는 경우, Money.add 메서드와 같이 매개변수로 Money 자료형만 받을 수 있도록 하면, 의도하지 않게 다른 값이 섞이는 상황을 원천적으로 차단할 수 있다.
-
값 객체 + 완전 생성자는 객체 지향 설계에서 폭넓게 사용되는 기법이라고 할 수 있다.
Reference
-
-
[내 코드가 그렇게 이상한가요?] 1장. 잘못된 구조의 문제 깨닫기
이 글은 내 코드가 그렇게 이상한가요? 책을 읽고 정리한 내용을 바탕으로 작성하였습니다.
1장. 잘못된 구조의 문제 깨닫기
의미를 알 수 없는 이름
-
프로그래밍이나 컴퓨터 용어를 기반으로 이름 붙이는 것을
기술 중심 명명이라 부른다. -
그리고 클래스와 메서드에 번호를 붙여서 이름을 짓는 것을
일련번호 명명이라 부른다. -
이렇게 이름을 지으면 코드를 읽고 이해하는데 시간이 오래걸리고, 충분히 이해하지 못한 코드를 변경하면 버그가 발생하게 됩니다.
-
따라서 의도와 목적을 드러내는 이름을 사용하는 것이 좋다.
이해하기 어렵게 만드는 조건 분기 중첩
-
if문의 중첩이 많을 수록 코드의 가독성이 나빠진다.
-
어디서부터 어디까지가 if 조건문 처리문인지 확인하기 힘들기 때문이다.
수많은 악마가 만들어 내는 데이터 클래스
-
데이터 클래스는 설계가 제대로 이루어지지지 않는 소프트웨어에서 빈번하게 등장하는 클래스 구조이다. -
금액을 다루는 서비스를 예로 들어 데이터 클래스의 어떤 점이 나쁜지 살펴보자.
데이터밖에 없는 클래스 구조
// 계약 금액 public class ContractAmount { public int amountIncludingTax; // 세금 포함 금액 public BigDecimal salesTaxRate; // 소비세율 }-
세금이 포함된 금액과 소비세율을
public인스턴스 변수로 갖고 있으므로, 클래스 밖에서도 데이터를 자유롭게 변경할 수 있는 구조이다. -
이처럼 데이터를 갖고 있기만 하는 클래스를
데이터 클래스라고 부른다. -
그런데 데이터 클래스에는 데이터뿐만 아니라, 세금이 포함된 금액을 계산하는 로직도 필요한데,
-
이러한 계산 로직을 데이터 클래스가 아닌 다른 클래스에 구현하는 일이 벌어지곤 한다.
-
이럴 경우, 작은 규모의 애플리케이션이라면 큰 문제가 되진 않지만, 규모가 큰 애플리케이션이라면 수많은 악마를 불러들인다.
예를 들어, 업무 계약 서비스에서 소비세와 관련된 사양이 변경되었다고 했을 때, 구현 담당자는 소비세율과 관련된 로직을 변경했다.
- 이때, 소비세와 관련된 부분을 소스 코드 전체에서 찾아서 확인해보니, 세금 포함 금액을 계산하는 로직이 수십 곳에 있음을 확인했다.
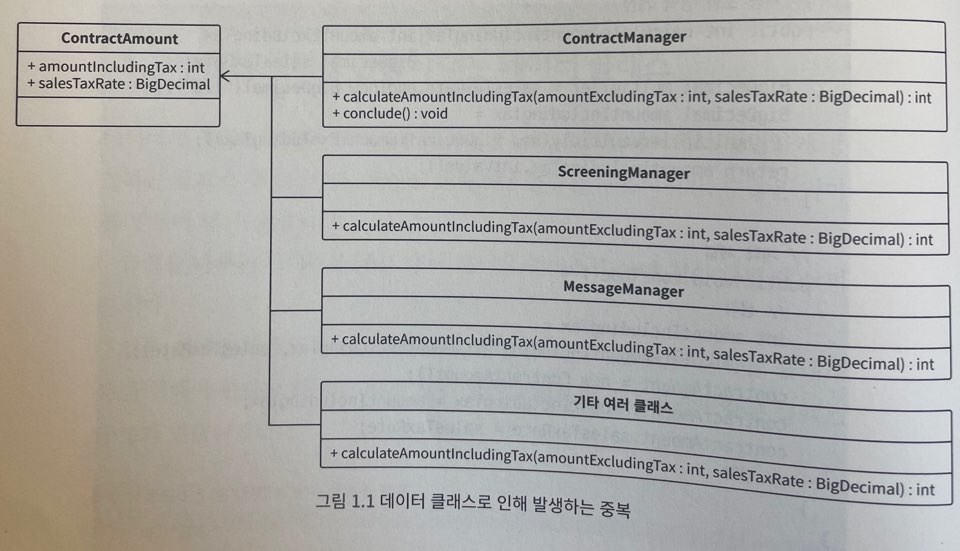
-
이런 상황은 데이터를 담고 있는 클래스와 데이터를 사용하는 계산 로직이 멀리 떨어져 있을 때 자주 일어난다.
-
이처럼 데이터와 로직 등이 분산되어 있는 것을 응집도가 낮은 구조라고 한다.
-
응집도가 낮아 생길 수 있는 여러 가지 문제는 아래와 같다.
[1] 코드 중복
-
관련된 코드가 서로 멀리 떨어져 있으면, 관련된 것끼리 묶어서 파악하기 힘들다.
-
이미 기능이 구현되어 있는데도, 해당 코드를 확인하지 못해서 같은 로직을 여러 곳에 구현할 수 있다.
-
정리하면, 의도하지 않게 코드 중복이 발생하는 것이다.
[2] 수정 누락
-
코드 중복이 많으면, 요구사항이 변경될 때 중복된 코드를 모두 고쳐야 한다.
-
하지만 이 과정에서 일부 코드를 놓칠 수 있으며, 결국 버그를 낳게 된다.
[3] 가독성 저하
-
가독성이란 코드의 의도나 처리 흐름을 얼마나 빠르게 정확하게 읽고 이해할 수 있는지 나타내는 지표다. -
코드가 분산되어 있으면, 찾기도 그 만큼 오래 걸린다.
[4] 초기화되지 않는 상태(쓰레기 객체)
-
초기화해야 하는 클래스라는 것을 모르면, 버그가 발생하기 쉬운 불완전한 클래스가 된다.
-
이처럼
초기화되지 않으면 쓸모 없는 클래스또는초기화하지 않는 상태가 발생할 수 있는 클래스를 안티 패턴 쓰레기 객체라고 부른다.
[5] 잘못된 값 할당
-
값이 잘못되었다는 것은 요구 사항에 맞지 않음을 의미한다.
-
예를 들면) 주문 건수가 음수가 나오는 경우이다.
결과적으로 이와 같은 문제들은 개발 생산성을 떨어뜨리게 된다.
Reference
-
-
Spring MVC 구조 이해
이 글은 스프링 MVC 1편 - 백엔드 웹 개발 핵심 기술 강의를 바탕으로 정리한 내용입니다.
Spring MVC에 대해서는 예전 글에서 배경, 장점, 한계에 대해 어느 정도 정리를 했다.
이번 글은 HTTP 요청 처리가 왔을 때
Spring MVC 구조가 어떻게 동작하는지 과정을 정리하는 글이다.동작에 대해 대해 설명하기 전에 MVC에 대해 간단하게 정리하고 넘어가보자.
MVC
MVC는 하나의 서블릿이나, JSP로 처리하는 것을 Controller와 View라는 영역으로 서로 역할을 나눈 것을 말한다.
-
Controller: HTTP 요청을 받아서 파라미터를 검증하고, 비즈니스 로직을 실행한다. 그리고 뷰에 전달할 결과 데이터를 조회해서 모델에 담는다. -
Model: 뷰에 출력할 데이터를 담아둔다. 뷰가 필요한 데이터를 모두 모델에 담아서 전달해주는 덕분에 뷰는 비즈니스 로직이나 데이터 접근을 몰라도 되고, 화면을 렌더링 하는 일에 집중할 수 있다. -
View: 모델에 담겨있는 데이터를 사용해서 화면을 그리는 일에 집중한다. 여기서는 HTML을 생성하는 부분을 말한다.
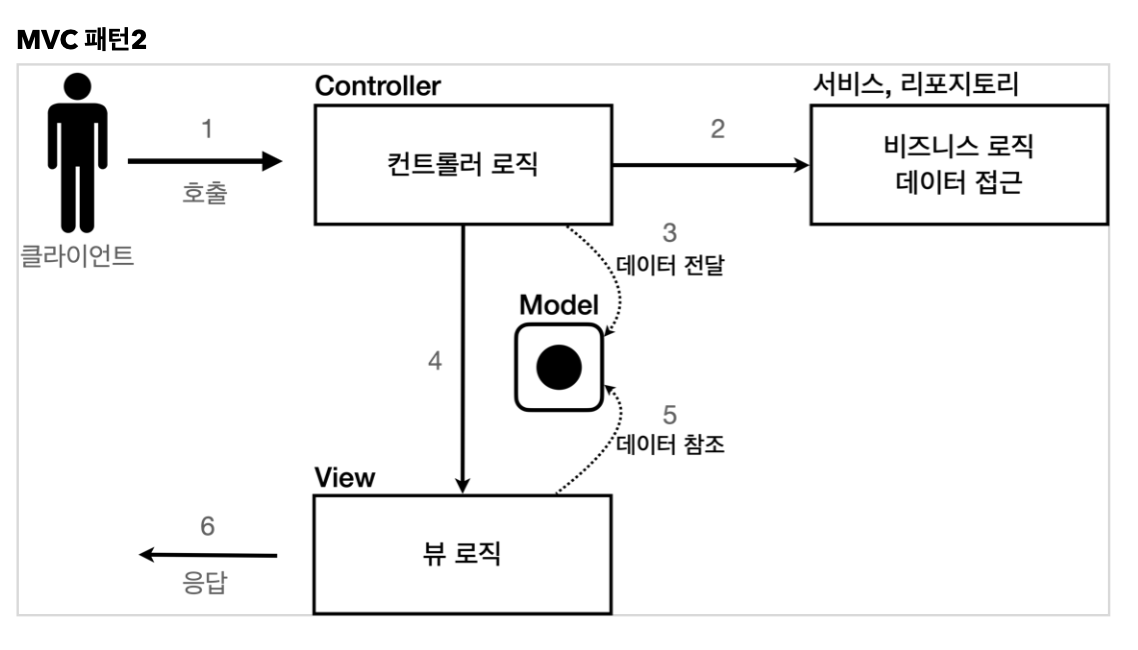
컨트롤러(Controller)에 비즈니스 로직을 둘 수도 있지만, 그렇게 되면 컨트롤러에 너무 많은 역할을 담당한다.
그래서 일반적으로 비즈니스 로직은 서비스(Service)라는 계층을 별도로 만들어서 처리한다.
그리고 컨트롤러(Controller)는 비즈니스 로직이 있는 서비스를 호출하는 역할을 담당한다.
Spring MVC 구조
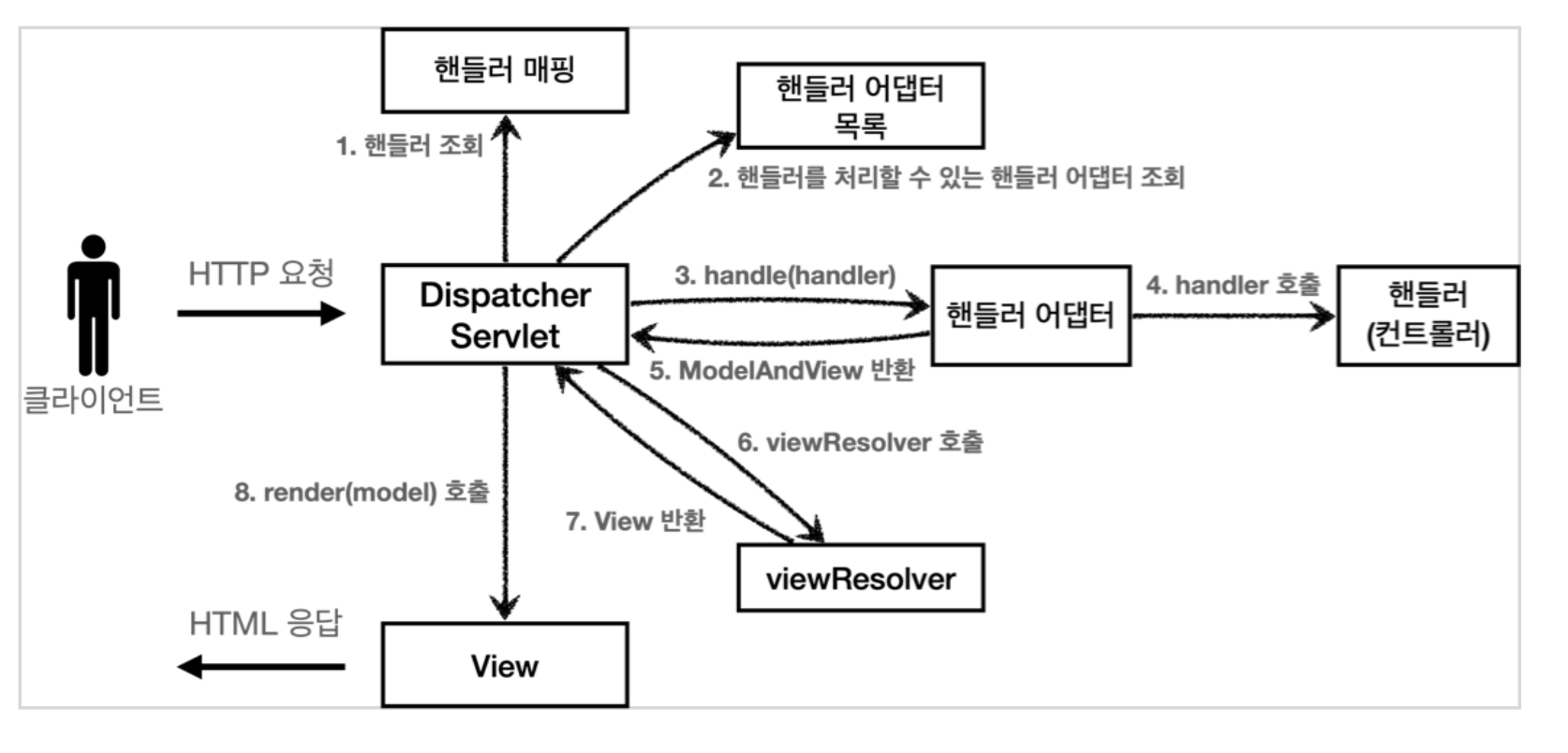
위 그림에서
디스패처 서블릿(DispatcherServlet)이 Spring MVC의 핵심이다.DispacherServlet 서블릿 등록
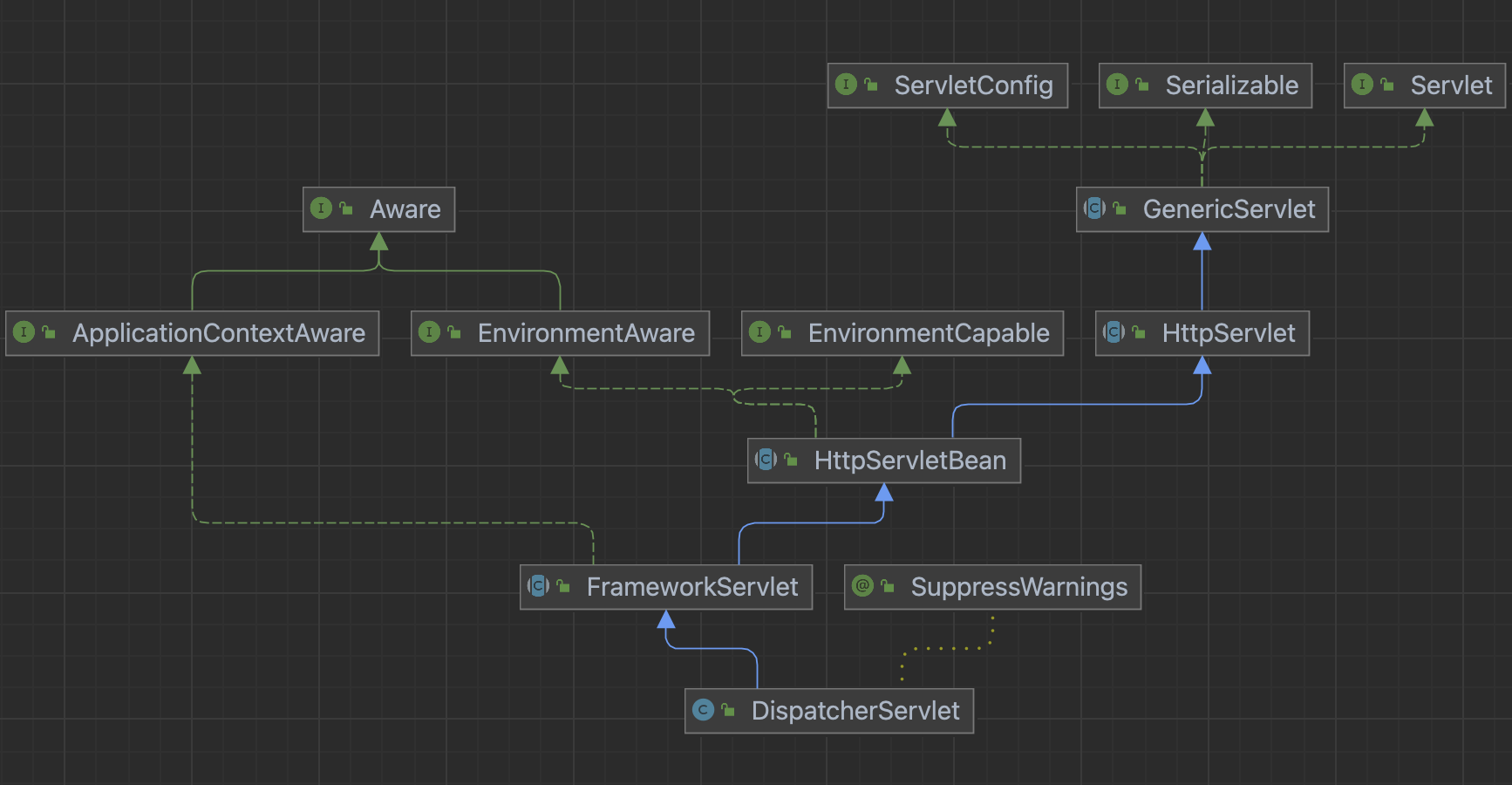
DispacherServlet도 부모 클래스에서HttpServlet을 상속 받아서 사용하고, 서블릿으로 동작한다.- DispatcherServlet → FrameworkServlet → HttpServletBean → HttpServlet
스프링 부트는
DispacherServlet을 서블릿으로 자동으로 등록하면서모든 경로(urlPatterns="/")에 대해서 매핑한다.요청 흐름
서블릿이 호출되면
HttpServlet이 제공하는serivce()가 호출된다.- Spring MVC는
DispatcherServlet의 부모인FrameworkServlet에서service()를 **오버라이드 **해두었다.
FrameworkServlet 클래스 -
service()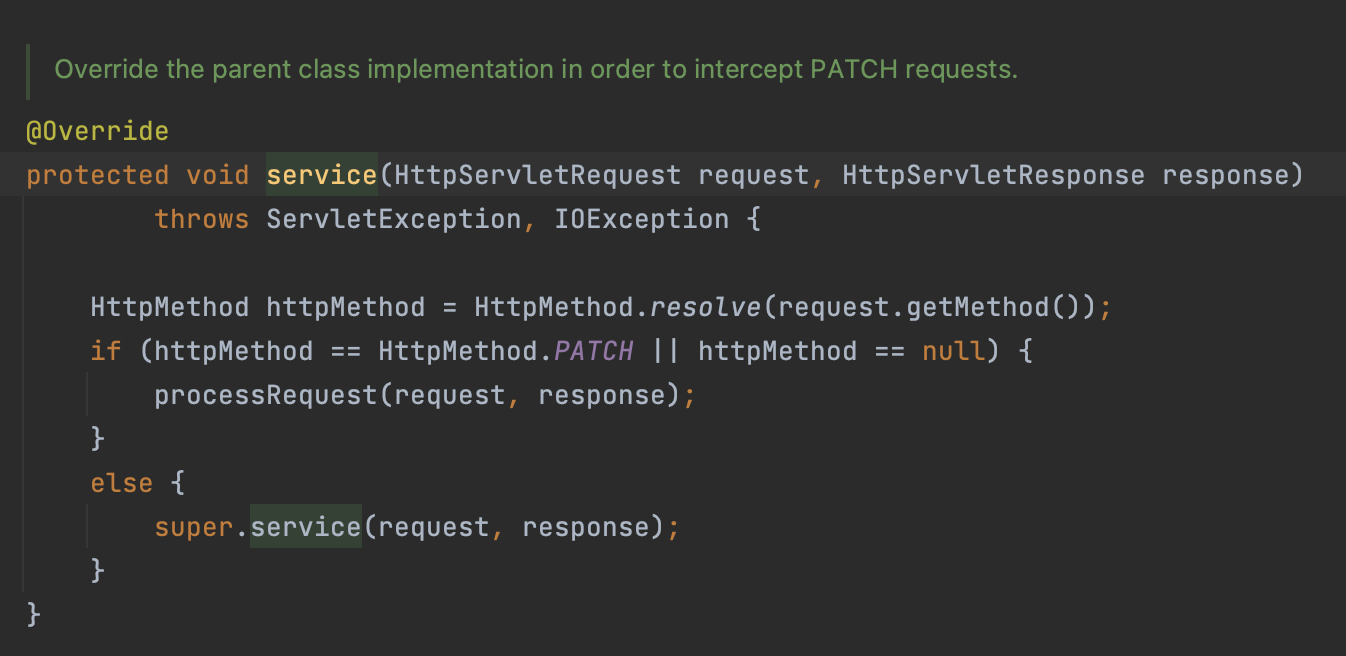
FrameworkServlet.service()를 시작으로 여러 메서드가 호출되면서DispacherServlet.doDispatch()가 호출된다.DispacherServlet클래스는 1500줄 가까이 되기 때문에요청 흐름에 필요한 부분만 가져왔다.DispacherServlet.doDispatch()
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet { @SuppressWarnings("deprecation") protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request; HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null; boolean multipartRequestParsed = false; WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); try { ModelAndView mv = null; Exception dispatchException = null; try { processedRequest = checkMultipart(request); multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request); // Determine handler for the current request. // 1. 핸들러 조회 mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest); if (mappedHandler == null) { noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response); return; } // Determine handler adapter for the current request. // 2. 핸들러 어댑터 조회-핸들러를 처리할 수 있는 어댑터 HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); // Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler. String method = request.getMethod(); boolean isGet = HttpMethod.GET.matches(method); if (isGet || HttpMethod.HEAD.matches(method)) { long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) { return; } } if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) { return; } // Actually invoke the handler. // 3. 핸들러 어댑터 실행 -> 4. 핸들러 어댑터를 통해 핸들러 실행 -> 5. ModelAndView 반환 mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { return; } applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv); mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv); } catch (Exception ex) { dispatchException = ex; } catch (Throwable err) { // As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well, // making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios. dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err); } // processDispatchResult -> 내부 로직 processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException); } // 밑 부분은 안봐도 됨 catch (Exception ex) { triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex); } catch (Throwable err) { triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err)); } finally { if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { // Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion if (mappedHandler != null) { mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response); } } else { // Clean up any resources used by a multipart request. if (multipartRequestParsed) { cleanupMultipart(processedRequest); } } } } }DispacherServlet.processDispatchResult()
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet { private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, @Nullable ModelAndView mv, @Nullable Exception exception) throws Exception { boolean errorView = false; // Did the handler return a view to render? if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) { // 뷰 랜더링 호출 render(mv, request, response); if (errorView) { WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request); } } else { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("No view rendering, null ModelAndView returned."); } } } }DispacherServlet.render()
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet { protected void render(ModelAndView mv, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { View view; String viewName = mv.getViewName(); // 6. 뷰 리졸버를 통해서 뷰 찾기 // 7.View 반환 view = resolveViewName(viewName, mv.getModelInternal(), locale, request); // 8. 뷰 렌더링 view.render(mv.getModelInternal(), request, response); } }동작 순서

Spring MVC 구조를 보면서 동작 순서에 대해 다시 한번 확인해보자.
- 핸들러 조회: 핸들러 매핑을 통해 요청 URL에 매핑된 핸들러(컨트롤러)를 조회한다.
- 핸들러 어댑터 조회: 핸들러를 실행할 수 있는 핸들러 어댑터를 조회한다.
-
핸들러 어댑터 실행: 핸들러 어댑터를 실행한다.
-
핸들러 실행: 핸들러 어댑터가 실제 핸들러를 실행한다.
-
ModelAndView 반환: 핸들러 어댑터는 핸들러가 반환하는 정보를 ModelAndView로 변환해서 반환한다.
-
viewResolver 호출: 뷰 리졸버를 찾고 실행한다.
- JSP의 경우:
InternalResourceViewResolver가 자동 등록되고, 사용된다.
- JSP의 경우:
-
View 반환: 뷰 리졸버는 뷰의 논리 이름을 물리 이름으로 바꾸고,렌더링역할을 담당하는뷰객체를 반환한다.
- JSP의 경우
InternalResourceView(JstlView)를 반환하는데, 내부에forward()로직이 있다.
- JSP의 경우
- 뷰 렌더링: 뷰를 통해서 뷰를 렌더링 한다.
인터페이스 살펴보기
Spring MVC의 큰 강점은
DispatcherServlet코드의 변경 없이, 원하는 기능을 변경하거나 확장할 수 있다는 점이다. 지금까지 설명한 대부분을 확장 가능할 수 있게 인터페이스로 제공한다.이 인터페이스들만 구현해서
DispatcherServlet에 등록하면 나만의 컨트롤러를 만들 수도 있다.주요 인터페이스 목록
-
핸들러 매핑:
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping -
핸들러 어댑터:
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerAdapter -
뷰 리졸버:
org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver -
뷰:
org.springframework.web.servlet.View
정리
Spring MVC는 코드 분량도 매우 많고, 복잡해서 내부 구조를 다 파악하기 쉽지 않다.
MVC는 이미 전세계 수 많은 개발자들의 요구사항에 맞추어 기능을 계속 확장했기 때문에 나만의 컨트롤러를 만드는 일은 없다.
그래서 애플리케이션을 만들 때 필요로 하는 대부분의 기능이 이미 다 구현되어 있다.
그래도 이렇게 핵심 동작방식을 알아두면 향후 문제가 발생했을 때 어떤 부분에서 문제가 발생했는지 쉽게 파악하고, 문제를 해결할 수 있다.
우선 전체적인 구조가 이렇게 되어있구나 하고 이해하자.
Reference
-
-
NGINX란?
-
[Goodfriends] Set-Cookie의 보안 속성 적용기
- DevHistory 4
- Essay 1
- Java 10
- Spring 15
- SpringBoot 17
- JPA 13
- MySQL 3
- Flyway 1
- Kafka 8
- Technology 22
- GoodCode 7
- Side_Project 20
- Retrospective 4
- AlgorithmSkill 3
- LeetCode 2
- Algorithm 70
- SQL 9
- OS 14
- Database 8
- Network 7
- HTTP 7
- DataStructure 5
- Linux 4
- Woowacourse 4
- Git 9
- AssertJ 1
- IntelliJ 5
- Probability-Statistics 5
- Electronic-Finance 13
- Business-Statistics 13
- Competition 1
- Book 6
- Workout 7
- E.T.C 8